今天我们来攻克第二项——可交互式中国地图。
一开始我想用webview配合Echart来实现相应的效果,但奈何我json和html传值那一部分根本就没学,所以即使实现了效果也无法向其中传值……
所幸后来我又找到了一种新方法——SVG转XML绘图法
首先我们需要一个SVG文件,这里有个地图SVG的整合包,找到China就可以了
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Z1E_hwG73IM39idcWoJx2w 提取码:e6br
因为这个SVG是转成xml格式,不需要额外导入包,所以这样咱们就算准备完全了
我们先找到chinaHigh.svg(low也行,但high分辨率高更细节)
然后访问这个网址:http://inloop.github.io/svg2android/,这是一个把SVG改组成xml的工具,只要把它拖进去就OK,非常便利
点击下载之后,把它放到咱们Android工程的app\src\main\res\raw下
之后先包装工具类:Chinaitem
public class chinaitem {
private Path path;
private int drawColor;
String name;
public chinaitem(Path path) {
this.path = path;
}
/**
* 绘制地图path
* @param canvas
* @param paint
* @param isSelect
*/
public void draw(Canvas canvas, Paint paint, boolean isSelect){
if(isSelect){
//画阴影图层
paint.setStrokeWidth(2);
paint.setShadowLayer(8,0,0,0xffffff);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
canvas.drawPath(path,paint);
//画区域path
paint.clearShadowLayer();
paint.setStrokeWidth(2);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#FBED6C"));
canvas.drawPath(path,paint);
}else{
//画线条
paint.clearShadowLayer();
paint.setStrokeWidth(1);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setColor(0xFFD0E8F4);
canvas.drawPath(path,paint);
//画区域
paint.setStrokeWidth(2);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setColor(drawColor);
canvas.drawPath(path,paint);
}
}
/**
* 判断当前点击坐标是否在path范围内
* @param x
* @param y
* @return
*/
public boolean isTouch(int x,int y){
RectF rectF = new RectF();
path.computeBounds(rectF,true);
Region region = new Region();
region.setPath(path,new Region((int)rectF.left,(int)rectF.top,(int)rectF.right,(int)rectF.bottom));//判断X,Y是否在region区域范围内
if(region.contains(x,y)) return true;
return false;
}
public void setDrawColor(int drawColor) {
this.drawColor = drawColor;
}
}
编写新的view控件
public class ChinaMapView extends View {
private static final String TAG = ChinaMapView.class.getName();
public List<chinaitem> chinaitems = new ArrayList<chinaitem>();
//被点击的区域
private chinaitem selectItem;
//缩放1.3倍
public float scale = 1.3f;
private Context mContext;
private Paint mPaint;
private int[] colors = new int[]{0xFF239BD7,0xFF30A9E5,0xFF80CBF1,0xFFF0E68C};
GestureDetectorCompat gestureDetectorCompat;
public ChinaMapView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public ChinaMapView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(context);
}
private void init(Context context) {
mContext = context;
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
gestureDetectorCompat = new GestureDetectorCompat(context,new GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener(){
@Override
public boolean onDown(MotionEvent e) {
Log.d(TAG,"onDown x:"+e.getX()+";y:"+e.getY());
handleTouch(e.getX(),e.getY());
return true;
}
});
thread.start();
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.save();
