SpringBoot运行流程
一、准备阶段
我们先看一下这个SpringApplication的构造方法中做了什么事情,为run方法准备了那些事情
通常在一个spring boot的应用中,会看到下面一段代码作为应用的入口
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
那么这段代码究竟做了什么呢,让我们深入来分析它背后的原理。当我们点击run来查看源代码时,会看到下面这段代码,这段注释说明这是一个助手方法,可以通过指定一个primarySource的source源来启动,这个primarySource其实就是我们的启动类Application
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
接着,我们继续进入run方法,你会看到另外一个helper方法,这个helper方法首先初始化一个SpringApplication,然后再一次执行SpringApplication实例的run方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
SpringApplication构造方法又调用了其重载构造方法
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 步骤 1 初始化webApplicationType
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 步骤 2 初始化ApplicationContextInitializer
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 步骤 3 初始化ApplicationListener
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 步骤 4 获取Main方法所在类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
1.1 初始化webApplicationType
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
webApplicationType确定当前应用的类型,进入deduceFromClasspath()可以看到spring boot是如何确定类型的,从下面这段代码中可以看出当前应用属于哪一种类型取决于classpath中是否加载到了相应的类。
- 如果
classpath中有org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler类,但是没有DispatcherServlet和ServletContainer类,则类型为Reactive web application,会启动一个嵌入式的reactive web server。 - 如果
classpath中既没有javax.servlet.Servlet又没有org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext,那么该应用不是一个web application。 - 如果不是以上两种,那么就判断为一个
servlet的web application,会启动一个嵌入式的servlet web server。
1.2 初始化ApplicationContextInitializer
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
通过getSpringFactoriesInstances最终获得META-INF/spring.factories中所有的ApplicationContextInitializer,而ApplicationContextInitializer是用来初始化ConfigurableApplicationContext
1.3 初始化ApplicationListener
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
通过getSpringFactoriesInstances最终获得META-INF/spring.factories中所有的ApplicationListener
1.4 获取Main方法所在类
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
通过构造一个RuntimeException,然后得到StackTrace的方法,来获得main方法所在的类,这样做的原因是因为primarySource是作为数组形式传入方法的,如果有超过一个primarySource,那么就没法直接从primarySource来判断哪个source是main方法所在实例。
二、运行阶段
SpringApplication类的构造方法看完后,我们就来看一下他的run方法吧:
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//创建StopWatch对象用于统计run方法的执行耗时
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
//调用start方法表示开始启动计时
stopWatch.start();
//声明上下文
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
//故障分析集合
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//设置headless模式 就是设置系统属性java.awt.headless
configureHeadlessProperty();
//通过SPI机制加载所有的SpringApplicatoinRunListener监听器
//SpringBoot启动过程的不同阶段会回调该监听器的不同方法
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//使用组合对象的设计模式 迭代的执行starting()
