flex 和 bison 概述
overview of flex & bison
BNF language
expression : expression '+' expression
| expression '-' expression
| NUMBER
;
After writting the text above, we can say that we have defined a expression rule. This rule has three productions, each production has a LHS and a RHS.
- production 1:
expression : expression '+' expression - production 2:
expression : expression '-' expression - production 3:
expression: NUMBER
The NUMBER is a terminal symbol, and the expression is a nonterminal symbol.
work flow
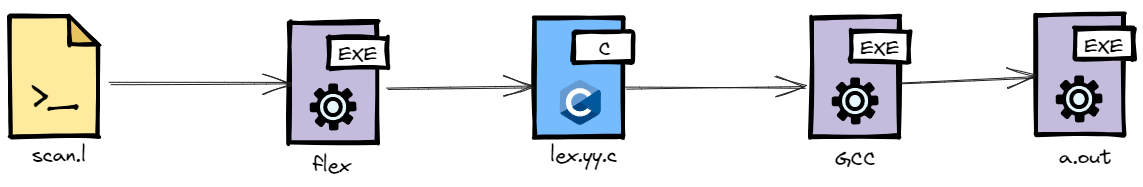
flex-only
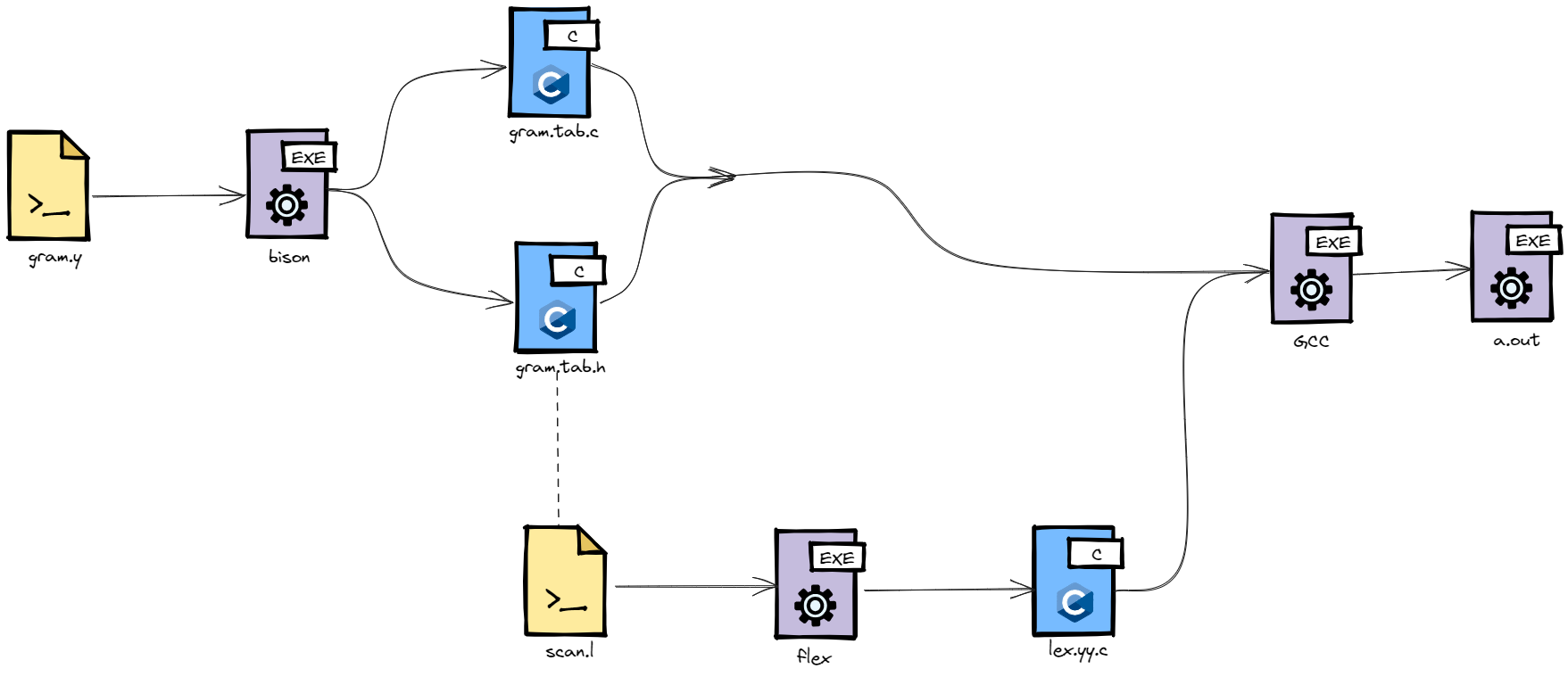
flex with bison
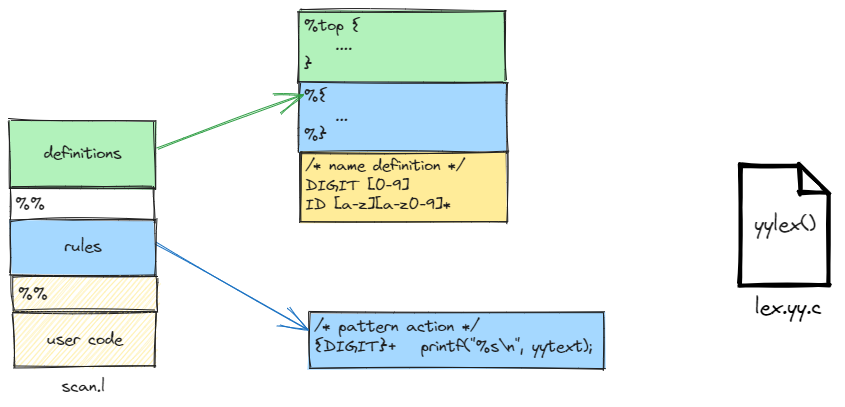
flex file structure
flex
How the input is matched
When the generated scanner runs, it scans input text to try to find
characters which match predefined patterns. If it finds more than one
match, it takes the one matching the most text. If it finds two or more matches of
the same length, the rule listed first in the 'flex' input file is
chosen.
