生产线平衡问题的+Leapms线性规划方法
知识点
第一类生产线平衡问题,第二类生产线平衡问题
整数线性规划模型,+Leapms模型,直接求解,CPLEX求解
装配生产线平衡问题 (The Assembly Line Balancing Problem)
装配生产线又叫做组装生产线, 是把产品的工艺做串行生产安排的流水生产线。一个产品的组装需要不同的工序来完成,且工序之间有先后次序要求。
下表是Jackson, J. R. . (1956)给出一个产品工序的装配次序要求:
| 工序 | 执行时长 | 紧前工序 |
| 1 | 6 | -- |
| 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | 7 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 |
| 6 | 2 | 2 |
| 7 | 3 | 3,4,5 |
| 8 | 6 | 6 |
| 9 | 5 | 7 |
| 10 | 5 | 8 |
| 11 | 4 | 10,9 |
上表也可以用有向图表示:
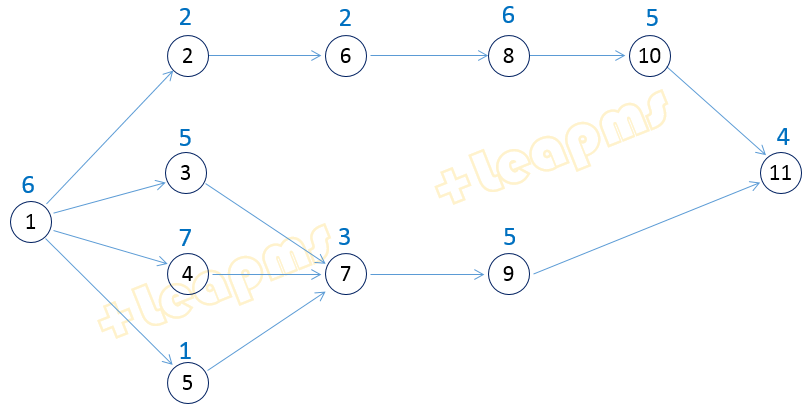
生产线平衡问题的目的是:把工序划分成工作站,且满足工序紧前要求。优化目标有两种:(1)在生产节拍被指定时使得工作站数量最少;或(2)在工作站数量被限定情况下使得生产节拍最小。
前一种目标被称为第一类生产线平衡问题,后一种目标被称为第二类生产线平衡问题。
第二类问题生产线平衡问题的建模
(1)问题
已知工作站共有m=5个,工序共有n=11个,极小化生产节拍。
(2)有向图的表达
有向图可以表达为节点的点对集合,例如 e={ 1 2, 1 3, 1 4,...,10 11}
第k条边的前后两个顶点一般被写成 a[k], 和 b[k]。第k条边被记为 (a[k], b[k])
边的数目 ne 是 e 中元素数除以2,即:ne=_$(e)/2
(3)决策变量
设 x[i][j] 为0-1变量,表示工序j是否被分配给工作站i。其中i=1,...,m; j=1,...,n。
(4)依赖变量
设变量c为生产线的节拍
(5)目标是极小化生产节拍,即:
minimize c
(6)约束1: 每个工序被分配给且仅被分配给一个工作站:
sum{i=1,...,m} x[i][j] =1 | j =1,...,n
(7)约束2:节拍大于等于任何一个工作站的执行时长:
c >= sum{j=1,...,n}x[i][j]t[j] | i=1,...,m
(8)约束3:对任何边k,如果其后节点b[k]被分配到工作站i,则其前节点 a[k] 必须被分配到 j=1,...,i 中的某个节点,即:
x[i][b[k]] <= sum{j=1,...,i}x[j][a[k]] | i=1,...,m;k=1,...,ne
第二类问题生产线平衡问题的+leapms模型
//第二类生产线平衡问题
minimize c
subject to
sum{i=1,...,m} x[i][j] =1 | j =1,...,n
c >= sum{j=1,...,n}x[i][j]t[j] | i=1,...,m
x[i][b[k]]<=sum{j=1,...,i}x[j][a[k]]|i=1,...,m;k=1,...,ne
where
m,n,ne are integers
t[j] is a number | j=1,...,n
e is a set
a[k],b[k] is an integer|k=1,...,ne
c is a variable of number
x[i][j] is a variable of binary|i=1,...,m;j=1,...,n
data
m=5
n=11
t={6 2 5 7 1 2 3 6 5 5 4}
e={
1 2
1 3
1 3
1 5
2 6
3 7
4 7
5 7
6 8
7 9
8 10
9 11
10 11
}
data_relation
ne=_$(e)/2
a[k]=e[2k-1]|k=1,...,ne
b[k]=e[2k]|k=1,...,ne
第二类问题生产线平衡问题的模型求解
Welcome to +Leapms ver 1.1(162260) Teaching Version -- an LP/LMIP modeling and
solving tool.欢迎使用利珀 版本1.1(162260) Teaching Version -- LP/LMIP 建模和求
解工具.
