XML文件中的常用属性
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"——这个是xml的命名空间,有了他,你就可以alt+/作为提示,提示你输入什么,不该输入什么,什么是对的,什么是错的,也可以理解为语法文件。或者语法判断器什么的。
tools:context="activity name"———这一句不会被打包进APK。只是ADT的Layout Editor在你当前的Layout文件里面设置对应的渲染上下文,说明你当前的Layout所在的渲染上下文是activity name对应的那个activity,如果这个activity在manifest文件中设置了Theme,那么ADT的Layout Editor会根据这个Theme来渲染你当前的Layout。就是说如果你设置的MainActivity设置了一个Theme.Light(其他的也可以),那么你在可视化布局管理器里面看到的背景阿控件阿什么的就应该是Theme.Light的样子。仅用于给你看所见即所得的效果而已。
RelativeLayout:
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" 水平居中
android:layout_centerVertical="true" 垂直居中
android:layout_above="@id/mButton_center" 该控件位于mButton_center控件上方
android:layout_below="@id/mButton_center" 该控件位于mButton_center控件下方
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/mButton_center" 该控件位于mButton_center控件左方
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/mButton_center" 该控件位于mButton_center控件右方
android:singleLine="true" 将控件的内容在同一行当中进行显示
android:background="#0000aa" 指定该控件所使用的背景色,RGB命名法
android:padding="3dip" 指定控件的内边距,也就是说控件当中的内容
LinearLayout示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/firstText"
android:text="第一行"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:textSize="15pt"
android:background="#aa0000"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="10000"
android:singleLine="true"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/secondText"
android:text="第二行"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:textSize="15pt"
android:background="#0000aa"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
</LinearLayout>
TableLayout示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:stretchColumns="0">
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:text="@string/row1_column1"
android:background="#aa0000"
android:padding="3dip" />
<TextView
android:text="@string/row1_column1"
android:padding="3dip"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#00aa00"
></TextView>
<TextView
android:text="@string/row1_column2"
android:gravity="right"
android:background="#0000aa"
android:padding="3dip" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:text="@string/row2_column1"
android:padding="3dip" />
<TextView
android:text="@string/row2_column2"
android:gravity="right"
android:padding="3dip" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
RelativeLayout示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--
android:layout_above 将该控件的底部至于给定ID的控件之上
android:layout_below 将该控件的顶部至于给定ID的控件之下
android:layout_toLeftOf 将该控件的右边缘和给定ID的控件的左边缘对齐
android:layout_toRightOf 将该控件的左边缘和给定ID的控件的右边缘对齐
android:layout_alignBaseline 该控件的baseline和给定ID的控件的baseline对齐
android:layout_alignBottom 将该控件的底部边缘与给定ID控件的底部边缘
android:layout_alignLeft 将该控件的左边缘与给定ID控件的左边缘对齐
android:layout_alignRight 将该控件的右边缘与给定ID控件的右边缘对齐
android:layout_alignTop 将给定控件的顶部边缘与给定ID控件的顶部对齐
android:alignParentBottom 如果该值为true,则将该控件的底部和父控件的底部对齐
android:layout_alignParentLeft 如果该值为true,则将该控件的左边与父控件的左边对齐
android:layout_alignParentRight 如果该值为true,则将该控件的右边与父控件的右边对齐
android:layout_alignParentTop 如果该值为true,则将空间的顶部与父控件的顶部对齐
android:layout_centerHorizontal 如果值为真,该控件将被至于水平方向的中央
android:layout_centerInParent 如果值为真,该控件将被至于父控件水平方向和垂直方向的中央
android:layout_centerVertical 如果值为真,该控件将被至于垂直方向的中央
-->
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="10px" >
<TextView android:id="@+id/label"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Type here:" />
<EditText android:id="@+id/entry"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:drawable/editbox_background"
android:layout_below="@id/label" />
<Button android:id="@+id/ok"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/entry"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="10px"
android:text="OK" />
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/ok"
android:layout_alignTop="@id/ok"
android:text="Cancel" />
</RelativeLayout>
margin与padding:
Android的Margin和Padding跟Html的是一样的。如下图所示:黄色部分为Padding,灰色部分为Margin。

通俗的理解 Padding 为内边框,Margin 为外边框
在程序中使用触力反馈:
触力反馈又名:hapticFeedbackEnabled
一般有两种实现方式
第一种是在XML布局文件里面设置
android:hapticFeedbackEnabled="true"
第二种是在使用硬编码,在Java文件里面写
单击某个图片或者是按钮,用于引起用户的注意,使手机震动一下,就要使用这个触力反馈,系统提供一个触力反馈(震动一下),我们需要写两个地方:
1、在xml配置文件中,对要提供触力反馈的视图控件,我们以button1为例,设置其属性android:hapticFeedbackEnabled="true",这是必需的,只有在isHapticFeedbackEnabled()为真即android:hapticFeedbackEnabled="true"时,下面的方法
performHapticFeedback(intfeedbackConstant,intflags)才会被执行
2、注册该视图的单击事件处理器,并在其中执行
1: public void onClick(View yourView) {
2: button1.performHapticFeedback(HapticFeedbackConstants.LONG_PRESS,HapticFeedbackConstants.FLAG_IGNORE_GLOBAL_SETTING);
3: }
android:soundEffectsEnabled:
点击和触摸时是否有声音效果
开发中很常见的一个问题,项目中的listview不仅仅是简单的文字,常常需要自己定义listview,自己的Adapter去继承BaseAdapter,在adapter中按照需求进行编写,问题就出现了,可能会发生点击每一个item的时候没有反应,无法获取的焦点。原因多半是由于在你自己定义的Item中存在诸如ImageButton,Button,CheckBox等子控件(也可以说是Button或者Checkable的子类控件),此时这些子控件会将焦点获取到,所以常常当点击item时变化的是子控件,item本身的点击没有响应。
这时候就可以使用descendantFocusability来解决啦,API描述如下:
android:descendantFocusability
Defines the relationship between the ViewGroup and its descendants when looking for a View to take focus.
Must be one of the following constant values.
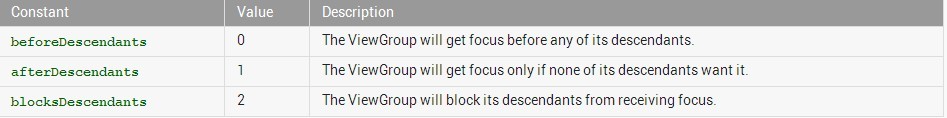
该属性是当一个为view获取焦点时,定义viewGroup和其子控件两者之间的关系。
属性的值有三种:
beforeDescendants:viewgroup会优先其子类控件而获取到焦点
afterDescendants:viewgroup只有当其子类控件不需要获取焦点时才获取焦点
blocksDescendants:viewgroup会覆盖子类控件而直接获得焦点
通常我们用到的是第三种,即在Item布局的根布局加上android:descendantFocusability=”blocksDescendants”的属性就好了,至此listview点击的灵异事件告一段落。
android:ems = "10" 设置TextView或者Edittext的宽度为10个字符的宽度。当设置该属性后,控件显示的长度就为10个字符的长度,超出的部分将不显示。
posted on 2013-06-14 16:04 leihupqrst 阅读(779) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报

