R绘制韦恩图 | Venn图 | UpSetR图
网页版venn图
- 维恩(Venn)图绘制工具大全 (在线+R包)
- 在线数据可视化系列一:维恩图 - 内含推荐指数
发表级venn图
如果对venn图颜值要求较高,强烈推荐venneuler
理由:
- 面积比例代表数量,信息含量更高
- 可以直接与ggplot对接,自定义修改
参考代码:human/singleCell/HSCR/2-HSCR_additional_analysis.ipynb
集群上不好装rJava,所以只能在本地Mac上使用venneuler
2024年04月23日
已经全部解决,rJava和venneuler都可以用conda安装成功!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | # step 1: prepare datalength(ctrl.targets)length(common.target)length(chip.target)# best venn by venneuler# step 2: prepare dftmp.genes <- unique(c(chip.target, common.target, ctrl.targets))tmp.df <- data.frame(`Predicted targets`=as.integer(tmp.genes %in% c(ctrl.targets, common.target)), `ChIP-seq_target`=as.integer(tmp.genes %in% c(chip.target, common.target)), row.names = tmp.genes)y <- venneuler::venneuler(tmp.df)d <- data.frame(y$centers, diameters = y$diameters, labels = y$labels, stringsAsFactors = FALSE)d$labels <- plyr::mapvalues(d$labels, from = c('ChIP.seq_target','Predicted.targets'), to = c('ChIP-seq targets','Predicted targets'))d$labels <- factor(d$labels, levels = c('Predicted targets', 'ChIP-seq targets'))geom_circle <- rvcheck::get_fun_from_pkg("ggforce", "geom_circle")options(repr.plot.width=6, repr.plot.height=4)g2 <- ggplot(d) + geom_circle(aes_(x0 = ~x, y0 = ~y, r = ~diameters/2, fill = ~labels, color = ~labels), size=1.5) + coord_fixed() + theme_void() + scale_color_manual(values = c("#E41A1C", "#984EA3")) + scale_fill_manual(values = alpha(c("#E41A1C", "#984EA3"), .2)) + theme(legend.position = c(0.58, 0.38), legend.title = element_blank(), legend.text = element_text(size = 15))+ geom_text(x=0.16, y=0.5, label="1493", size=6) + geom_text(x=0.54, y=0.5, label="722", size=8, fontface="bold") + geom_text(x=0.82, y=0.5, label="543", size=6)g2ggsave(filename = "PHOX2B.targets.venn.pdf", width = 6, height = 4)write.csv(tmp.df, file="PHOX2B.targets.venn.csv") |
Venn
解决方案有好几种:
- 网页版,无脑绘图,就是麻烦,没有写代码方便
- 极简版,gplots::venn
- 文艺版,venneuler,不好安装rJava,参见Y叔
- 酷炫版,VennDiagram
特别注意:
目前主流的韦恩图最多只支持5个类别,多了不能使用韦恩图,也不好看。
UpSet某种程度上可以显示多于5个类别,但是结果不是很直观,不推荐,图也很难解读。
1 2 3 | library(ComplexHeatmap)m = make_comb_mat(venn.list)UpSet(m) |
1. 网页版
就不说了,非常简单,直接输入数据就行;
- 2-30 Venn Diagrams (non-proportional) - 常用的web版
- 2-6 Venn Diagrams (non-proportional)
- http://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html
- http://genevenn.sourceforge.net/
local
- https://github.com/linguoliang/VennPainter
- https://sysbio.uni-ulm.de/?Software:VennMaster
- http://omics.pnl.gov/software/venn-diagram-plotter
R版的输入都是一种数据结构list,可以单独出来。
2. 极简版
1 2 3 | options(repr.plot.width=4, repr.plot.height=5)vp <- gplots::venn(list(Nup=names(moduleListN_DEG[["up"]]), Ndown=names(moduleListN_DEG[["down"]]), Gup=names(moduleListG_DEG[["up"]]), Gdown=names(moduleListG_DEG[["down"]]))) |
获取任意区域的元素
1 | attributes(g)$intersections |
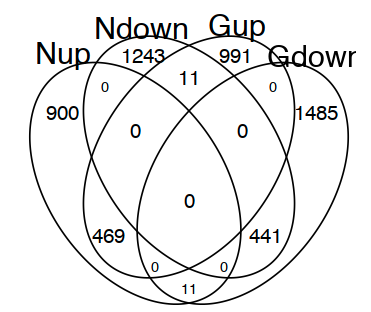
3. 还没成功过,需安装rJava,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 | set.seed(2017-11-08)x <- matrix(sample(0:4, 40, TRUE, c(.5, .1, .1, .1, .1)), ncol=4)colnames(x) <- LETTERS[1:4]yyplot::ggvenn(x) |
4. VennDiagram
只能保存图为文件(三种可选:tiff, png or svg),非常实用和美观,但是不能做下游美化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | library(VennDiagram)venn.diagram(list(Nup=names(moduleListN_DEG[["up"]]), Ndown=names(moduleListN_DEG[["down"]]), Gup=names(moduleListG_DEG[["up"]]), Gdown=names(moduleListG_DEG[["down"]])), fill=c("red","green","blue","yellow"), alpha=c(0.5,0.5,0.5,0.5), imagetype = "tiff", category.names = rep("", 4), height = 600, width = 600, resolution = 100, cex=2, cat.fontface=4, filename="VennDiagram.tiff") |
参考:
R作图 在R中绘制韦恩图的几种方法 和 一些漂亮的venn图
ggplot2版本的维恩图 - Y叔公众号