+Leapms>load
Current directory is "ROOT".
.........
p2.leap
.........
please input the filename:p2
================================================================
1: //第二类生产线平衡问题
2: minimize c
3:
4: subject to
5: sum{i=1,...,m} x[i][j] =1 | j =1,...,n
6: c >= sum{j=1,...,n}x[i][j]t[j] | i=1,...,m
7: x[i][b[k]]<=sum{j=1,...,i}x[j][a[k]]|i=1,...,m;k=1,...,ne
8:
9: where
10: m,n,ne are integers
11: t[j] is a number | j=1,...,n
12: e is a set
13: a[k],b[k] is an integer|k=1,...,ne
14: c is a variable of number
15: x[i][j] is a variable of binary|i=1,...,m;j=1,...,n
16:
17: data
18: m=5
19: n=11
20: t={6 2 5 7 1 2 3 6 5 5 4}
21: e={
22: 1 2
23: 1 3
24: 1 3
25: 1 5
26: 2 6
27: 3 7
28: 4 7
29: 5 7
30: 6 8
31: 7 9
32: 8 10
33: 9 11
34: 10 11
35: }
36: data_relation
37: ne=_$(e)/2
38: a[k]=e[2k-1]|k=1,...,ne
39: b[k]=e[2k]|k=1,...,ne
40:
================================================================
>>end of the file.
Parsing model:
1D
2R
3V
4O
5C
6S
7End.
..................................
number of variables=56
number of constraints=81
..................................
+Leapms>mip
relexed_solution=9.2; number_of_nodes_branched=0; memindex=(2,2)
nbnode=230; memindex=(24,24) zstar=13; GB->zi=10
The Problem is solved to optimal as an MIP.
找到整数规划的最优解.非零变量值和最优目标值如下:
.........
c* =10
x1_1* =1
x1_5* =1
x2_2* =1
x2_6* =1
x2_8* =1
x3_3* =1
x3_10* =1
x4_4* =1
x4_7* =1
x5_9* =1
x5_11* =1
.........
Objective*=10
.........
+Leapms>
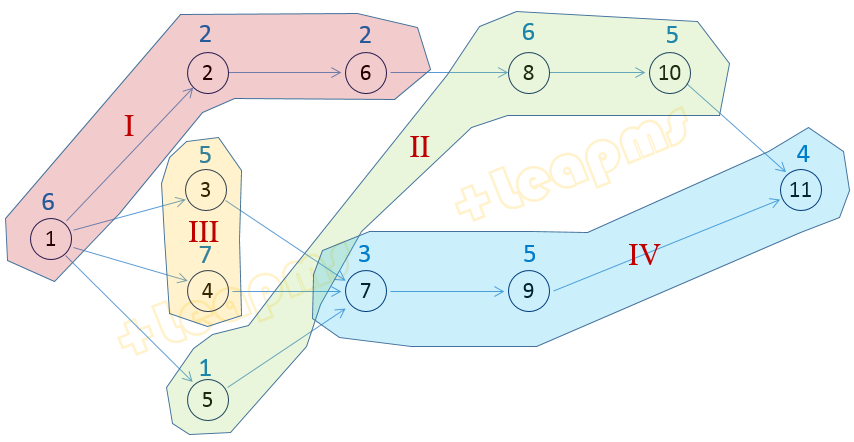
上面的结果显示, 目标值即最小节拍为10, 分配方案是: 工序1,5分配在工作站1, 工序2,6,8 分配在工作站2, 工序3,10 分配在工作站3, 工序4,7分配在工作站4, 工序9,11分配在工作站5。
第二类生产线平衡问题求解结果图示
第二类生产线平衡问题的+Leapms-Latex数学概念模型
在+Leapms环境下,使用 “latex"命令可以把上面的+Leapms模型直接转换为如下Latex格式的数学概念模型。

第一类生产线平衡问题
由求解第2类生产线平衡问题知道,工作站数是5时,最小节拍是10。假设如果将节拍上限增加到10,问是否能够减小工作站数目。
第一类生产线平衡问题的建模
