Redis的分布式锁问题(十)最强分布式锁工具Redisson及源码分析
Redis的分布式锁问题(十)最强分布式锁工具Redisson及源码分析
为什么使用redissonClient.getMultiLock(...)就行?
Redis的分布式锁问题(十)最强分布式锁工具Redisson及源码分析
Redisson的引入
我们先来看看之前的基于setnx实现的分布式锁存在的问题:

我们之前实现的分布式锁是基于redis的setnx命令的特性的!
但是,这样子实现起来会有很多弊端!
不可重入
简单的来说就是一旦setnx [key] [value]后,就不能再对这个key做任何操作了(除了删除)
假设我们在开发中有A和B两个业务,在业务A中,执行了setnx操作,然后在业务A中调用业务B。
然后在业务B中也有setnx的操作(同一个KEY)
此时,业务B就会阻塞在这里,等待业务A释放锁
但是,业务A肯定不会释放锁,因为业务A还没有执行完(调B)。故就会发生死锁。
不可重试
在我们之前业务逻辑中,尝试获取锁,如果获取不到就直接return了,没有“重来”的机会!也无法提供重试的机制!
超时释放
我们之前,分析过分布式锁被误删的问题。这个问题是已经解决了。
但是,仍然会存在隐患!我们这里是用TTL来控制它。业务执行,时间多少,这是一个未知数,TTL要怎么设置?如何处理业务阻塞?
主从一致性
在主节点上获取到了锁,但是主节点突然宕机了,就会从从结点中选出一个节点,作为主节点。
但由于,因为之前的那个主节点宕机了。在新选举出来的这个主节点中是无法获取到之前的锁。
所以之前的那个锁相当于失效了!
Redisson
要解决上述问题并不是那么容易的,如果我们自己实现很有可能会出一些问题!所以最好的办法就是使用市面上的一些框架来解决!
什么是Redisson?
Redisson是一个在Redis的基础上实现的Java驻内存数据网格(In-Memory Data Grid)。它不仅提供了一系列的分布式的Java常用对象,还提供了许多分布式服务,其中就包含了各种分布式锁的实现。
Redisson使用手册
0. 项目介绍 - 《Redisson 使用手册》 - 书栈网 · BookStack![]() https://www.bookstack.cn/read/redisson-wiki-zh/Redisson%E9%A1%B9%E7%9B%AE%E4%BB%8B%E7%BB%8D.md里面提到了Redisson可以实现大致如下的分布式锁
https://www.bookstack.cn/read/redisson-wiki-zh/Redisson%E9%A1%B9%E7%9B%AE%E4%BB%8B%E7%BB%8D.md里面提到了Redisson可以实现大致如下的分布式锁

Redisson快速入门(Demo)
(1)导依赖
<!-- redis-redisson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.13.6</version>
</dependency>(2)配置Redisson客户端
/**
* 配置 Redisson
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() {
// 配置
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.89.128:6379").setPassword("888888");
// 创建 RedissonClient 对象
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}(3)使用Redisson的分布式锁
@Test
void testRedisson() throws Exception {
RLock anyLock = redissonClient.getLock("anyLock");
boolean isLock = anyLock.tryLock(1, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(isLock) {
try {
System.out.println("执行业务");
} finally {
anyLock.unlock();
}
}
}测试结果

一、Redisson实现可重入锁
这里可重入锁的实现 和 Java的 ReentrantLock 类似!
获取锁的时候,先判断是不是同一个对象,是就将 value+1,释放锁的时候就 value-1,当其小于0时就将该key删除!(Redisson帮我们做好了)
在Redis中使用 Hash结构 去存储!

