JavaIO流
流的概述
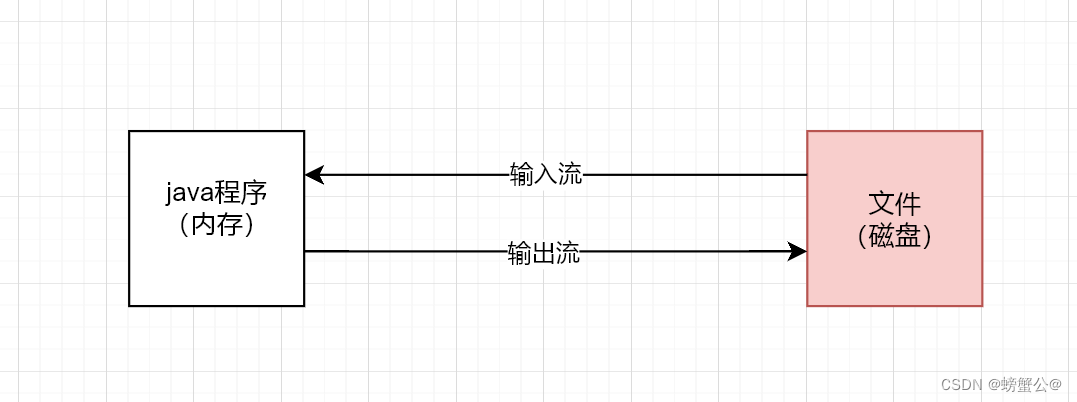
要完成文件的读写操作,就必须了解C#中另外一个重要的概念——流(Stream)
C#中流的概念可以和生活中的流相对应。在生活中有水流和电流,首先要有一个源头,还需要有传输的管道,
水流有河道、水管作为传输管道,电流有电线,而这些流都会有一个目的,就是它的流向。C#的流也需要源头——文件、数据流入流出管道以及数据的访问。
1、输出流和输入流
.Net Framework中进行的所有输入、输出工作都需要用到流。
1、输出流:当向某些外部目标写入数据时,就要用到输出流。
2、输入流:用于将数据读到程序访问的内存或变量中。
在程序的控制台中的可以理解为:
输出流:控制台程序中,将信息从程序中输出的处理:Console.WriteLine();
输入流:通过用户键盘来输入到程序当中处理:Console.ReadLine();
2、文件读写,常用的三个类
对于文件读写,常见的三个类:
1、FileStream(文件流):这个类主要用于在二进制文件中读写二进制数据——也可以使用它读写任何文件。
2、StreamWriter(流写入器)和StreamReader(流读取器):这二个类是专门用来读写文本文件的。
常用的文件操作
1、创建文件对象相关构造器和方法
new File(String pathname)//根据路径构建一个File 对象
new File(File parent,String child)//根据父目录文件+子路径构建
new File(String parent,String child)//根据父目录+子路径构建
createNewFile)//创建文件
-3、常用的文件操作<'
1、创建文件对象相关构造器和方法-
new File(String pathname)//根据路径构建一个File 对象
new File(File parent,String child)//根据父目录文件+子路径构建e
new File(String parent,String child)//根据父目录+子路径构建
(
createNewFile)//创建文件
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileCreate {'
import org.testng.annotations.Test;e
-
import java.io.File;e'
import java.io.IOException;e'
c'
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
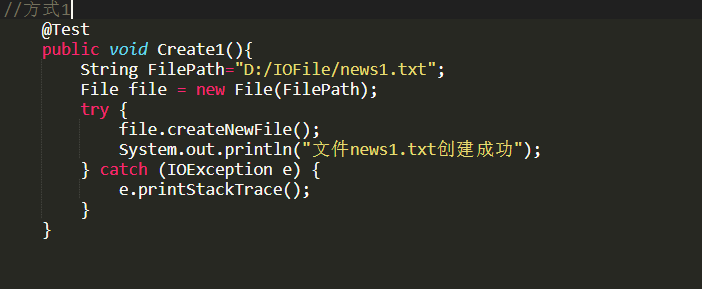
//方式1
@Test
publicvoidcreate1(){
StringfilePath="D:\\file1.txt";Filefile=newFile(filePath);
try{file.createNewFile();System.out.println("创建文件1成功");
}catch(IOExceptione){e.printStackTrace();
}
}
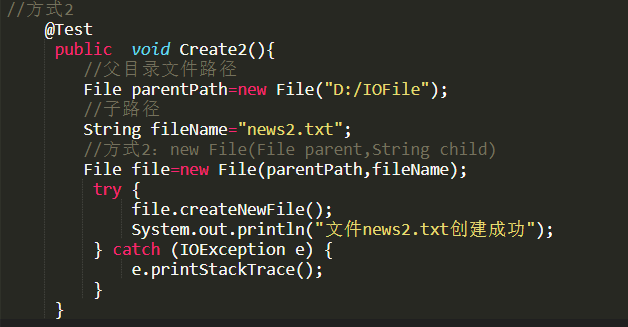
//方式2
@Test
publicvoidcreate2(){
FileparentFile=newFile("D:\\");
StringfileNane="file2.txt";
Filefile=newFile(parentFile,fileNane);
