JavaScript中面相对象OOP
方法
方法的原型链
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
//原型链:a1对象(实例对象)还让A.prototype对象(原型对象)之间的连接,叫做原型链
//2个对象。之间有一个链接 _proto_
//a1下是没有num1(A中没有this.num1=20),会继续通过a1._proto_找num1。
//a1下有num1(A中没有this.num1=20),不再会继续通过a1._proto_找num1,
//即使A.prototype.num1 = 10; alert(a1.num1);依然是20
//....
//原型链最外层:Object.prototype
function A() {
//this.num1=20
}
//A.prototype.num1 = 10;
/*Function.prototype.num1 = 30;*/
Object.prototype.num1 = 40;
/*A.prototype.num1 = 60*/
A.prototype.fun = function () {
alert(this.num1)
};
var a1 = new A();
a1.fun();
alert(a1.num1);
</script>
<body>
</body>
</html>
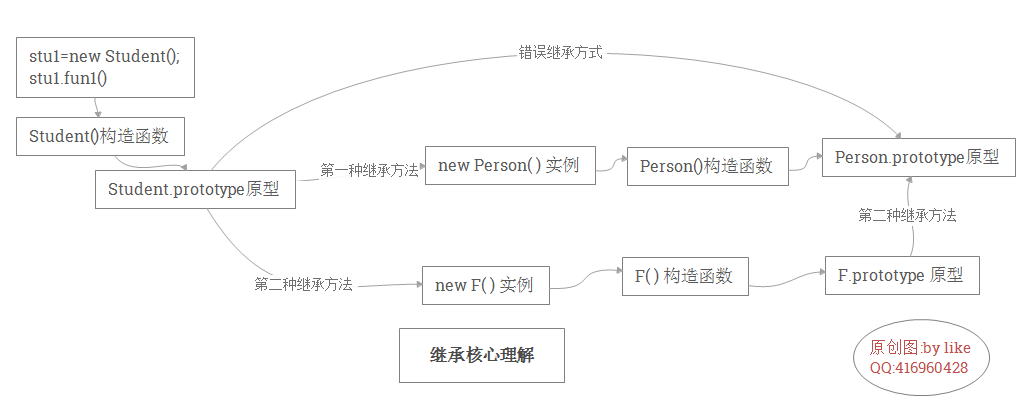
创建 本质继承
继承:子对象的属性修改,不能导致父对象的属性的改变
1:Object.create(对象原型)
2:inherit4objfun
我画了一张图
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ZH-CN">
<head></head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function inherit4fun(Child, Parent) {
function F() {}; // 定义一个临时函数
F.prototype = Parent.prototype; // 把父类的原型赋给临时函数的原型
Child.prototype = new F(); // 把子类的原型赋值为f的对象
}
function inherit4objfun(p){
if(p == null) throw TypeError();
//可以不用es5中的Object.create
//if(Object.create)return Object.create(p);
var t = typeof p;
if(t !== "object" && t !== "function") throw TypeError();
function f(){}
f.prototype = p;
return new f();
}
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.aler = function () {
console.log(`Person.function-aler`);//``es6 的字符串 可以换行
// console.log(`Per
// son.function-aler`);//``es6 的字符串 可以换行
}
}
//因为prototype是对象,可以写成无序键值对
Person.prototype = {
sayHi: function () {
console.log('Person.prototype-sayhi');
},
sayHello: function () {
console.log('Person.prototype-sayhello');
}
}
function Student(sname, sage) {
Person.call(this, sname, sage);
}
/* 错误重现1
//Student.prototype = Person.prototype;
//当修改Student.prototype时候,Person.prototype也会被修改
//Student.prototype.saystu =function () {console.log('saystu');}
*/
/* 错误重现2
//当改变Student.prototype时候,原来的会被覆盖
// Student.prototype = {
// saystu: function () {
// console.log('saystu');
// }
// }
*/
/* 正确重现1
//当改变Student.prototype时候,原来的会被覆盖,达不到子类继承父类,或者子类原型可以增加方法不影响到父类原型
//此时就需要将两者的方法合并。-->将基类原型的方法拷贝到子类原型上 类似$.extend 拷贝继承 (浅拷贝就好了,原型中一般存方法)
// Student.prototype = new Person();
// Student.prototype.constructor = Student;
// Student.prototype.saystu =function () {console.log('saystu');}