Redisson 解决重入问题
获取锁
@Override
public boolean tryLock() {
return get(tryLockAsync());
}@Override
public RFuture<Boolean> tryLockAsync() {
return tryLockAsync(Thread.currentThread().getId());
}private RFuture<Boolean> tryAcquireOnceAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// 锁自动释放的时间,这里没有传,默认 -1
if (leaseTime != -1) {
return tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);
}
// tryLockInnerAsync 具体实现
RFuture<Boolean> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime,
commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_NULL_BOOLEAN);
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
return;
}
if (ttlRemaining) {
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}tryLockInnerAsync() 里面是通过一个Lua脚本来实现获取锁!
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
// 在Lua脚本中起始位是1
return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}上述代码中字符串部分就是Lua脚本,Redisson用其实现可重入锁!
Redisson 获取锁中的Lua脚本源码解析
-- 判断锁是否存在
if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then
-- 不存在,获取锁
redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1);
-- 设置有效期
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]);
return nil;
end;
-- 锁已经存在,判断是否是自己?!
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then
-- 自增+1
redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1);
-- 重置有效期
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]);
return nil;
end;
return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);释放锁
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}Redisson 释放锁中的Lua脚本源码解析
-- 判断当前锁是否还是被自己持有
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then
-- 不是就就直接返回
return nil;
end;
-- 是自己,则重入次数 -1
local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1);
-- 判断重入次数是否已经为0
if (counter > 0) then
-- 大于0,说明不能释放,重置有效期即可
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]);
return 0;
else
-- 等于0,说明可以直接删除
redis.call('del', KEYS[1]);
-- 发消息
redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]);
return 1;
end;
return nil;测试代码
可重入锁的原理就如同上面描述的那样,但是单纯使用起来我们只要调 lock.tyrLock() 的API就行了,无需关注那么多!
我们这边模拟一下锁重入的场景。方法A上锁后调方法B,方法B也获取锁(如果是不可重入,这里就会阻塞!)
/**
* Redisson的单元测试
*/
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class RedissonTest {
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
private RLock lock;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
lock = redissonClient.getLock("order");
}
@Test
void method1() {
boolean isLock = lock.tryLock();
if (!isLock) {
log.error("获取锁失败 ... 1");
return;
}
try {
log.info("获取锁成功 ... 1");
method2();
log.info("开始执行业务 ... 1");
} finally {
log.warn("准备释放锁 ... 1");
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Test
void method2() {
boolean isLock = lock.tryLock();
if (!isLock) {
log.error("获取锁失败 ... 2");
return;
}
try {
log.info("获取锁成功 ... 2");
log.info("开始执行业务 ... 2");
} finally {
log.warn("准备释放锁 ... 2");
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
运行结果

Redis 中值的情况

二、Redisson实现重试、超时续约问题
实现重试、超时续约问题流程
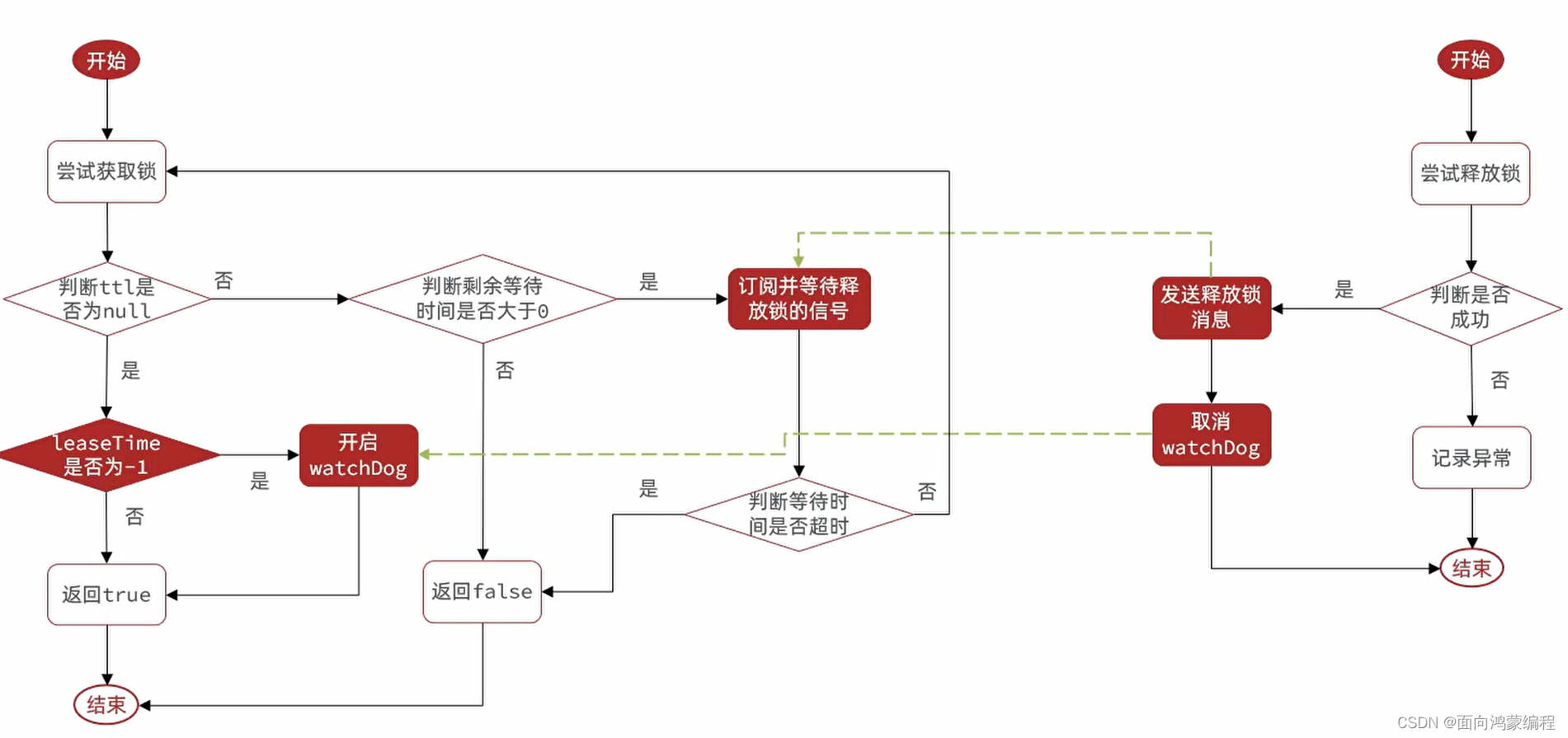
- 可重试:利用信号量和PubSub功能实现等待、唤醒,获取锁失败的重试机制
- 超时续约:利用watchDog,每隔一段时间(releaseTime / 3),重置超时时间
API参数
waitTime:是最大等待时间,如果使用 tryLock() 的时候,有传参数表明是可重试的锁;反之,不是!
leaseTime:超时释放时间,默认是-1,建议不要设定,Redisson看门狗机制可以就行锁续约!