第一类生产线平衡问题的数学模型见Ritt, M. , & Costa, A. M. . (2015)。
第一类生产线平衡问题的+Leapms模型
//第一类生产线平衡问题
minimize sum{i=1,...,m}y[i]
subject to
sum{i=1,...,m} x[i][j] =1 | j =1,...,n
y[i]c >= sum{j=1,...,n}x[i][j]t[j] | i=1,...,m
x[i][b[k]]<=sum{j=1,...,i}x[j][a[k]]|i=1,...,m;k=1,...,ne
y[i]<=y[i-1]|i=2,...,m
where
m,n,ne are integers
t[j] is a number | j=1,...,n
e is a set
a[k],b[k] is an integer|k=1,...,ne
c is a number
x[i][j] is a variable of binary|i=1,...,m;j=1,...,n
y[i] is a variable of binary|i=1,...,m
data
m=6
n=11
c=12
t={6 2 5 7 1 2 3 6 5 5 4}
e={
1 2
1 3
1 3
1 5
2 6
3 7
4 7
5 7
6 8
7 9
8 10
9 11
10 11
}
data_relation
ne=_$(e)/2
a[k]=e[2k-1]|k=1,...,ne
b[k]=e[2k]|k=1,...,ne
第一类生产线平衡问题的模型求解
Welcome to +Leapms ver 1.1(162260) Teaching Version -- an LP/LMIP modeling and
solving tool.欢迎使用利珀 版本1.1(162260) Teaching Version -- LP/LMIP 建模和求
解工具.
+Leapms>load
Current directory is "ROOT".
.........
p1.leap
p2.leap
.........
please input the filename:p1
1: //第一类生产线平衡问题
2: minimize sum{i=1,...,m}y[i]
3:
4: subject to
5: sum{i=1,...,m} x[i][j] =1 | j =1,...,n
6: y[i]c >= sum{j=1,...,n}x[i][j]t[j] | i=1,...,m
7: x[i][b[k]]<=sum{j=1,...,i}x[j][a[k]]|i=1,...,m;k=1,...,ne
8: y[i]<=y[i-1]|i=2,...,m
9:
10: where
11: m,n,ne are integers
12: t[j] is a number | j=1,...,n
13: e is a set
14: a[k],b[k] is an integer|k=1,...,ne
15: c is a number
16: x[i][j] is a variable of binary|i=1,...,m;j=1,...,n
17: y[i] is a variable of binary|i=1,...,m
18:
19: data
20: m=6
21: n=11
22: c=12
23: t={6 2 5 7 1 2 3 6 5 5 4}
24: e={
25: 1 2
26: 1 3
27: 1 3
28: 1 5
29: 2 6
30: 3 7
31: 4 7
32: 5 7
33: 6 8
34: 7 9
35: 8 10
36: 9 11
37: 10 11
38: }
39: data_relation
40: ne=_$(e)/2
41: a[k]=e[2k-1]|k=1,...,ne
42: b[k]=e[2k]|k=1,...,ne
43:
>>end of the file.
Parsing model:
1D
2R
3V
4O
5C
6S
7End.