yytext: matched token
yyleng: the length of yytext
working with bison

gram.tab.h contains definitions of all the %tokens appearing in the gram.y file.
scan.l file then includes the gram.tab.h file.
flex uses yyflex() function to match user input string with each pattern and returns the type of the token in action as well as putting any associated value in the global yylval.
%{
#include "y.tab.h"
%}
%%
[0-9]+ yylval = atoi( yytext ); return TOK_NUMBER;
passing
-doption tobisoncommand to instruct it to generate the filegram.tab.h
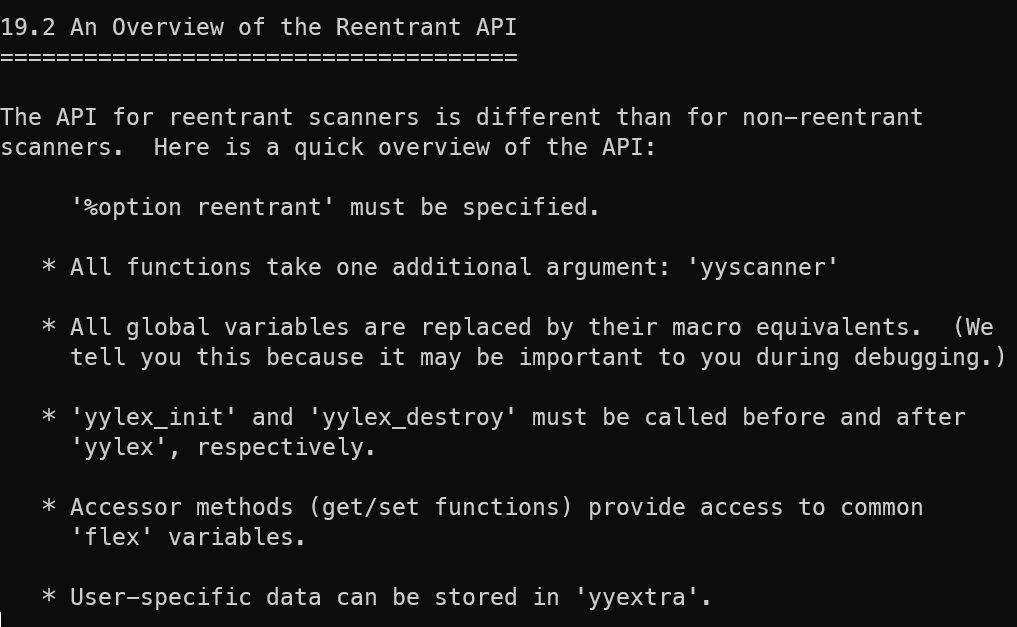
reentrant scanner
workflow
![[Pasted image 20230702183937.png]]
demo
%{
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
%}
%option reentrant
%option extra-type="struct stat *"
%%
__filesize__ printf( "%ld", yyextra->st_size );
__lastmod__ printf( "%ld", yyextra->st_mtime );
%%
void scan_file( char* filename )
{
yyscan_t scanner;
struct stat buf;
FILE *in;
in = fopen( filename, "r" );
stat( filename, &buf );
yylex_init_extra( buf, &scanner );
yyset_in( in, scanner );
yylex( scanner );
yylex_destroy( scanner );
fclose( in );
}
redefine YY_EXTRA_TYPE
![[Pasted image 20230702190414.png]]

%option extra-type="struct stat *"
Or,
#define YY_EXTRA_TYPE struct stat *
You use yyget_extra and yyset_extra to access the extra data.