重试、超时续约的源码分析
(1)锁重试
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return tryLock(waitTime, -1, unit);
}tryLock()
里面实现了重试机制!通过消息订阅和信号量机制,避免了 while(true) 让其一直无效尝试,避免了CPU空转问题!
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
// 转成毫秒,后面都是以毫秒为单位
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
// 当前时间
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 线程ID-线程标识
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
// 尝试获取锁 tryAcquire() !!!
Long ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// 如果上面尝试获取锁返回的是null,表示成功;如果返回的是时间则表示失败。
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
}
// 剩余等待时间 = 最大等待时间 -(用现在时间 - 获取锁前的时间)
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
// 剩余等待时间 < 0 失败
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
// 再次获取当前时间
current = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 重试逻辑,但不是简单的直接重试!
// subscribe是订阅的意思
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId);
// 如果在剩余等待时间内,收到了释放锁那边发过来的publish,则才会再次尝试获取锁
if (!subscribeFuture.await(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) {
subscribeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
// 取消订阅
unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
});
}
// 获取锁失败
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
try {
// 又重新计算了一下,上述的等待时间
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
// 重试!
while (true) {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// 成功
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
}
// 又获取锁失败,再次计算上面的耗时
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 采用信号量的方式重试!
if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) {
subscribeFuture.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
subscribeFuture.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// 重新计算时间(充足就继续循环)
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
}
} finally {
unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId);
}
}在 tryLock() 中调 tryAcquire() 执行获取锁的操作
private Long tryAcquire(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
return get(tryAcquireAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId));
}private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
if (leaseTime != -1) {
return tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
// leaseTime我们没有传,这里设定默认值(看门狗)30s
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime,
commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
// 回调函数 ttlRemaining:剩余有效期,e:异常
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
return;
}
// 剩余有效期为null,表示获取锁成功!
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
// 锁续约
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
// 把 leaseTime锁释放时间 记录成一个本地的成员变量
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
// 获取锁成功返回nil(空),失败返回时间,锁的剩余有效期(pttl是以毫秒为单位)
return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}(2)锁超时续约
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
if (leaseTime != -1) {
return tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
// leaseTime我们没有传,这里设定默认值(看门狗)30s
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime,
commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(),
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
// 回调函数 ttlRemaining:剩余有效期,e:异常
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
return;
}
// 剩余有效期为null,表示获取锁成功!
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
// 锁续约
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry entry = new RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry();
/* putIfAbsent() 是ConcurrentHashMap的API
* (1)如果是新的记录,那么会向map中添加该键值对,并返回null
* (2)如果已经存在,那么不会覆盖已有的值,直接返回已经存在的值
* EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP 是静态的,key为锁的名称
*/
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry oldEntry = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(getEntryName(), entry);
// 新的、旧的都会加
if (oldEntry != null) {
oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);
} else {
entry.addThreadId(threadId);
// 新的,还会多一步操作(更新有效期)
renewExpiration();
}
}renewExpiration
private void renewExpiration() {
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ee = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ee == null) {
return;
}
Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
RedissonLock.ExpirationEntry ent = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ent == null) {
return;
}
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId == null) {
return;
}
// 刷新有效期
RFuture<Boolean> future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
log.error("Can't update lock " + getName() + " expiration", e);
return;
}
if (res) {
// 自己调自己
renewExpiration();
}
});
}
}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
ee.setTimeout(task);
}刷新有效期(重置)
protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return 0;",
Collections.singletonList(getName()),
internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}renewExpiration执行流程
renewExpiration() 函数在执行时,会开启一个任务
这个任务会在10s后执行 (internalLockLeaseTime / 3)
10s后执行的这个任务会更新有效期,并“调自己”!
“调自己”说明又会建立这个任务,而这个任务又在10s后执行.......
这也是为什么在oldEntry中不会调这个函数,而新的entry需要调的原因!!!
因为在oldEntry中本身就有这个任务(之前调过,当它刚刚成为entry的时候) ,最后,在释放锁的时候将这个定时任务清除(通过cancelExpirationRenewal()清除任务)
三、Redisson实现主从一致性问题
问题描述
为了Redis的可靠性,我们一般会使用Redis的主从模式。
使用了主从模式,一般会采用读写分离的策略,主节点写,从节点读!

