第04次作业-树
1.学习总结
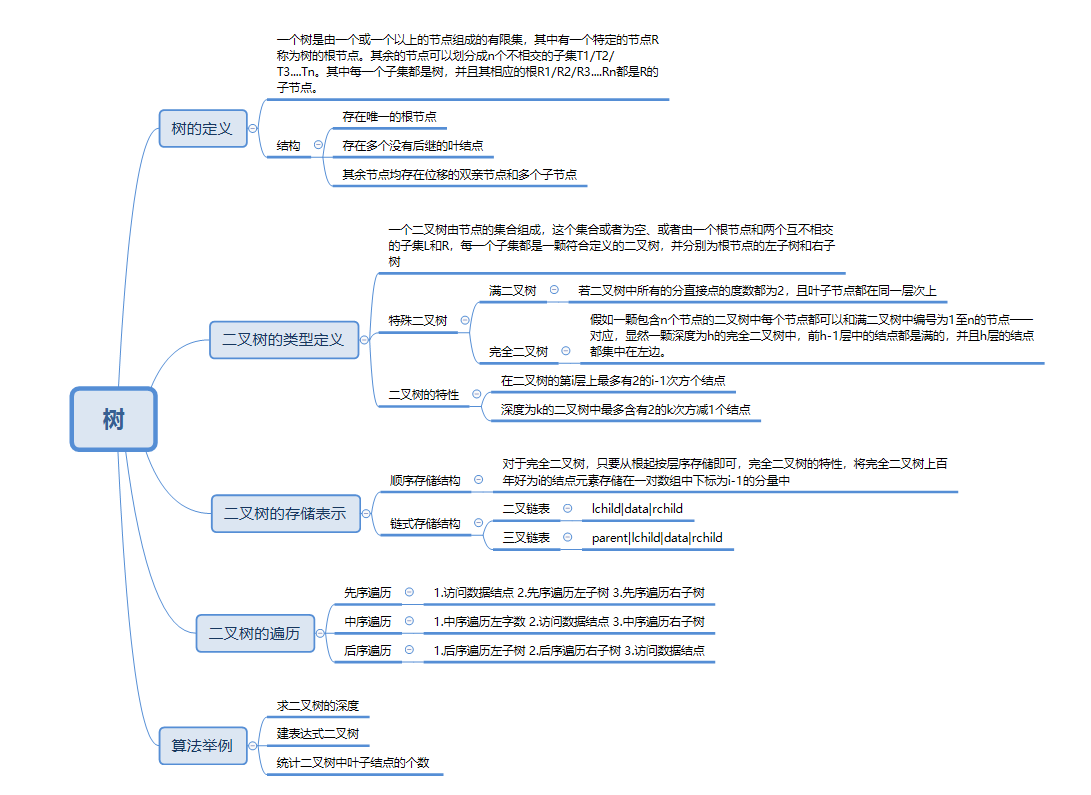
1.1树结构思维导图
1.2 树结构学习体会
树结构属于非线性数据结构,表示数据之间一对多的关系,是由n个节点组成的有层次关系的集合。树中运用比较重要的就是其递归性质。
在结构的学习过程中,需要认清树的结构模型,将其转化为实际上的代码,此项是我认为树结构中的难点。
但是相对的,树结构可以解决非常多的问题。最为典型的即计算机中文件系统,而代码应用中可以使用二叉树来解决计算、转换等问题。
2.PTA实验作业
2.1.1 题目1:二叉树操作集
本题要求用层次法创建二叉树,层次法输入序列是按树的从上到下从左到右的顺序形成,各层的空节点用字符 #表示,如:
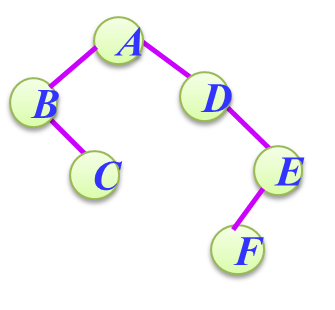
这颗树对应的层次字符串序列为ABD#C#E##F###,即结点的空孩子用#表示。
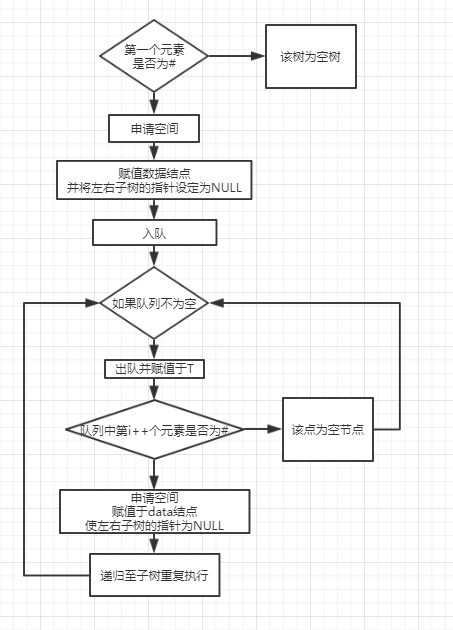
2.1.2 设计思路(伪代码或流程图)
2.1.3 代码截图

2.1.4 PTA提交列表说明
 最后一个字符不带有空格,之后重新编排即可。
最后一个字符不带有空格,之后重新编排即可。
2.2.1 题目2:先序输出叶结点
本题要求按照先序遍历的顺序输出给定二叉树的叶结点。
2.2.2 设计思路(伪代码或流程图)
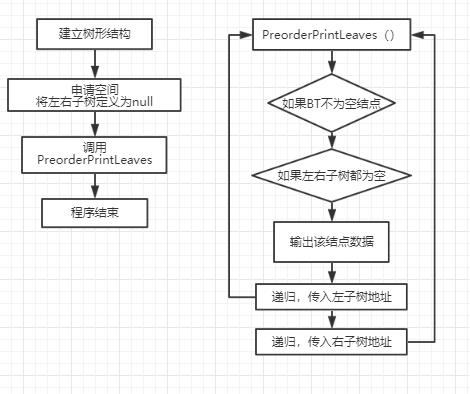
2.2.3 代码截图
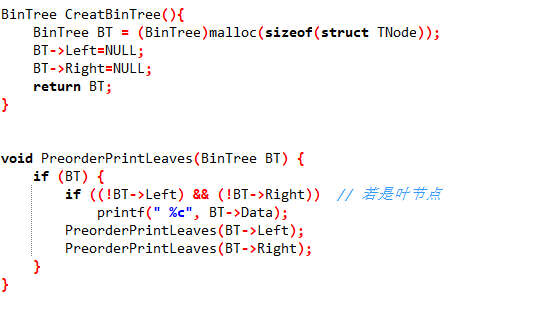
2.2.4 PTA提交列表说明
 较为简单,一次通过。
较为简单,一次通过。
2.3.1 题目3:jmu-ds-表达式树
输入一行中缀表达式,转换一颗二叉表达式树,并求解. 表达式只包含+,-,*,/,(,)运算符,操作数只有一位,且为整数(有兴趣同学可以考虑负数小数,两位数做法)。按照先括号,再乘除,后加减的规则构造二叉树。 如图所示是"1+(2+3)*2-4/5"代数表达式对应二叉树,用对应的二叉树计算表达式的值。 转换二叉树如下:
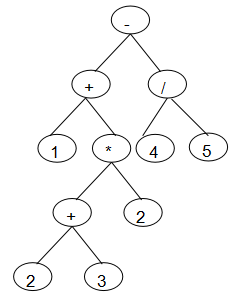
2.3.2 设计思路(伪代码或流程图)
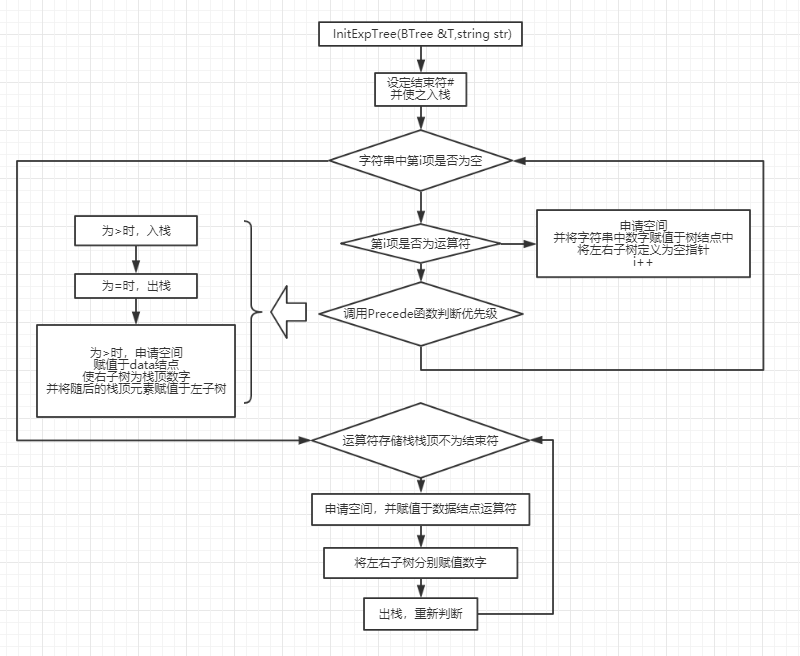
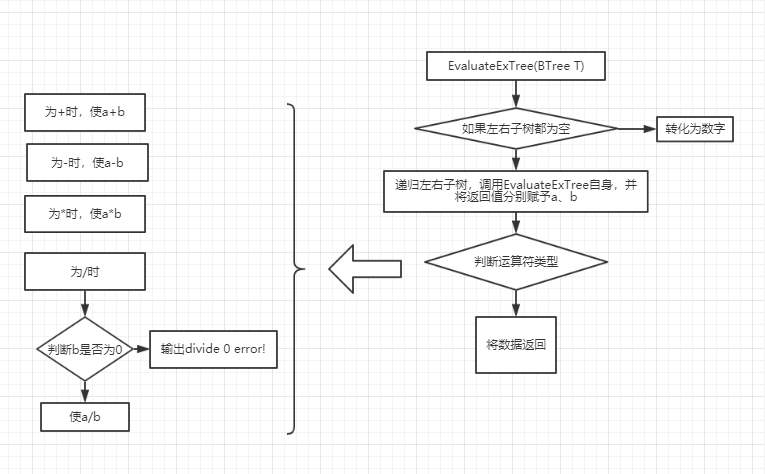
2.3.3 代码截图


2.2.4 PTA提交列表说明
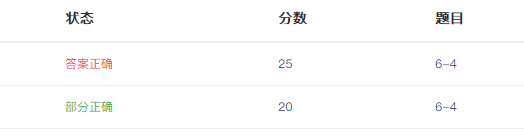 代码不完整,没有考虑到除数为0的时候出现的情况,后补上
代码不完整,没有考虑到除数为0的时候出现的情况,后补上
3.1 PTA排名截图
3.2 我的总分:2.5
本题评分规则:
(1)2个题目集PTA总分285分:3分(全部题目都做) (2)PTA总分在230分--340分:2.5分(必做题全部做完,选做题做部分) (3)PTA总分在180--230分:2分(必做题大部分做完) (4)PTA总分在130--180分:1.5分 (5)PTA总分在105分-130分:1分 (6)PTA总分在105分以下:0分