listeners.starting();
try {
//将SpringApplication的启动参数封装为ApplicationArguments
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//创建SpringBoot应用使用的环境变量对象,内部会根据webApplicationType创建不同的环境对象,
//这里会创建StandardServletEnvironment对象
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//打印Banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建使用的ApplicationContext上下文对象,这里会根据webApplicationType创建不同的对象上下文对象
//这里会创建StandardServletEnvironment对象
context = createApplicationContext();
//获取启动错误报告实例
//通过SPI机制加载SpringBoot的异常报告对象SpringBootExceptionReporter
//当SpringBoot启动过程中抛出异常时,会通过该对象打印错误日志
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//ApplicationContext上下文对象创建完毕后,会调用prepareContext为ApplicationContext做一些准备工作
//比如为ApplicationContext设置环境变量,回调ApplicationContextInitializer对象的initialize方法等
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//调用ApplicationContext的refresh方法,启动整个Spring应用程序
refreshContext(context);
//刷新后的上下文处理
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
//计时结束
stopWatch.stop();
//打印日志
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//调用SpringApplcationListener对象的started监听方法
//监听spring上下文,此时上下文已启动,Spring Bean已初始化完成
listeners.started(context);
//回调Spring中的的ApplicationRunner对象和CommandLineRunner对象
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
//启动成功,则调用SpringApplicationListener对象的running监听方法
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
//抛出异常,则使用SpringExceptionReporter打印异常报告
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
//返回创建的ApplicationContext应用上下文
return context;
}
1.创建 Spring Application 实例,调用 run 方法,同时将启动入口类作 为参数传递进去;
2.通过 Spring Factories Loader 加载 META-INF/spring.factories 文件;
3.然后由 SpringApplicationRunListener 来发出 starting 消息;
4.创建参数,并配置当前 SpringBoot 应用需要使用的 Environment 实例;
5.完成之后,依然由 SpringApplicationRunListener 来发出 environmentPrepared 消息;
6.创建 Spring 的应用上下文实例:ApplicationContext,初始化该实例 并设置应用环境配置实例:Environment,同时加载相关的配置项;
7.由 SpringApplicationRunListener 发出 contextPrepared 消息,告知 SpringBoot 应用当前使用的 ApplicationContext 已准备完毕;
8.将各种 Bean 组件装载入 Spring 的 IO 容器/应用上下文: ApplicationContext 中,继续由 SpringApplicationRunListener 来发出 contextLoaded 消息,告知 SpringBoot 应用当前使用的 ApplicationContext 已准备完毕;
9.重新刷新 Refresh Spring 的应用上下文实例:ApplicationContext, 完成 IOC 容器可用的最后一步;
10.由 SpringApplicationRunListener 发出 started 消息,完成最终的程序的启动;
11.由 SpringApplicationRunListener 发出 running 消息,告知程序已成功运行起来了。
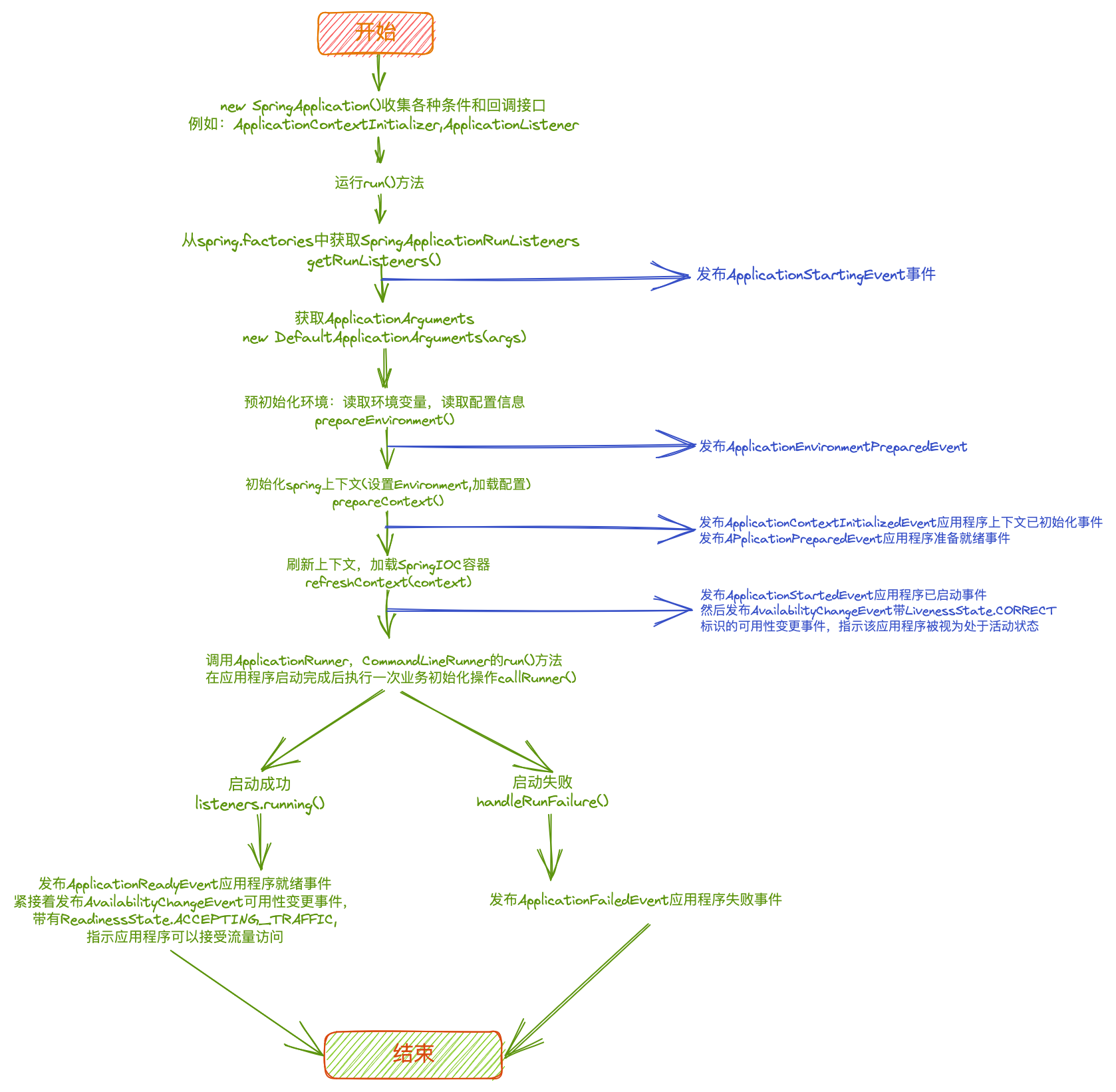
SpringApplication运行阶段主要就分为:
- 加载:SpringApplication运行监听器(SpringApplicationRunListener)
- 运行:SpringApplication运行监听器(SpringApplicationRunListeners)
- 监听:Spring-boot事件,spring事件。
- 创建:创建上下文,Environment,其他。
- 失败:打印故障分析报告。
- 回调。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix