小橙书阅读指南(七)——优先队列和索引优先队列
算法描述:许多应用程序都需要按照顺序处理任务,但是不一定要求他们全部有序,或是不一定要一次就将他们排序。很多情况下我们只需要处理当前最紧急或拥有最高优先级的任务就可以了。面对这样的需求,优先队列算法是一个不错的选择。
算法图示:
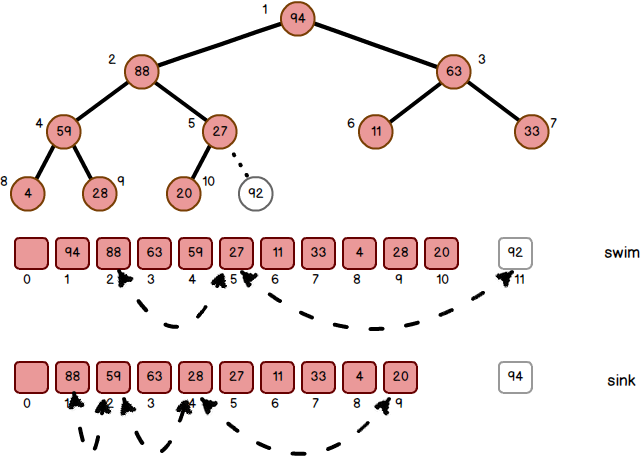
算法解释:上图所展示的是最大优先队列(大顶堆)的算法逻辑,在这个标准的二叉树中,任意节点的元素都大于其叶子节点的元素。利用数组表示该二叉树即Array[2]和Array[3]是Array[1]的叶子节点,Array[4]和Array[5]是Array[2]的叶子节点,Array[6]和Array[7]是Array[3]的叶子节点,以此类推。通过计算可知,有任意节点K,K/2是它的根节点,2*K和2*K+1是它的叶子节点。(注:Array[0]通常不使用)。于是对于任意节点的调整可以通过上浮(swim)或下称(sink)来达到目的。
当有新的元素插入的时候,我们会首先把它分配在数组的尾部(Array[size+1]),然后自下而上的根据子节点到根节点的路径不断上浮到合适的位置。
当最大的元素被取走以后,我们会首先把数组尾部Array[size])的元素放到数组的头部(Array[1]),然后自上而下的从根节点下称到子节点的合适位置。
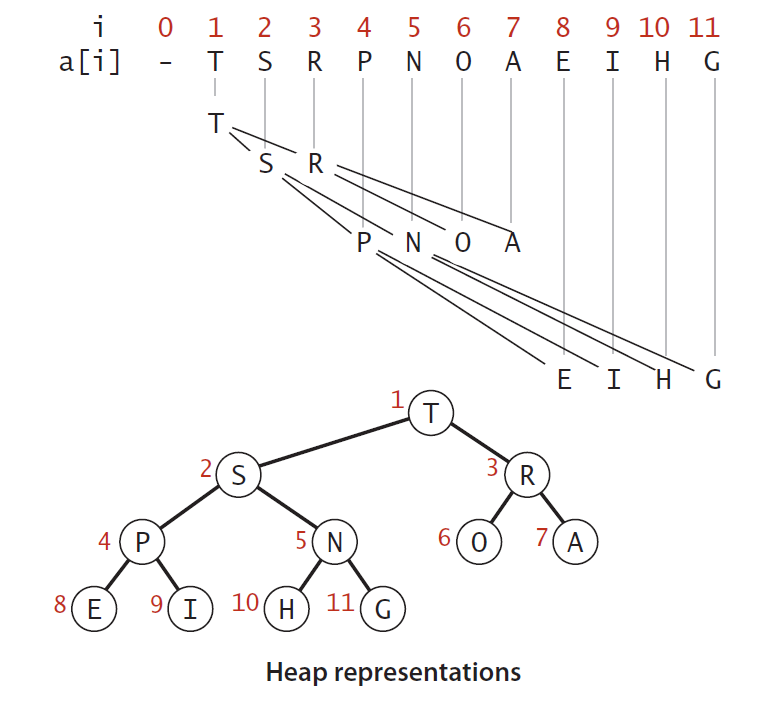
数组和二叉树互换的算法图例:
Java代码示例:
package algorithms.sorting.pq; import algorithms.common.ArraysGenerator; /** * 最大优先队列(大顶堆) * @param <T> */ public class MaxPriorityQueue<T extends Comparable<T>> { private T[] heap; private int size = 0; public MaxPriorityQueue(int maxSize) { heap = (T[]) new Comparable[maxSize + 1]; } /** * 判单是否为空 * @return {@code true}当前队列未空 * {@code false}否则不为空 */ public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } /** * 插入新元素至末尾,并上浮至合适的位置 * @param value */ public void insert(T value) { heap[++size] = value; swim(size); } /** * 移除堆顶元素并调整堆 * @return T 返回最大元素 */ public T remove() { T maxValue = heap[1]; // 堆顶的元素和堆底元素交换位置,并减少数组长度 exch(1, size--); heap[size + 1] = null; sink(1); return maxValue; } // 元素上浮 private void swim(int k) { // 下层元素如果大于上层元素且该元素非顶层元素时,循环上浮 while (k > 1 && heap[k / 2].compareTo(heap[k]) < 0) { exch(k / 2, k); k = k / 2; } } private void sink(int k) { while (2 * k <= size) { int leafIndex = 2 * k; // 选择两个子节点中更大的那个元素作为交换目标 if (leafIndex < size && heap[leafIndex].compareTo(heap[leafIndex + 1]) < 0) { leafIndex++; } if (heap[k].compareTo(heap[leafIndex]) < 0) { exch(k, leafIndex); } else { // 如果本轮比较未发生元素交换则不用继续下沉 break; } k = leafIndex; } } private void exch(int i, int j) { T tmp = heap[i]; heap[i] = heap[j]; heap[j] = tmp; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(); buffer.append("["); for (int i = 1; i <= size; ++i) { buffer.append(heap[i]); buffer.append(","); } return buffer.deleteCharAt(buffer.length() - 1).append("]").toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { MaxPriorityQueue maxPriorityQueue = new MaxPriorityQueue(100); Integer[] array = ArraysGenerator.generate(10, 1, 100); for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { maxPriorityQueue.insert(array[i]); } System.out.println(maxPriorityQueue); while(!maxPriorityQueue.isEmpty()) { System.out.println(maxPriorityQueue.remove()); } } }