*/
/* 正确重现2
// inherit4fun(Student,Person);
// Student.prototype.saystu =function () {console.log('saystu');}
*/
/* 正确重现3
*/
Student.prototype=inherit4objfun(Person.prototype);
Student.prototype.saystu =function () {console.log('saystu');}
/* 正确重现4 对象的继承
*/
var o={x:1}
var childObj=inherit4objfun(o);
childObj.y=2;
console.log(childObj)//打印不出继承的属性。
console.log(childObj.x+childObj.y)//3
var stu1 = new Student("zg", 18);
var p1 = new Person(" ls", 20);
console.log(stu1,p1)
//Student.prototype增加saystu方法,然后看Person.prototype是否增加,增加便是错误的
console.log(Student.prototype,Person.prototype )
stu1.aler();
stu1.sayHi();
stu1.sayHello();
//stu1.saystu();
</script>
<body>
</body>
</html>
对象
叫法:散列 散列表 hash hashtable``字典 dictionary``关联数组 associate array
种类:1,宿主对象(浏览器定义),dom对象 bom对象(window location navigatior),这些浏览器定义的方法可以当成普通的js函数,可以把宿主浏览器对象当成内置对象。
2,内置对象(js定义)50多种。3,自定义对象
特性:扩展标记(是否可以向改对象 添加新属性)!!,类(class),原型(prototype)
/*
内置对象举例 更多https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects
错误 Error,EvalError,InternalError,RangeError,ReferenceError,SyntaxError,TypeError,URIError 8种
带索引的集合Array,Int8Array,Uint8Array,Uint8ClampedArray,Int16Array,Uint16Array,Int32Array,Uint32Array,Float32Array,Float64Array 10种
带键的集合Map, Set ,WeakMap ,WeakSet 4种
结构化数据ArrayBuffer ,SharedArrayBuffer, Atomics, DataView, JSON 5种
控制抽象对象 Promise, Generator ,GeneratorFunction 3种
反射 Reflect, Proxy 2种
国际化ECMA脚本的多语言附加组件。Intl,Intl.Collator,Intl.DateTimeFormat,Intl.NumberFormat
非标准对象Iterator ,ParallelArray ,StopIteration
其他arguments
*/
console.log({}.toString.call(new Error())) //[object Error]
console.log({}.toString.call(new SyntaxError('errmsg'))) //[object Error]
var buffer = new ArrayBuffer(2);
var a=new DataView(buffer)
console.log({}.toString.call(a)) //[object DataView]
function* gen() { yield 1;yield 2;yield 3;}
var g = gen()
onsole.log({}.toString.call(g)) //[object Generator]
console.log({}.toString.call(Infinity)) //[object Number]
console.log({}.toString.call(new Float32Array(2))) //[object Float32Array]
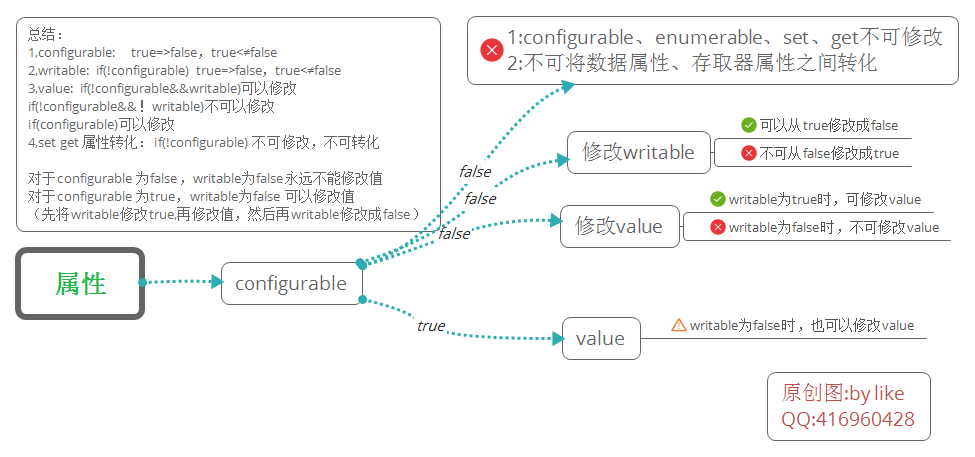
属性(这里真的很复杂)------------------
种类:继承属性(inherited property),自有属性(own property)
属性特性(property attribute)
1,数据属性特性
可枚举(enumerable) 默认true。for-in遍历出,可配置(configurable),可写(writable),值(value)
2,访问器属性特性
将数据属性的 可写和值特性换成set(val), get()方法function!