那么,当数据被写入主节点的时候,主节点时需要向从节点去同步数据的!
这个过程一定会有延时,一致性问题也就发生在这里!
假如,在主节点中获取到了锁,在主节点向从节点同步这个锁信息的时候,主节点宕机了!那么从节点就会从中挑选一个作为主节点!
可是,此时之前的锁信息就丢失了!也就发生了锁失效的问题!!!

Redisson的解决方案——MultiLock
之前我们分析了,主从模式是导致锁失效的原因,所以Redisson中就直接将它们视为相同的角色!
此时,我们获取锁的方式就变了,获取锁的时候,我们需要依次向全部节点获取锁,只有都获取成功时才算成功!!!

如果此时也发生了刚刚描述的问题,是不会出现锁失效的问题的!
分析如下

这套方案就是Redisson中的联锁——MultiLock
官网对于MultiLock的描述
代码实现
配置Redis连接的客户端——3个Client
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() {
// 配置
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.89.128:6379").setPassword("888888");
// 创建 RedissonClient 对象
return Redisson.create(config);
}
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient2() {
// 配置
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.89.128:6380");
// 创建 RedissonClient 对象
return Redisson.create(config);
}
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient3() {
// 配置
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.89.128:6381");
// 创建 RedissonClient 对象
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}联锁的使用
其实和我们之前的代码没有什么差别!
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class RedissonTest {
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient2;
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient3;
private RLock lock;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
RLock lock1 = redissonClient.getLock("order");
RLock lock2 = redissonClient.getLock("order");
RLock lock3 = redissonClient.getLock("order");
// 创建联锁
lock = redissonClient.getMultiLock(lock1, lock2, lock3);
}
@Test
void method1() throws InterruptedException {
boolean isLock = lock.tryLock(1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (!isLock) {
log.error("获取锁失败 ... 1");
return;
}
try {
log.info("获取锁成功 ... 1");
method2();
log.info("开始执行业务 ... 1");
} finally {
log.warn("准备释放锁 ... 1");
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Test
void method2() {
boolean isLock = lock.tryLock();
if (!isLock) {
log.error("获取锁失败 ... 2");
return;
}
try {
log.info("获取锁成功 ... 2");
log.info("开始执行业务 ... 2");
} finally {
log.warn("准备释放锁 ... 2");
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
为什么使用redissonClient.getMultiLock(...)就行?
我们可以跟一下代码看看!
@Override
public RLock getMultiLock(RLock... locks) {
return new RedissonMultiLock(locks);
}在这里就可以发生,不管是哪一个对象来调,其实都是一样的,这里面其实是在new一个对象RedissonMultiLock() ,所以谁去调getMultiLock()都是一样的!!!
final List<RLock> locks = new ArrayList<>();
public RedissonMultiLock(RLock... locks) {
if (locks.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Lock objects are not defined");
}
this.locks.addAll(Arrays.asList(locks));
}在这里可以发现,这个可变参数被视为集合,然后都添加到数组(集合)里面去了!
所以,按照联锁的原理,在获取锁的时候,也会依次把集合中的每一个锁都获取一次!
MultiLock源码分析 !!!
我们这里跟一下tryLock的源码(RedissonMultiLock)
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return tryLock(waitTime, -1, unit);
}// 这里的tryLock() 是RedissonMultiLock的
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long newLeaseTime = -1;
if (leaseTime != -1) {
// waitTime 为 -1,表示不重试
if (waitTime == -1) {
newLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
} else {
// 如果重试就会对时间做个扩容(放弃waitTime,使用newLeaseTime!)
newLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(waitTime)*2;
}
}
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 剩余时间
long remainTime = -1;
if (waitTime != -1) {
remainTime = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
}
// 锁等待时间 与 剩余时间是一样的!
long lockWaitTime = calcLockWaitTime(remainTime);
int failedLocksLimit = failedLocksLimit();
// 定义一个获取锁成功的集合,初始化肯定是0
List<RLock> acquiredLocks = new ArrayList<>(locks.size());
for (ListIterator<RLock> iterator = locks.listIterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
RLock lock = iterator.next();
boolean lockAcquired;
try {
if (waitTime == -1 && leaseTime == -1) {
// 不重试
lockAcquired = lock.tryLock();
} else {
long awaitTime = Math.min(lockWaitTime, remainTime);
// 重试
lockAcquired = lock.tryLock(awaitTime, newLeaseTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
} catch (RedisResponseTimeoutException e) {
unlockInner(Arrays.asList(lock));
lockAcquired = false;
} catch (Exception e) {
lockAcquired = false;
}
// 判断获取锁是否成功
if (lockAcquired) {
// 成功,加入集合中
acquiredLocks.add(lock);
} else { // 失败
// 锁的数量 - 已获取的数量 如果为0,直接break
if (locks.size() - acquiredLocks.size() == failedLocksLimit()) {
break;
}
if (failedLocksLimit == 0) {
// 释放已获取到的锁
unlockInner(acquiredLocks);
// 失败后是否要重试
if (waitTime == -1) {
return false;
}
failedLocksLimit = failedLocksLimit();
// 把整个获取到的锁集合清空
acquiredLocks.clear();
// 将指针移到第一个
while (iterator.hasPrevious()) {
iterator.previous();
}
} else {
failedLocksLimit--;
}
}
// 时间是否耗尽?
if (remainTime != -1) {
// 用当前时间 - 获取锁开始的时间 = 获取锁的耗时
// 剩余时间 - 耗时 = 现在的剩余时间
remainTime -= System.currentTimeMillis() - time;
time = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 判断是否还有时间
if (remainTime <= 0) {
// 解锁
unlockInner(acquiredLocks);
return false;
}
}
}
// 当leaseTime 为 -1 ,会触发看门狗机制,锁会自动续有效期
// 自定义锁的释放时间(建议不要设置!)
if (leaseTime != -1) {
List<RFuture<Boolean>> futures = new ArrayList<>(acquiredLocks.size());
// 遍历拿到的每一把锁,并给它们重新设置有效期
for (RLock rLock : acquiredLocks) {
RFuture<Boolean> future = ((RedissonLock) rLock).expireAsync(unit.toMillis(leaseTime), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
futures.add(future);
}
for (RFuture<Boolean> rFuture : futures) {
rFuture.syncUninterruptibly();
}
}
return true;
}
关于Redisson分布式锁的可重入、重试、联锁问题的总结





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)