===========================================
number of variables=72
number of constraints=100
int_obj=0
===========================================
+Leapms>mip
relexed_solution=3.83333; number_of_nodes_branched=0; memindex=(2,2)
nbnode=117; memindex=(12,12) zstar=5.22619; GB->zi=6
nbnode=314; memindex=(38,38) zstar=5.625; GB->zi=6
nbnode=587; memindex=(24,24) zstar=5.01852; GB->zi=5
nbnode=861; memindex=(26,26) zstar=4.25; GB->zi=5
nbnode=1128; memindex=(22,22) zstar=3.83333; GB->zi=5
nbnode=1395; memindex=(38,38) zstar=3.83333; GB->zi=5
nbnode=1680; memindex=(40,40) zstar=6; GB->zi=5
nbnode=1959; memindex=(46,46) zstar=6; GB->zi=5
nbnode=2230; memindex=(30,30) zstar=3.9246; GB->zi=5
nbnode=2487; memindex=(26,26) zstar=4.44444; GB->zi=5
nbnode=2774; memindex=(36,36) zstar=4.16667; GB->zi=4
nbnode=2971; memindex=(20,20) zstar=3.83333; GB->zi=4
nbnode=3149; memindex=(26,26) zstar=4.16667; GB->zi=4
nbnode=3343; memindex=(36,36) zstar=3.91667; GB->zi=4
nbnode=3546; memindex=(20,20) zstar=4.04167; GB->zi=4
The Problem is solved to optimal as an MIP.
找到整数规划的最优解.非零变量值和最优目标值如下:
.........
x1_1* =1
x1_2* =1
x1_6* =1
x2_5* =1
x2_8* =1
x2_10* =1
x3_3* =1
x3_4* =1
x4_7* =1
x4_9* =1
x4_11* =1
y1* =1
y2* =1
y3* =1
y4* =1
.........
Objective*=4
.........
+Leapms>
结果显示工作站数可减少到4。分配方式如下面的图示。
第一类生产线平衡问题求解结果图示
第一类生产线平衡问题的CPLEX求解
在+Leapms环境中输入cplex命令即可触发在另外窗口内启动CPLEX求解器对模型进行求解:
+Leapms>cplex You must have licience for Ilo Cplex, otherwise you will violate corresponding copyrights, continue(Y/N)? 你必须有Ilo Cplex软件的授权才能使用此功能,否则会侵犯相应版权, 是否继续(Y/N)?y +Leapms>
Tried aggregator 1 time.
MIP Presolve eliminated 24 rows and 3 columns.
MIP Presolve modified 71 coefficients.
Reduced MIP has 76 rows, 69 columns, and 362 nonzeros.
Reduced MIP has 69 binaries, 0 generals, 0 SOSs, and 0 indicators.
Presolve time = 0.11 sec. (0.33 ticks)
Found incumbent of value 6.000000 after 0.20 sec. (0.40 ticks)
Probing fixed 15 vars, tightened 0 bounds.
Probing changed sense of 1 constraints.
Probing time = 0.00 sec. (0.18 ticks)
Cover probing fixed 1 vars, tightened 0 bounds.
Tried aggregator 1 time.
MIP Presolve eliminated 20 rows and 16 columns.
MIP Presolve modified 45 coefficients.
Reduced MIP has 56 rows, 53 columns, and 247 nonzeros.
Reduced MIP has 53 binaries, 0 generals, 0 SOSs, and 0 indicators.
Presolve time = 0.01 sec. (0.21 ticks)
Probing fixed 1 vars, tightened 0 bounds.
Probing time = 0.02 sec. (0.11 ticks)
Tried aggregator 1 time.
MIP Presolve eliminated 3 rows and 1 columns.
MIP Presolve modified 12 coefficients.
Reduced MIP has 53 rows, 52 columns, and 230 nonzeros.
Reduced MIP has 52 binaries, 0 generals, 0 SOSs, and 0 indicators.
Presolve time = 0.02 sec. (0.15 ticks)
Probing time = 0.00 sec. (0.10 ticks)
Clique table members: 207.
MIP emphasis: balance optimality and feasibility.
MIP search method: dynamic search.
Parallel mode: deterministic, using up to 4 threads.