4. 阅读代码
1 /* 2 问题: 3 Given two non-empty binary trees s and t, check whether tree t has exactly the same structure 4 and node values with a subtree of s. A subtree of s is a tree consists of a node in s and all 5 of this node's descendants. The tree s could also be considered as a subtree of itself. 6 Example 1: 7 Given tree s: 8 3 9 / \ 10 4 5 11 / \ 12 1 2 13 Given tree t: 14 4 15 / \ 16 1 2 17 Return true, because t has the same structure and node values with a subtree of s. 18 Example 2: 19 Given tree s: 20 3 21 / \ 22 4 5 23 / \ 24 1 2 25 / 26 0 27 Given tree t: 28 4 29 / \ 30 1 2 31 Return false. 32 */ 33 /* 34 解答: 35 1.方法一直接前序遍历,然后在判断两个树是否相等。 36 2.方法二先通过计算树的高度,初步判断树t可能出现在树s的第几层,然后在判断两个树是否相等。 37 */ 38 /** 39 * Definition for a binary tree node. 40 * struct TreeNode { 41 * int val; 42 * TreeNode *left; 43 * TreeNode *right; 44 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 45 * }; 46 */ 47 /* 48 class Solution 49 { 50 public: 51 bool isSametree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) 52 { 53 if(!p && !q) return true; 54 if(!p || !q || p->val!=q->val) return false; 55 return isSametree(p->left, q->left) && isSametree(p->right, q->right); 56 } 57 bool isSubtree(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t) 58 { 59 if(!s && !t) return true; 