【Netty】WebSocket
一、前言
前面学习了codec和ChannelHandler之间的关系,接着学习WebSocket。
二、WebSocket
2.1. WebSocket介绍
WebSocket协议允许客户端和服务器随时传输消息,要求他们异步处理接收的消息,而几乎所有的浏览器都支持WebSocket协议,Netty支持WebSocket协议的所有实现,可以在应用中直接使用。
2.2. WebSocket应用示例
下面示例展示了如何使用WebSocket协议实现基于浏览器的实时聊天应用,示例逻辑图如下图所示。

处理逻辑如下
· 客户端发送消息。
· 消息转发至其他所有客户端。
本示例中只实现服务端部分,客户端网页为index.html。
2.3 添加WebSocket支持
升级握手机制可用于从标准HTTP或HTTPS协议切换到WebSocket,使用WebSocket的应用程序以HTTP/S开头,当请求指定URL时将会启动该协议。本应用有如下惯例:如果URL请求以/ ws结尾,我们将使用升级的WebSocket协议,否则,将使用HTTP/S协议,连接升级后,所有数据将使用WebSocket传输。下图展示服务端的逻辑。
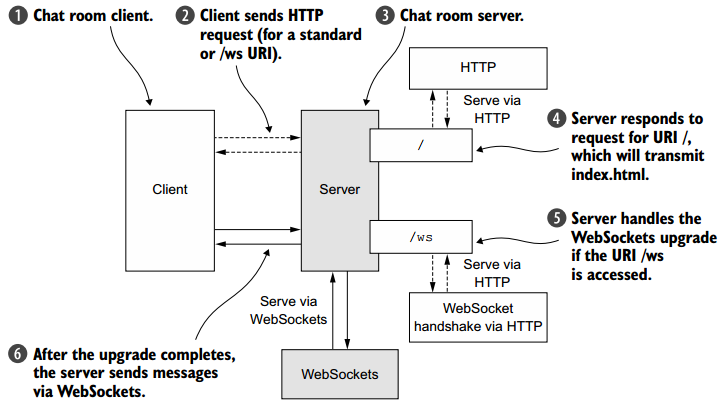
1. 处理HTTP请求
首先我们实现处理HTTP请求的组件,该组件将为访问聊天室的页面提供服务,并显示连接的客户端发送的消息。下面是HttpRequestHandler代码,其继承SimpleChannelInboundHandler。
public class HttpRequestHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> { private final String wsUri; private static final File INDEX; static { URL location = HttpRequestHandler.class .getProtectionDomain() .getCodeSource().getLocation(); try { String path = location.toURI() + "index.html"; path = !path.contains("file:") ? path : path.substring(5); INDEX = new File(path); } catch (URISyntaxException e) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Unable to locate index.html", e); } } public HttpRequestHandler(String wsUri) { this.wsUri = wsUri; } @Override public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest request) throws Exception { if (wsUri.equalsIgnoreCase(request.getUri())) { ctx.fireChannelRead(request.retain()); } else { if (HttpHeaders.is100ContinueExpected(request)) { send100Continue(ctx); } RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile(INDEX, "r"); HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse( request.getProtocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK); response.headers().set( HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain; charset=UTF-8"); boolean keepAlive = HttpHeaders.isKeepAlive(request); if (keepAlive) { response.headers().set( HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_LENGTH, file.length()); response.headers().set( HttpHeaders.Names.CONNECTION, HttpHeaders.Values.KEEP_ALIVE); } ctx.write(response); if (ctx.pipeline().get(SslHandler.class) == null) { ctx.write(new DefaultFileRegion( file.getChannel(), 0, file.length())); } else { ctx.write(new ChunkedNioFile(file.getChannel())); } ChannelFuture future = ctx.writeAndFlush( LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT); if (!keepAlive) { future.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } } } private static void send100Continue(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse( HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.CONTINUE); ctx.writeAndFlush(response); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
上述代码用于处理纯HTTP请求,对于WebSocket而言,数据使用帧进行传输,完整的数据包含多帧。
2. 处理WebSocket帧
WebSocket定义了六种帧,如下图所示。
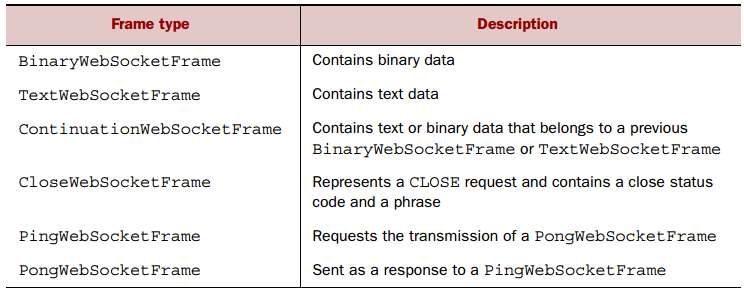
对于聊天应用而言,其包含如下帧:CloseWebSocketFrame、PingWebSocketFrame、PongWebSocketFrame、TextWebSocketFrame。
下面代码展示了用于处理TextWebSocketFrames的ChannelHandler。
public class TextWebSocketFrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> { private final ChannelGroup group; public TextWebSocketFrameHandler(ChannelGroup group) { this.group = group; } @Override public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception { if (evt == WebSocketServerProtocolHandler .ServerHandshakeStateEvent.HANDSHAKE_COMPLETE) { ctx.pipeline().remove(HttpRequestHandler.class); group.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame( "Client " + ctx.channel() + " joined")); group.add(ctx.channel()); } else { super.userEventTriggered(ctx, evt); } } @Override public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception { group.writeAndFlush(msg.retain()); } }
3. 初始化ChannelPipeline
为在ChannelPipeline中添加ChannelHandler,需要继承ChannelInitializer并且实现initChannel方法,下面是ChatServerInitializer的代码。
public class ChatServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { private final ChannelGroup group; public ChatServerInitializer(ChannelGroup group) { this.group = group; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec()); pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler()); pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(64 * 1024)); pipeline.addLast(new HttpRequestHandler("/ws")); pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/ws")); pipeline.addLast(new TextWebSocketFrameHandler(group)); } }
对于使用HTTP协议(升级前)和WebSocket协议(升级后)的管道中的处理器分别如下图所示。