UpSetR
超过4个类别以上就不推荐使用韦恩图了,非常不直观,此时可以用UpSetR图替代。
https://github.com/hms-dbmi/UpSetR
UpSet: Visualizing Intersecting Sets
教程:
UpSetR的输入数据比较奇特,不是list格式的数据,而是0、1格式的data.frame
第一列是Name(全集);后面每一列都是一个set,如果set里的数据在全集里,那么就是1,不在则是0;
以下是准备输入输入数据的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | all.genes <- unique(c(HSCR_5c3.DEG, HSCR_10c2.DEG, HSCR_20c7.DEG, HSCR_23c9.DEG, HSCR_1c11.DEG, HSCR_17c8.DEG))length(all.genes)DEG.UpSetR.df <- data.frame(Name=all.genes, `HSCR#5`=as.integer(all.genes %in% HSCR_5c3.DEG), `HSCR#10`=as.integer(all.genes %in% HSCR_10c2.DEG), `HSCR#20`=as.integer(all.genes %in% HSCR_20c7.DEG), `HSCR#23`=as.integer(all.genes %in% HSCR_23c9.DEG), `HSCR#1`=as.integer(all.genes %in% HSCR_1c11.DEG), `HSCR#17`=as.integer(all.genes %in% HSCR_17c8.DEG) ) |
Y叔的经典代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | require(UpSetR)movies <- read.csv( system.file("extdata", "movies.csv", package = "UpSetR"), header=T, sep=";" )p1 <- upset(movies)# head(movies)# p1require(ggplotify)g1 <- as.ggplot(p1)library(yyplot)require(yyplot)g2 <- ggvenn(movies[, c(3,6,9,15,17)])require(ggimage)g3 <- g1 + geom_subview(subview = g2 + theme_void(), x=.7, y=.7, w=.6, h=.6)# g3 |
我的代码
问题:
1. 无法精准控制set的order;
2. 无法在列名里保留#号;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | require(UpSetR)p1 <- upset(DEG.UpSetR.df, nsets = 6, text.scale = 2, keep.order = T, sets = rev(c("HSCR.5", "HSCR.10", "HSCR.20", "HSCR.1", "HSCR.17", "HSCR.23")), intersections = list(list("HSCR.5", "HSCR.10", "HSCR.20"), list("HSCR.5", "HSCR.10", "HSCR.20", "HSCR.1"), list("HSCR.23", "HSCR.17"), list("HSCR.23", "HSCR.1", "HSCR.17"), list("HSCR.5", "HSCR.10", "HSCR.20", "HSCR.23", "HSCR.1", "HSCR.17") )) |
1 2 | require(ggplotify)g1 <- as.ggplot(p1) |
拆解ggvenn函数,精准控制order和color
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | y <- venneuler(DEG.UpSetR.df[, 2:7])d <- data.frame(y$centers, diameters = y$diameters, labels = y$labels, stringsAsFactors = FALSE)d$labels <- plyr::mapvalues(d$labels, from = c("HSCR.5", "HSCR.10", "HSCR.20", "HSCR.23", "HSCR.1", "HSCR.17"), to = c("HSCR#5", "HSCR#10", "HSCR#20", "HSCR#23", "HSCR#1", "HSCR#17"))d$labels <- factor(d$labels, levels = c("HSCR#5", "HSCR#10", "HSCR#20", "HSCR#1", "HSCR#17", "HSCR#23"))geom_circle <- rvcheck::get_fun_from_pkg("yyplot", "geom_circle")require(yyplot)require(ggplot2)# require(ggforce)g2 <- ggplot(d) + geom_circle(aes_(x0 = ~x, y0 = ~y, r = ~diameters/2, fill = ~labels, color = ~labels), size=1.5) + # geom_text(aes_(x = ~x, y = ~y, label = ~labels)) + coord_fixed() + theme_void() + scale_color_manual(values = sample.colors) + scale_fill_manual(values = alpha(sample.colors, .2))g2 |
参考:http://localhost:17435/notebooks/projects/BAF_SOX9/diffbind/6.DMSO_only.ipynb
组合
1 2 | options(repr.plot.width=10, repr.plot.height=7)cowplot::plot_grid(g1,g2,ncol = 2) |
取出交集函数,https://github.com/hms-dbmi/UpSetR/issues/85
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | get_intersect_members <- function (x, ...){ require(dplyr) require(tibble) x <- x[,sapply(x, is.numeric)][,0<=colMeans(x[,sapply(x, is.numeric)],na.rm=T) & colMeans(x[,sapply(x, is.numeric)],na.rm=T)<=1] n <- names(x) x %>% rownames_to_column() -> x l <- c(...) a <- intersect(names(x), l) ar <- vector('list',length(n)+1) ar[[1]] <- x i=2 for (item in n) { if (item %in% a){ if (class(x[[item]])=='integer'){ ar[[i]] <- paste(item, '>= 1') i <- i + 1 } } else { if (class(x[[item]])=='integer'){ ar[[i]] <- paste(item, '== 0') i <- i + 1 } } } do.call(filter_, ar) %>% column_to_rownames() -> x return(rownames(x))} |


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)