canvas.scale(scale,scale);
if(taiwanItems != null){
for(chinaitem:taiwanItems){
if(item != selectItem){
item.draw(canvas,mPaint,false);
}
}
if(selectItem != null){
selectItem.draw(canvas,mPaint,true);
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return gestureDetectorCompat.onTouchEvent(event);
}
public void handleTouch(float x,float y){
chinaitem chinaitem = null;
if(chinaitems != null){
for(chinaitem item :chinaitems){
if(item.isTouch((int)(x/scale),(int)(y/scale))){
chinaitem = item;
break;
}
}
if(chinaitem!= null) {
selectItem = chinaitem;
postInvalidate();
}
}
}
Thread thread = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
InputStream inputStream = mContext.getResources().openRawResource(R.raw.chinahigh);
//采用Dom解析器解析xml
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = null;
try {
builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = builder.parse(inputStream);
Element rootelement = doc.getDocumentElement();
NodeList items = rootelement.getElementsByTagName("path");
for(int i=0;i<items.getLength();i++){
Element element = (Element) items.item(i);
String pathData = element.getAttribute("android:pathData");
Path path = PathParser.createPathFromPathData(pathData);
TaiWanItem item = new TaiWanItem(path);
taiwanItems.add(item);
}
handler.sendEmptyMessage(1);
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
Handler handler = new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if(taiwanItems == null || taiwanItems.size()==0)
return;
int colorNum = taiwanItems.size();
int color = Color.WHITE;
//赋予颜色
for(int i=0;i<colorNum;i++){
int flag = i % 4;
switch(flag){
case 1:
color = colors[0];
break;
case 2:
color = colors[1];
break;
case 3:
color = colors[1];
break;
default:
color = colors[2];
}
chinaitem.get(i).setDrawColor(color);
}
postInvalidate();
}
};
}
这样我们就实现了地图显示,之后我们要在Activity里使用它,并且在后台Java代码里
再次重载onTouch函数来完成变色和取值。在那之前,我们先定义这样一个字符串
String[] pos=new String[]{"安徽","北京","重庆","福建","广东","甘肃","广西"
,"贵州","海南","河北","河南","香港","黑龙江","湖南","湖北","吉林"
,"江苏","江西","辽宁","澳门","内蒙古","宁夏","青海","陕西","四川","山东","上海","山西","天津","台湾","新疆","西藏","云南","浙江"};
由于地图的构筑是靠一个Arraylist数组逐个完成的,所以可以用这个字符串按照构造时的直接得到点击时的地理位置(我就没呢么好运啦,是照着返回结果和地图一个个对过来的。)
之后重写控件的onTouch函数:
tp.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
for(int i=0;i<tp.chinaitem.size();i++) {
if(tp.chinaitem.get(i).isTouch((int)(event.getX()/tp.scale),(int)(event.getY()/tp.scale))){
op.setText(pos[i]);
tp.handleTouch(event.getX(),event.getY());
po.setText("该省/直辖市/特别行政区有"+dao.sere(pos[i]).size()+"条记录,其中异常记录"+dao.sered(pos[i]).size()+"条");
os.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
break;
}else {
os.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
}
}
return true;
}
});
其中先调用了isTouch函数判断触点是否在合法区域,之后再调用handleTouch函数改变颜色。
最后的效果就像这样:
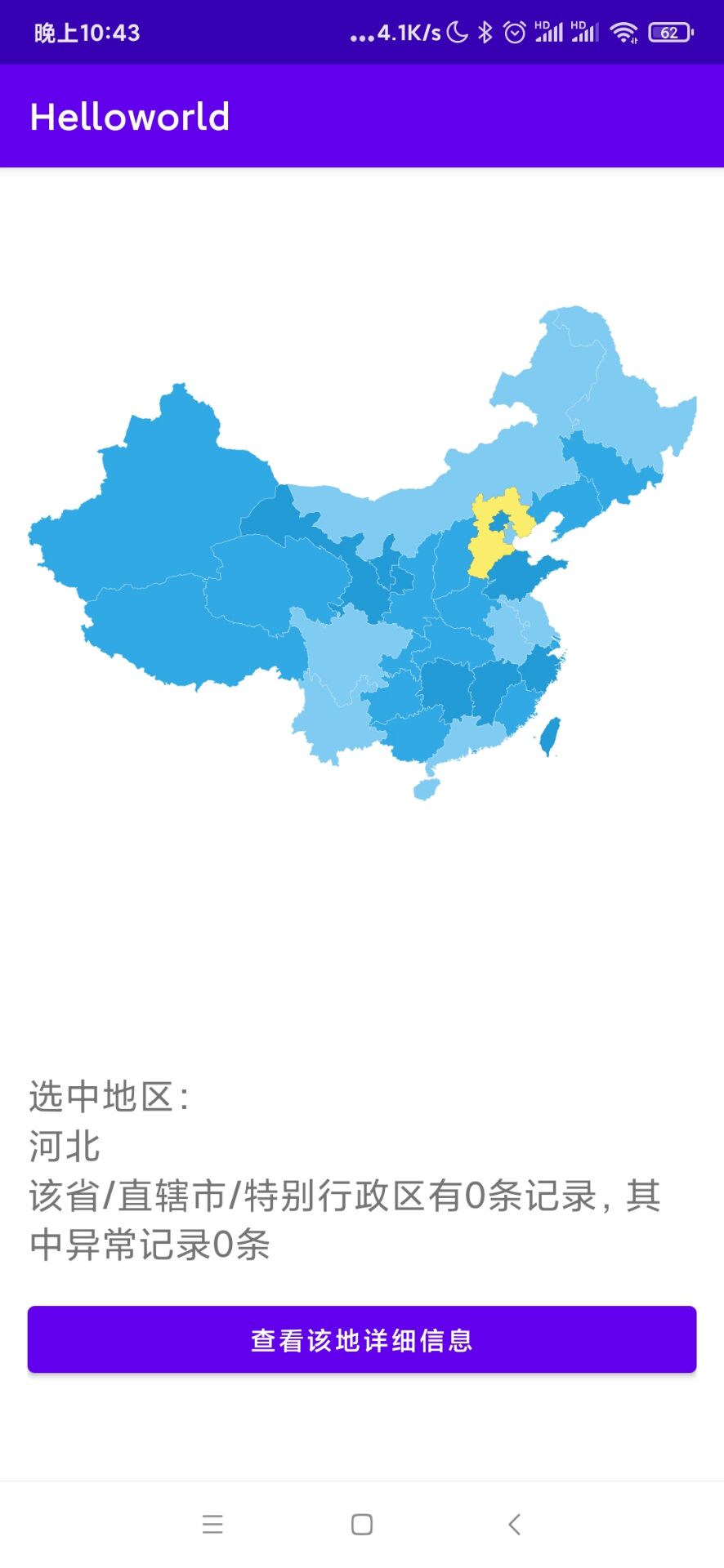
好,这就算成功了!那么今天就到这里,我们明天见咯!