Root relaxation solution time = 0.05 sec. (0.33 ticks)
Nodes Cuts/
Node Left Objective IInf Best Integer Best Bound ItCnt Gap
* 0+ 0 6.0000 4.0000 33.33%
* 0+ 0 5.0000 4.0000 20.00%
0 0 4.0000 21 5.0000 4.0000 54 20.00%
* 0+ 0 4.0000 4.0000 0.00%
0 0 cutoff 4.0000 4.0000 54 0.00%
Elapsed time = 0.45 sec. (1.85 ticks, tree = 0.00 MB, solutions = 3)
Root node processing (before b&c):
Real time = 0.45 sec. (1.85 ticks)
Parallel b&c, 4 threads:
Real time = 0.00 sec. (0.00 ticks)
Sync time (average) = 0.00 sec.
Wait time (average) = 0.00 sec.
------------
Total (root+branch&cut) = 0.45 sec. (1.85 ticks)
Solution status = Optimal
Solution value = 4
x1_1=1
x1_2=1
x1_5=1
x1_6=1
x2_8=1
x2_10=1
x3_3=1
x3_4=1
x4_7=1
x4_9=1
x4_11=1
y1=1
y2=1
y3=1
y4=1
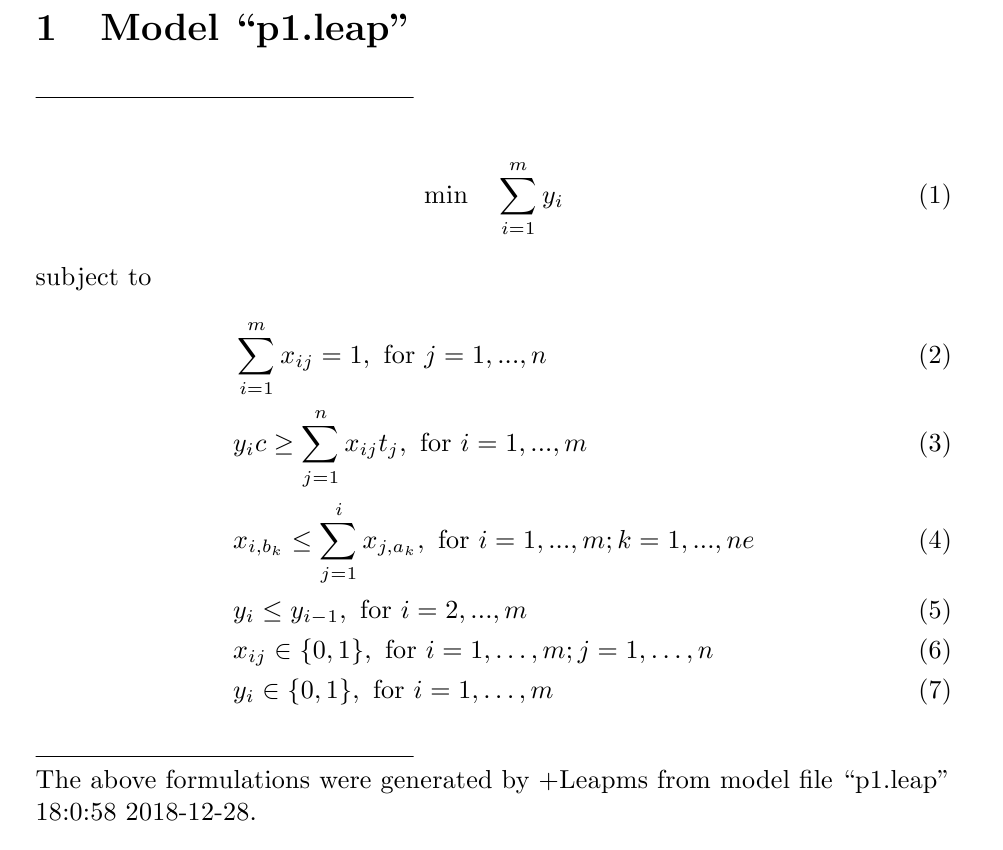
第一类生产线平衡问题的+Leapms-Latex数学概念模型
在+Leapms环境下,使用 “latex"命令可以把上面的+Leapms模型直接转换为如下Latex格式的数学概念模型
参考文献
[1] Jackson, J. R. . (1956). A computing procedure for a line balancing problem. Management Science, 2(3), 261-271.
[2] Ritt, M. , & Costa, A. M. . (2015). Improved integer programming models for simple assembly line balancing, and related problems. International Transactions in Operational Research, 19(8), 455-455.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号