Mybatis-注解开发(单表)
Mybatis注解开发
什么是Mybatis注解开发?
这几年来注解开发越来越流行,Mybatis也可以使用注解开发方式,这样我们就可以减少编写Mapper映射文件了。
所以使不使用Mybatis注解,都可以实现我们想要实现的功能!Mybatis注解开发最大的优势就是简化映射配置文件!减少代码量。
MyBatis的常用注解
(1)@Insert("新增的SQL语句"):实现新增
(2)@Update("更新的SQL语句"):实现更新
(3)@Delete("删除的SQL语句"):实现删除
(4)@Select("查询的SQL语句"):实现查询
详细案例
项目骨架
由于过于简单就不使用MVC设计模式了!
数据准备
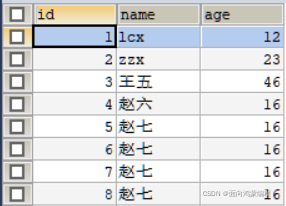
我们使用的是db1数据库下的student表,表的结构如下所示,具体的SQL语句这里就不再提供了,在本人的Mybatis的专栏的其他文章中有。
bean包下存放的就是实体类对象Student
package com.itheima.bean;
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(Integer id,String name,Integer age){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
mapper包下的StudentMapper接口
public interface StudentMapper {
// 查询全部
@Select("SELECT * FROM student")
public abstract List<Student> selectAll();
// 新增操作
@Insert("INSERT INTO student VALUES (#{id},#{name},#{age})")
public abstract Integer insert(Student stu);
// 修改操作
@Update("UPDATE student SET name=#{name},age=#{age} WHERE id=#{id}")
public abstract Integer update(Student stu);
// 删除操作
@Delete("DELETE FROM student WHERE id=#{id}")
public abstract Integer delete(Integer id);
}由于使用了注解,就不用去编写关于映射的xml文件了,大大提高了开发的速度,简化了代码
核心配置文件还是要的MyBatisConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--configuration 核心根标签-->
<configuration>
<!-- 引入数据库连接的配置文件 -->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 配置log4j -->
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="log4j"/>
</settings>
<!-- 使用通用的配置方式起别名 ,别名默认是类名 -->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.itheima.bean"/>
</typeAliases>
<!--environments配置数据库环境,环境可以有多个。default属性指定使用的是哪个-->
<environments default="mysql">
<!--environment配置数据库环境 id属性唯一标识-->
<environment id="mysql">
<!-- transactionManager事务管理。 type属性,采用JDBC默认的事务-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!-- dataSource数据源信息 type属性 连接池-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- property获取数据库连接的配置信息 -->
<property name="driver" value="${driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${url}" />
<property name="username" value="${username}" />
<property name="password" value="${password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- mappers引入映射配置文件 -->
<mappers>
<!-- mapper 引入指定的映射配置文件 resource属性指定映射配置文件的名称 -->
<!-- package 的name属性用来指定包的路径-->
<package name="com.itheima.mapper"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
注意:
在<mappers>标签中的子标签<package>,通过name属性指定StudentMapper接口所在的包名 ,此时对应的映射文件必须与接口位于同一路径下,并且名称相同。即:这里我们是只有一个StudentMapper接口,之后如果有更多的接口需要编写,我们只要将接口放置于mapper包下就行了。
测试类Test01
public class Test01 {
@Test
public void selectAll() throws IOException {
// 1.加载核心配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
// 2.获取SqlSession工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
// 3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
// 4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象
// 通过StudentMapper的字节对象 来得到实现类对象
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
// 5.调用实现类对象中的方法
List<Student> list = mapper.selectAll();
// 6.处理结果
for (Student student : list) {
System.out.println(student);
}
// 7.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
is.close();
}
@Test
public void insert() throws IOException {
// 1.加载核心配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
// 2.获取SqlSession工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
// 3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
// 4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象
// 通过StudentMapper的字节对象 来得到实现类对象
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
// 5.调用实现类对象中的方法
Student stu = new Student(9,"张九",90);
Integer result = mapper.insert(stu);
// 6.处理结果
System.out.println(result);
// 7.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
is.close();
}
@Test
public void update() throws IOException {
// 1.加载核心配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
// 2.获取SqlSession工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
// 3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
// 4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象
// 通过StudentMapper的字节对象 来得到实现类对象
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
// 5.调用实现类对象中的方法
Student stu = new Student(9,"张九",1000);
Integer result = mapper.update(stu);
// 6.处理结果
System.out.println(result);
// 7.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
is.close();
}
@Test
public void delete() throws IOException {
// 1.加载核心配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
// 2.获取SqlSession工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
// 3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
// 4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象
// 通过StudentMapper的字节对象 来得到实现类对象
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
// 5.调用实现类对象中的方法
Integer result = mapper.delete(9);
// 6.处理结果
System.out.println(result);
// 7.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
is.close();
}
}
运行结果
就不一一演示了。只展示一个查询的就好了
※代码分析※
我们以select查询为例,在Test中的第四步,获取到了mapper接口的实现类对象,该对象调用selectAll()方法,在selectAll()方法上我们通过注解的方式指定了一条关于查询的SQL语句,底层就会为我们去解析这个注解,来拿到我们写的SQL语句,并执行它,再将结果返回。
比之前使用映射配置文件的方式简单多了!




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)