try{file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件2创建成功");
}catch(IOExceptione){thrownewRuntimeException(e);
}
}
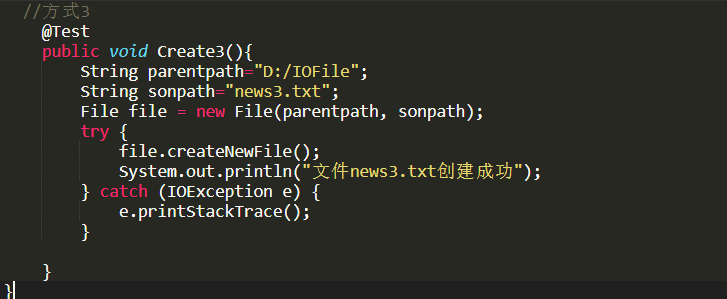
//方式三
@Test
publicvoidcreate3(){StringparentPath="d:\\";
StringfilePath="file3.txt";Filefile=newFile(parentPath,filePath);
try{file.createNewFile();System.out.println("文件3创建成功");
}catch(IOException e)
{thrownewRuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
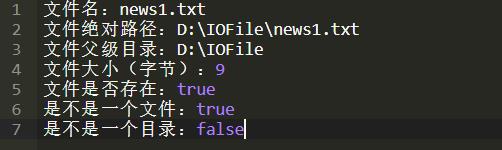
获取文件相关信息
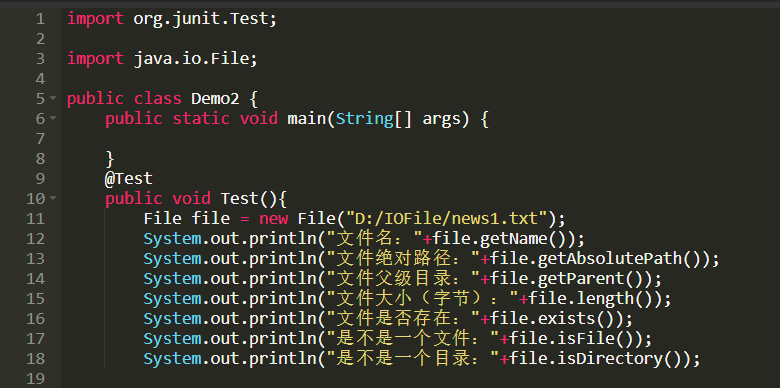
输出结果:
3、Scanner与Println的练习
3.1 基本键盘输入,代码如下:
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class scanPrintTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建Scanner对象,接受从控制台输入
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
//接受Sting类型
String str = input.next();
//输出结果
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}
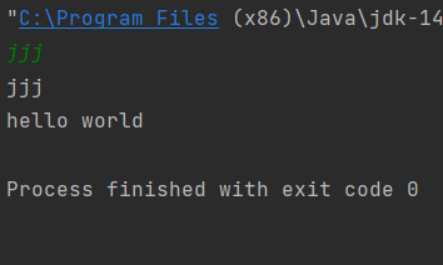
输入相应的string类型的数得到结果截图如下
3.2 常见键盘输入类型,代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class scanTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建Scanner对象,接受从控制台输入
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
//double类型的数据
System.out.print("请输入一个double类型的数");
double d = input.nextDouble();
System.out.println(d);
//int类型的数据
System.out.println("请输入一个int类型的数");
int i = input.nextInt();
System.out.println(i);
//字符串类型的数据
System.out.println("请输入一个string类型的数");
String s=input.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
利用IDEA运行代码,输入相应的double类型的数,int类型的数,string类型的数得到结果截图如下:




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律