JavaIO流之字节缓冲流
字节流缓冲流
字节缓冲流介绍
BufferOutputStream:该类实现缓冲输出流.通过设置这样的输出流,应用程序可以向底层输出流写入字节,而不必为写入的每个字节导致底层系统的调用
BufferedInputStream:创建BufferedInputStream将创建一个内部缓冲区数组.当从流中读取或跳过字节时,内部缓冲区将根据需要从所包含的输入流中重新填充,一次很多字节
构造方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) | 创建字节缓冲输出流对象 |
| BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) | 创建字节缓冲输入流对象 |
 为什么构造方法需要的是字节流,而不是具体的路径?
为什么构造方法需要的是字节流,而不是具体的路径?
这是因为,字节缓冲流仅仅提供缓冲区,而真正的读写数据还要依靠基本的字节流对象进行操作。
Coding
public class OutputDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("b.txt"));
int b;
while((b = bis.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(b);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}
源码解析
BufferedInputStream
private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192;public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {
this(in, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
} public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {
super(in);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}其中这个参数DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE默认为8192,也就是只默认创建了一个长度为8192的buf字节数组
BufferedOutputStream
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) {
this(out, 8192);
}public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) {
super(out);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}同上面类似,都是创建了一个长度为8192的字节数组。
close方法
public void close() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer;
while ( (buffer = buf) != null) {
if (bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, null)) {
InputStream input = in;
in = null;
if (input != null)
input.close();
return;
}
// Else retry in case a new buf was CASed in fill()
}
}其中input就表示传递进来的字节流,即如果传递进来的字节流不为空,就将其close。
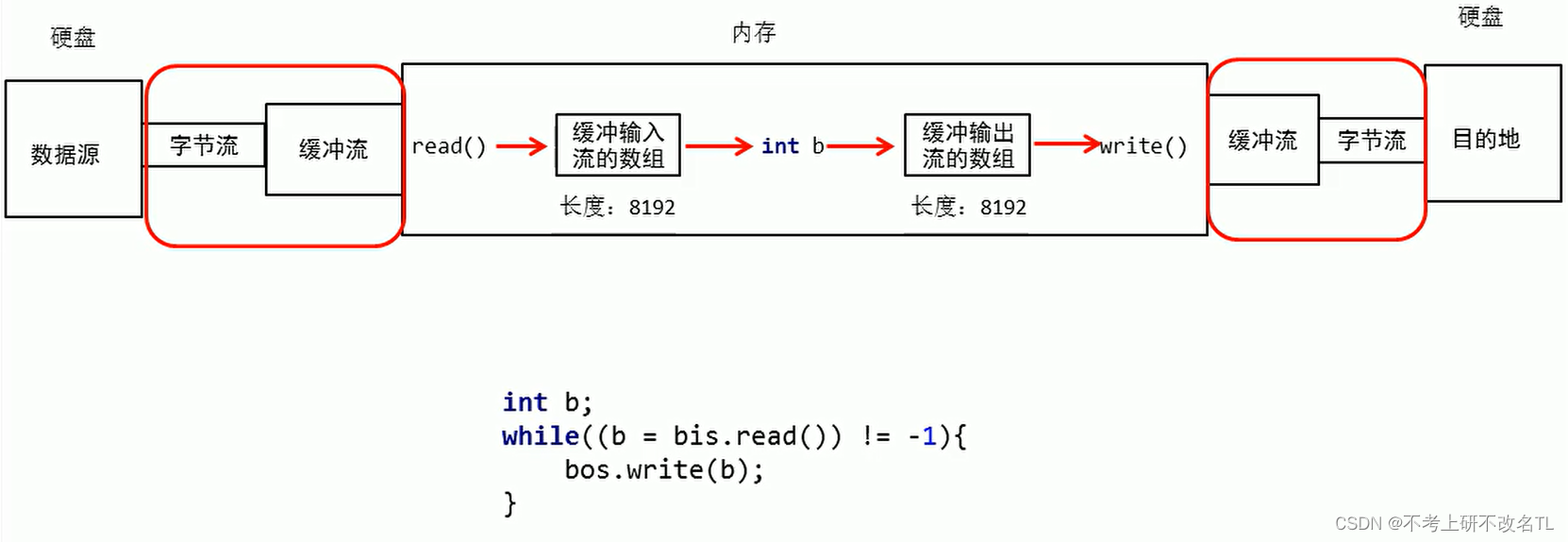
为什么可以快?
相当于Java底层为我们提供了一个长度为8192的数组,使用缓冲流可以减少IO的次数,从而达到提高效率。
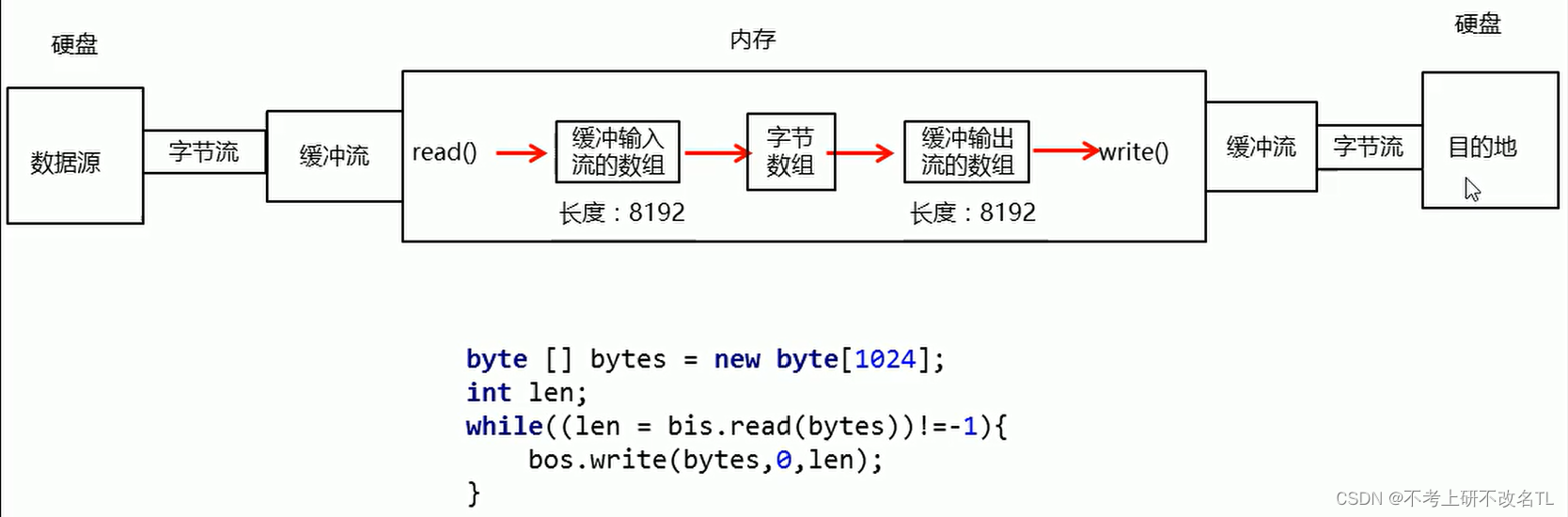
案例:一次读写一个字节数组
public class OutputDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("copy.txt"));
byte [] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}
与之前的区别就在于内存中前者是一次read一个字节,后者是一次read一个数组




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)