Qt/C++代码示例:
// MaxPriorityQueue.h class QString; class MaxPriorityQueue { public: MaxPriorityQueue(); ~MaxPriorityQueue(); bool isEmpty(); void insert(int val); int remove(); QString toString(); private: void increase(); void decrease(); void swim(int k); void sink(int k); void exch(int i, int j); int size; int maxSize; int *heap = 0; static int initialCapacity; }; // MaxPriorityQueue.cpp #include "maxpriorityqueue.h" #include <QDebug> #include <QString> int MaxPriorityQueue::initialCapacity = 16; MaxPriorityQueue::MaxPriorityQueue() :maxSize(initialCapacity), size(0) { heap = new int[maxSize]; } MaxPriorityQueue::~MaxPriorityQueue() { if (heap) { delete heap; } } bool MaxPriorityQueue::isEmpty() { return size == 0; } void MaxPriorityQueue::insert(int val) { if (size >= maxSize) { increase(); } heap[++size] = val; swim(size); } int MaxPriorityQueue::remove() { int maxValue = heap[1]; exch(1, size--); sink(1); if (size < maxSize / 2 && maxSize > initialCapacity) { decrease(); } return maxValue; } QString MaxPriorityQueue::toString() { QString buf; buf.append("["); for (int i = 1; i < size; ++i) { buf.append(QString::number(heap[i])); buf.append(","); } return buf.left(buf.length() - 1).append("]"); } void MaxPriorityQueue::increase() { maxSize *= 2; int *newheap = new int[maxSize]; for (int i = 1; i <= size; ++i) { newheap[i] = heap[i]; } heap = newheap; } void MaxPriorityQueue::decrease() { maxSize /= 2; int *newheap = new int[maxSize]; for (int i = 1; i <= size; ++i) { newheap[i] = heap[i]; } heap = newheap; } void MaxPriorityQueue::swim(int k) { while (k > 1 && heap[k / 2] < heap[k]) { exch(k / 2, k); k /= 2; } } void MaxPriorityQueue::sink(int k) { while (2 * k <= size) { int j = 2 * k; if (j < size && heap[j] < heap[j + 1]) { j++; } if (heap[k] < heap[j]) { exch(k, j); } else { break; } k = j; } } void MaxPriorityQueue::exch(int i, int j) { int temp = heap[i]; heap[i] = heap[j]; heap[j] = temp; }
C++的代码增加了动态数组扩容的实现。
算法总结:上面提供的是最大优先队列算法,适合获取最大优先值的应用。如果需要获取最小值则需要构造最小优先队列,即在完全二叉树的任意节点都小于其子节点。但是,优先队列存在一个缺点,即我们无法自由访问队列中的元素并且也无法提供修改的操作。试想在一个多任务的应用系统中,我们对已经加入处理队列的任务需要调整优先级。这就是索引优先队列的由来。
算法图示:
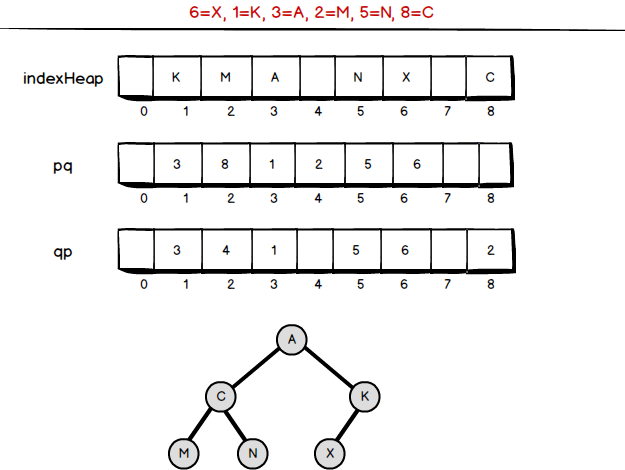
算法分析:索引优先队列对于刚刚接触算法的同学是非常难的,主要是在这个数据结构中我们引入了三个平行数组。观察上图,indexHeap是索引和元素的对应数组,由于我们需要随时根据索引(indexHeap数组的下标)找到对应的元素,所以这个数组中的元素实际是不会移动的。因此我们就需要引入新的数pq。注意,pq是三个数组中唯一的紧密数组(其余的两个都是稀松数组)。pq负责保存元素排序后的索引顺序,因此pq数组可以和完全二叉树相互转换。
现在假设我们需要维护3=A这对映射关系,需要修改成3=T:indexHeap[3]=T。可是接下来就有点麻烦了,我们不知道A在树中的具体位置。因此我们还需要再引入一个数组用来保存每一个索引在二叉树中的位置(否则就只能通过遍历的方法),qp[pq[key]]=key。
