哈密尔顿回路(旅行售货员问题)的回溯算法
1. 回溯法的基本原理: 回溯算法也叫试探法,它是一种系统地搜索问题的解的方法。回溯算法的基本思想是:从一条路往前走,能进则进,不能进则退回来,换一条路再试。用回溯算法解决问题的一般步骤为: 1、定义一个解空间,它包含问题的解。 2、利用适于搜索的方法组织解空间。 3、利用深度优先法搜索解空间。 4、利用限界函数避免移动到不可能产生解的子空间。 问题的解空间通常是在搜索问题的解的过程中动态产生的,这是回溯算法的一个重要特性。 2.旅行售货员问题的回溯算法实现 算法具体实现主要代码如下: // TravelSaler.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // //旅行员售货员问题 回溯法求解 #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include<stdlib.h> using namespace std;
ifstream fin("input.txt"); const int N = 4;//图的顶点数
template<class Type> class Traveling { template<class Type> friend Type TSP(Type **a, int n); private: void Backtrack(int i); int n, // 图G的顶点数 *x, // 当前解 *bestx; // 当前最优解 Type **a, // 图G的领接矩阵 cc, // 当前费用 bestc; // 当前最优值 int NoEdge; // 无边标记 };
template <class Type> inline void Swap(Type &a, Type &b);
template<class Type> Type TSP(Type **a, int n);
int main() { cout << "图的顶点个数 n=" << N << endl;
int **a = new int*[N + 1]; for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) { a[i] = new int[N + 1]; }
cout << "图的邻接矩阵为:" << endl;
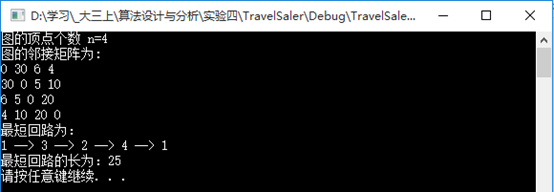
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) { fin >> a[i][j]; cout << a[i][j] << " "; } cout << endl; } cout << "最短回路的长为:" << TSP(a, N) << endl;
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) { delete[]a[i]; } delete[]a;
a = 0; system("pause"); return 0;
}
template<class Type> void Traveling<Type>::Backtrack(int i) { if (i == n) { if (a[x[n - 1]][x[n]] != 0 && a[x[n]][1] != 0 && (cc + a[x[n - 1]][x[n]] + a[x[n]][1] < bestc || bestc == 0)) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) bestx[j] = x[j]; bestc = cc + a[x[n - 1]][x[n]] + a[x[n]][1]; } } else { for (int j = i; j <= n; j++) { // 是否可进入x[j]子树? if (a[x[i - 1]][x[j]] != 0 && (cc + a[x[i - 1]][x[i]] < bestc || bestc == 0)) { // 搜索子树 Swap(x[i], x[j]); cc += a[x[i - 1]][x[i]]; //当前费用累加 Backtrack(i + 1); //排列向右扩展,排列树向下一层扩展 cc -= a[x[i - 1]][x[i]]; Swap(x[i], x[j]); } } } }
template<class Type> Type TSP(Type **a, int n) { Traveling<Type> Y; Y.n = n; Y.x = new int[n + 1]; Y.bestx = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { Y.x[i] = i; }
Y.a = a; Y.cc = 0; Y.bestc = 0;
Y.NoEdge = 0; Y.Backtrack(2);
cout << "最短回路为:" << endl; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cout << Y.bestx[i] << " --> "; } cout << Y.bestx[1] << endl;
delete[] Y.x; Y.x = 0; delete[] Y.bestx;
Y.bestx = 0; return Y.bestc; }
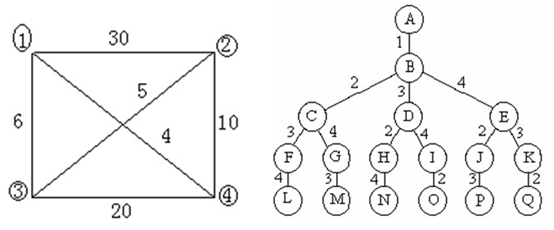
template <class Type> inline void Swap(Type &a, Type &b) { Type temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } 其中input.txt的内容为: 0 30 6 4 30 0 5 10 6 5 0 20 4 10 20 0 |
编译并运行程序。 3. 旅行售货员问题的回溯算法的解空间树以及搜索过程:
(3)算法的时间复杂性和空间复杂性 算法backtrack在最坏情况下可能需要更新当前最优解O((n-1)!)次,每次更新bestx需计算时间O(n),从而整个算法的计算时间复杂性为O(n!)。 |
程序运行结果如下:
开始测试时每次都要输入图的邻接矩阵,非常麻烦,后面改为直接从input文件中读取,大大简化了调试过程 |




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号