小橙书阅读指南(二)——选择排序
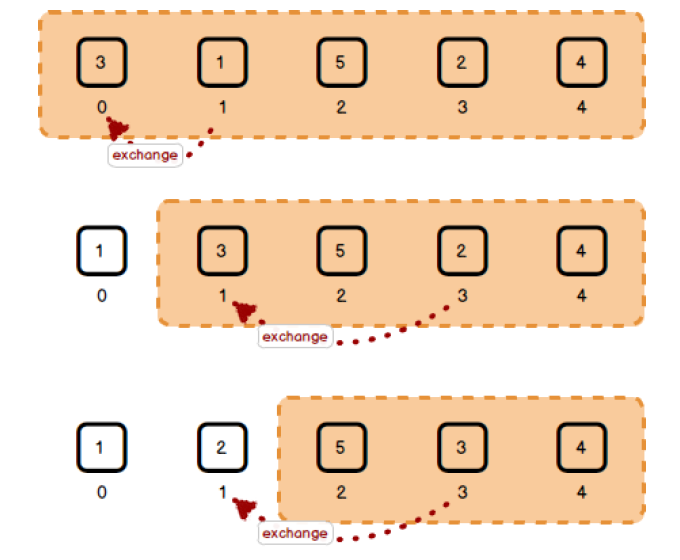
算法描述:一种最简单的排序算法是这样的:首先,找到数组中最小的那个元素,其次,将它和数组的第一个元素交换位置。再次,再剩下的元素中找到最小的元素,将它与数组的第二个元素交换位置。如此往复,知道将整个数组排序。这种方法叫做选择排序,因为它在不断地选择剩余元素之中的最小者。
算法图示:
Java代码示例:
import common.ArraysGenerator; import common.Sortable; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Arrays; public class Selection implements Sortable<Integer> { @Override public void sort(Integer[] array) { for (int i = 0; i < array.length; ++i) { int minIndex = i; for (int j = i + i; j < array.length; ++j) { if (array[j] < array[minIndex]) { minIndex = j; } } int tmp = array[minIndex]; array[minIndex] = array[i]; array[i] = tmp; } } public static void main(String arg[]) throws IOException { Integer[] arr = ArraysGenerator.fromFile("disorder.txt", 1000000); Selection selection = new Selection(); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); selection.sort(arr); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); System.out.println(end - start); } }
Qt/C++代码示例:
void Selection::sort(int * arr, int len) { for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) { int minIndex = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < len; ++j) { if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) { minIndex = j; } } int tmp = arr[minIndex]; arr[minIndex] = arr[i]; arr[i] = tmp; } } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QCoreApplication a(argc, argv); // 从文件中读取数组的方法,指定文件名与数组长度,返回数组指针 int *arr = Arrays::fromFile("disorder.txt", 1000000); Selection selection; QTime rt; rt.start(); selection.sort(arr, 1000000); int el = rt.elapsed(); qDebug() << el; return a.exec(); }
总的来说,选择排序是一种很容易理解和实现的简单排序算法,它有两个很明显的特点——运行时间和输入无关。
相关链接:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号