YY_EXTRA_TYPE yyget_extra ( yyscan_t scanner );
void yyset_extra ( YY_EXTRA_TYPE arbitrary_data , yyscan_t scanner);
options
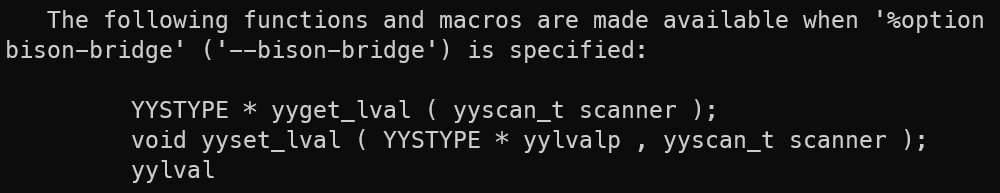
%option bison-bridge
![[Pasted image 20230702193425.png]]
%option bison-locations
![[Pasted image 20230702193459.png]]
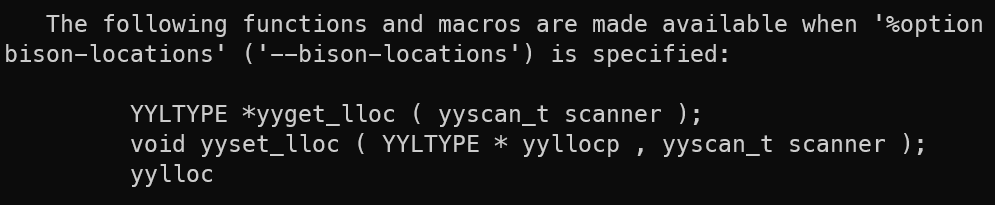
With defining the two options above, yylex declaration becomes:
int yylex(YYSTYPE * lvalp, YYLTYPE * llocp, yyscan_t scanner);
YYSTYPE is the data type of yylval;
start condition
https://github.com/winter-loo/snippets-flexbison/blob/main/04_fstring.l
scan in-memory strings instead of files
use yy_scan_buffer.
overriding the default memory management
- disable the default implementations
%option noyyalloc %option noyyrealloc %option noyyfree - override the memory management API
void * yyalloc(yy_size_t bytes, core_yyscan_t yyscanner) { return palloc(bytes); } void * yyrealloc(void *ptr, yy_size_t bytes, core_yyscan_t yyscanner) { if (ptr) return repalloc(ptr, bytes); else return palloc(bytes); } void yyfree(void *ptr, core_yyscan_t yyscanner) { if (ptr) pfree(ptr); }
bison
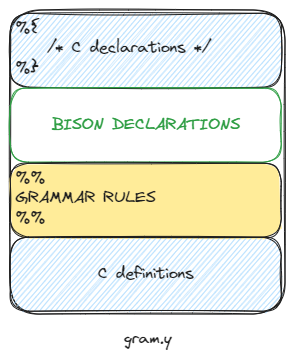
grammar file structure
![[bison_grammar_file_structure.excalidraw]]
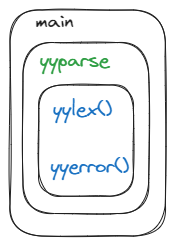
parser executable components
![[Pasted image 20230703110555.png]]

![[bison_parser_executable_components.excalidraw]]
lookahead token
when a reduction is possible, the parser sometimes “looks ahead” at the next token in order to decide what to do. When a token is read, it is not immediately shifted; first it becomes the “lookahead token”, which is not on the stack. Now the parser can perform one or more reductions of tokens and groupings on the stack, while the lookahead token remains off to the side. When no more reductions should take place, the lookahead token is shifted onto the stack. This does not mean that all possible reductions have been done; depending on the token kind of the lookahead token, some rules may choose to delay their application.
The lookahead token is stored in the variable ‘yychar’. Its semantic value and location, if any, are stored in the variables ‘yylval’ and 'yylloc’.
override memory management API
#define YYMALLOC palloc
#define YYFREE pfree
bison declarations
You must declare names for terminal symbols and nonterminal symbols if you use that name in grammar rules. If you use semantic value of the symbol in semantic action, you need also to annotate type of the symbol.
Use %token for terminal symbol and %type for nonterminal symbol.
%token CREATE TABLE
%token <ival> NUMBER
%type <node> create_table_stmt insert_stmt
The ival and node are defined in %union.
%union {
int ival;
Node* node;
}
The %union declaration specifies the entire collection of possible data types for semantic values. This declaration generates a union YYSTYPE in parser implementation file.
Other bison options listed below:
/* request a reentrant parser */
/* new syntax is: %define api.pure full */
%pure-parser
/* do not allow any shift/reduce conflicts */
%expect 0
/* change the first parameter of yyerror() to be `YYLTYPE* locp` */
%locations
/* add additional paramter `core_yyscan_t yyscanner` to yyparse() */
%parse-param {core_yyscan_t yyscanner}
/* tells bison that yylex() has additional parameter `core_yyscan_t yyscanner` */
%lex-param {core_yyscan_t yyscanner}
/* if yylex() and yyparse() have common parameters, use following declaration */
%param {core_yyscan_t yyscanner}
posted on 2023-07-03 21:17 winter-loo 阅读(294) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号