可枚举(enumerable)默认true。for-in遍历出,可配置(configurable),set(val)function,get()function
定义属性:Object.defineProperty(), Object.defineProperties()
获取属性:getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj,attr),getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj)(参数只有对象,注意返回值)
/*
不明确声明,特性值默认false,value默认undefined, 区分常用方式
*/
//defineProperty
var obj={};
Object.defineProperty(obj,'a',{configurable:true})
//{configurable:true,enumerable:false,value:undefined,writable:false}
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj,'a')
/*
{
a: Object
__proto__: Object
}
*/
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj)
-------------------------------------------------------
//defineProperties
/*
{
a:{configurable:false,enumerable:false,value:undefined,writable:false},
b:{configurable:false,enumerable:false,value:undefined,writable:false},
__proto__:Object...
}
*/
var obj={};
Object.defineProperties(obj,{a:{enumerable:false},b:{writable:false}})
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj)
-------------------------------------------------------
//常用默认true
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors({a:1},'a')//{configurable:true,enumerable:true,value:1,writable:true}
对象的可扩展Object.preventExtensions(o)(对象添加新属性,注意不是编辑原来属性)
var o={a:1};
o.b=2
console.dir(o)//{a:1,b:2}
Object.preventExtensions(o)
o.c=3
console.dir(o)//{a:1,b:2} 不可添加
o.b=4
console.dir(o)//{a:1,b:4} 可以编辑
遍历属性名------------------
自定义对象属性都是可枚举
继承对象的内置属性都是不可枚举
1,for in
2,Object.keys(obj)
3,Object.getOwnPropertyNames(obj) 查看隐藏不可枚举属性比较有用
var parentObj={a1:'a1'};
Object.defineProperties(parentObj,{a2:{enumerable:true,value:'a2'},a3:{enumerable:false,value:'a3'}})
var childObj=inherit4objfun(parentObj);
childObj.b1='b1';
Object.defineProperties(childObj,{b2:{enumerable:true,value:'b2'},b3:{enumerable:false,value:'b3'}})
/* ------------------------------------------ for in 本身,继承,可枚举 ---------------------------------------------------- */
for(var attr in childObj){console.info(`自身和继承的枚举属性`+attr)}//a1 a2 b1 b2
/* ------------------------------------------ Object.keys(obj) 本身,可枚举 ---------------------------------------------------- */
console.log(`自身的枚举属性`+Object.keys(childObj))//["b1", "b2"]
/* ------------------------------------------ Object.getOwnPropertyNames(obj) 本身所有属性,包括不可枚举---------------------------------------------------- */
console.log(`自身的所有属性,包括不可枚举`+Object.getOwnPropertyNames(childObj))//["b1", "b2"]
var arr=[6,'a']
Object.getOwnPropertyNames(arr)//["0", "1","length"]
Object.getOwnPropertyNames(Object.prototype)
//["__defineGetter__", "__defineSetter__", "hasOwnProperty", "__lookupGetter__", "__lookupSetter__", "propertyIsEnumerable", "constructor", "toString", "toLocaleString", "valueOf", "isPrototypeOf", "__proto__"]
Object.getOwnPropertyNames(Object)
//["length", "name", "arguments", "caller", "prototype", "assign", "create", "getOwnPropertyDescriptor", "getOwnPropertyNames", "getOwnPropertySymbols", "is",
//"preventExtensions", "seal", "defineProperties", "defineProperty", "freeze", "getPrototypeOf", "isExtensible", "isFrozen", "isSealed", "keys", "setPrototypeOf", "entries", "values", "getOwnPropertyDescriptors"]
检测属性------------------
除了for in ,要先知道属性名字,输入名字 检测。检测和遍历的区别
for in 带有遍历功能 自带检测功能
1,for in 自有和继承的枚举属性
2,hasOwnProperty()自有属性 包括不可枚举的
3,propertyIsEnumerable()是hasOwnProperty()增强版 1自有属性,2可枚举
childObj.hasOwnProperty('a1')//false 继承不能检测
childObj.hasOwnProperty('a3')//false
childObj.hasOwnProperty('b1')//true
childObj.hasOwnProperty('b3')//true 自有不可枚举的也能检测出来
childObj.propertyIsEnumerable('a1')//false 继承不能检测
childObj.propertyIsEnumerable('a3')//false
childObj.propertyIsEnumerable('b1')//true 只有自有可枚举属性
childObj.propertyIsEnumerable('b3')//false
删除
//防止内存泄漏
var a={b:{c:0}}
//delete b.c
delete a.b//切断b属性(对象)与宿主a(对象)的联系 删除的b对象的引用{{c:0}}依然存在 要检测遍历b属性中是否含有属性,再递归检测属性是否含有属性,直到最后不含有。防止内存泄漏
//假如从var a={b:{c:{d:{e:1}}}}删除b属性
//从里到外删除
//delete a.b.c.d.e
//delete a.b.c.d
//delete a.b.c
//delete a.b
var o={a:1};
var c;
Object.defineProperty(o,'b',{configurable: false,
enumerable: true,
get: function () {
return 11;
},
set: function proxySetter(newVal) {
}})
o.b=8
知识没有高低贵贱之分。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号