Java算法示例:
package algorithms.sorting.pq; /** * 最小索引优先数组 * * @param <T> */ public class IndexMinPriorityQueue<T extends Comparable<T>> { private T[] indexHeap; private int[] pq; private int[] qp; private int size; public IndexMinPriorityQueue(int maxSize) { size = 0; indexHeap = (T[]) new Comparable[maxSize + 1]; pq = new int[maxSize + 1]; qp = new int[maxSize + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= maxSize; ++i) { qp[i] = -1; } } /** * 插入新的索引和元素 * * @param key * @param value */ public void insert(int key, T value) { size++; indexHeap[key] = value; pq[size] = key; qp[key] = size; swim(size); } public void change(int key, T value) { if (contains(key)) { indexHeap[key] = value; swim(qp[key]); sink(qp[key]); } } /** * 移除堆顶的最小元素并返回该元素 * * @return */ public T remove() { int minKey = pq[1]; exch(1, size--); sink(1); qp[minKey] = -1; return indexHeap[minKey]; } /** * 移除指定索引的元素,并返回该元素 * * @param key * @return */ public T remove(int key) { int pos = qp[key]; exch(pos, size--); swim(pos); sink(pos); qp[key] = -1; return indexHeap[key]; } public int delete() { int minKey = pq[1]; exch(1, size--); sink(1); qp[minKey] = -1; return minKey; } public T get(int key) { return indexHeap[key]; } public boolean contains(int key) { return qp[key] != -1; } public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } private void swim(int k) { while (k > 1 && indexHeap[pq[k / 2]].compareTo(indexHeap[pq[k]]) > 0) { exch(k / 2, k); k /= 2; } } private void sink(int k) { while (2 * k <= size) { int leafIndex = 2 * k; // 当前节点存在两个叶子节点 且 右叶子节点 小于 左叶子节点 以右叶子节点作为比较目标 if (leafIndex < size && indexHeap[pq[leafIndex + 1]].compareTo(indexHeap[pq[leafIndex]]) < 0) { leafIndex++; } if (indexHeap[pq[k]].compareTo(indexHeap[pq[leafIndex]]) > 0) { exch(k, leafIndex); } else { break; } k = leafIndex; } } private void exch(int i, int j) { int temp = pq[i]; pq[i] = pq[j]; pq[j] = temp; qp[pq[i]] = i; qp[pq[j]] = j; } public static void main(String[] args) { IndexMinPriorityQueue<String> indexMinPriorityQueue = new IndexMinPriorityQueue<>(50); indexMinPriorityQueue.insert(5, "C"); indexMinPriorityQueue.insert(7, "A"); indexMinPriorityQueue.insert(2, "Z"); indexMinPriorityQueue.insert(6, "F"); indexMinPriorityQueue.change(6, "X"); while (!indexMinPriorityQueue.isEmpty()) { System.out.println(indexMinPriorityQueue.remove()); } } }
算法总结:qp可能是索引优先队列最难理解的部分。理解索引优先队列对于深入理解数据库的本地数据保存非常重要。希望对大家能有所帮助。
相关链接:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号