60 if(!s || !t) return false; 61 if(s->val == t->val) 62 if(isSametree(s, t)) 63 return true; 64 if(isSubtree(s->left, t)) 65 return true; 66 if(isSubtree(s->right, t)) 67 return true; 68 return false; 69 } 70 }; 71 */ 72 class Solution { 73 vector<TreeNode*> nodes; 74 75 public: 76 bool isSubtree(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t) { 77 if (!s && !t) return true; 78 if (!s || !t) return false; 79 80 getDepth(s, getDepth(t, -1)); 81 82 for (TreeNode* n: nodes) 83 if (identical(n, t)) 84 return true; 85 86 return false; 87 } 88 89 int getDepth(TreeNode* r, int d) { 90 if (!r) 91 return -1; 92 93 int depth = max(getDepth(r->left, d), getDepth(r->right, d)) + 1; 94 95 // Check if depth equals required value 96 // Require depth is -1 for tree t (only return the depth, no push) 97 if (depth == d) 98 nodes.push_back(r); 99 100 return depth; 101 } 102 103 bool identical(TreeNode* a, TreeNode* b) { 104 if (!a && !b) return true; 105 if (!a || !b || a->val != b->val) return false; 106 107 return identical(a->left, b->left) && identical(a->right, b->right); 108 } 109 };
给出树t以及树s,判断s是否为t的子树,若是返回真,若不是返回假。
个人较为喜欢第二种方法,通过计算树的高度,初步判断树t可能出现在树s的第几层,然后在判断两个树是否相等。这样能够使处理体量更为巨大的树时节省计算量。
地址:https://gitee.com/specialsoldier/codes/l05jietvp9zuq1mfars4360
5. 代码Git提交记录截图



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号