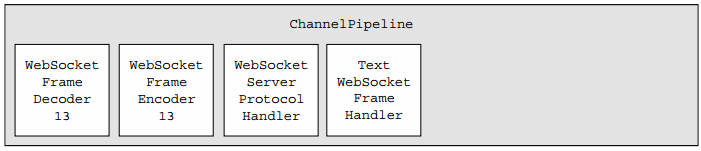
4. Bootstrapping
ChatServer类用于启动服务器并且安装ChatServerInitializer,其代码如下。
public class ChatServer { private final ChannelGroup channelGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(ImmediateEventExecutor.INSTANCE); private final EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); private Channel channel; public ChannelFuture start(InetSocketAddress address) { ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); bootstrap.group(group) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(createInitializer(channelGroup)); ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(address); future.syncUninterruptibly(); channel = future.channel(); return future; } protected ChannelInitializer<Channel> createInitializer( ChannelGroup group) { return new ChatServerInitializer(group); } public void destroy() { if (channel != null) { channel.close(); } channelGroup.close(); group.shutdownGracefully(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { if (args.length != 1) { System.err.println("Please give port as argument"); System.exit(1); } int port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); final ChatServer endpoint = new ChatServer(); ChannelFuture future = endpoint.start( new InetSocketAddress(port)); Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread() { @Override public void run() { endpoint.destroy(); } }); future.channel().closeFuture().syncUninterruptibly(); } }
上述代码就完成了服务端的所有代码,接着进行测试。
2.4 加密应用
上述代码中可正常进行通信,但是并未加密,首先需要添加SecureChatServerInitializer,其代码如下。
public class SecureChatServerInitializer extends ChatServerInitializer { private final SslContext context; public SecureChatServerInitializer(ChannelGroup group, SslContext context) { super(group); this.context = context; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { super.initChannel(ch); SSLEngine engine = context.newEngine(ch.alloc()); ch.pipeline().addFirst(new SslHandler(engine)); } }
然后添加SecureChatServerInitializer,代码如下。
public class SecureChatServer extends ChatServer { private final SslContext context; public SecureChatServer(SslContext context) { this.context = context; } @Override protected ChannelInitializer<Channel> createInitializer( ChannelGroup group) { return new SecureChatServerInitializer(group, context); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { if (args.length != 1) { System.err.println("Please give port as argument"); System.exit(1); } int port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); SelfSignedCertificate cert = new SelfSignedCertificate(); SslContext context = SslContext.newServerContext( cert.certificate(), cert.privateKey()); final SecureChatServer endpoint = new SecureChatServer(context); ChannelFuture future = endpoint.start(new InetSocketAddress(port)); Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread() { @Override public void run() { endpoint.destroy(); } }); future.channel().closeFuture().syncUninterruptibly(); } }
2.5 测试应用
在编译的classes文件夹中加入index.html(客户端),其中index.html的源码如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>WebSocket Chat</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var socket;
if (!window.WebSocket) {
window.WebSocket = window.MozWebSocket;
}
if (window.WebSocket) {
socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080/ws");
socket.onmessage = function(event) {
var ta = document.getElementById('responseText');
ta.value = ta.value + '\n' + event.data
};
socket.onopen = function(event) {
var ta = document.getElementById('responseText');
ta.value = "connected!";
};
socket.onclose = function(event) {
var ta = document.getElementById('responseText');
ta.value = ta.value + "connection is shutdown";
};
} else {
alert("your broswer do not support WebSocket!");
}
function send(message) {
if (!window.WebSocket) {
return;
}
if (socket.readyState == WebSocket.OPEN) {
socket.send(message);
} else {
alert("connection is not start.");
}
}
</script>
<form onsubmit="return false;">
<h3>WebSocket ChatRoom:</h3>
<textarea id="responseText" style="width: 500px; height: 300px;"></textarea>
<br>
<input type="text" name="message" style="width: 300px" value="">
<input type="button" value="Send Message" onclick="send(this.form.message.value)">
<input type="button" onclick="javascript:document.getElementById('responseText').value=''" value="Clear message">
</form>
<br>
<br>
</body>
</html>
然后启动ChatServer(非加密方式),最后在浏览器中访问localhost:8080(可打开多个窗口,多个客户端),其运行效果如下。


可以看到两个客户端之间可以正常进行通信,互相发送消息。
三、总结
本篇博文通过一个示例讲解了WebSocket协议的具体使用,可完成不同客户端之间的通信,也谢谢各位园友的观看~
PS:如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮,您的“推荐”,将会是我不竭的动力!
作者:leesf 掌控之中,才会成功;掌控之外,注定失败。
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
如果觉得本文对您有帮助,您可以请我喝杯咖啡!





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号