常见数据结构算法知识
-
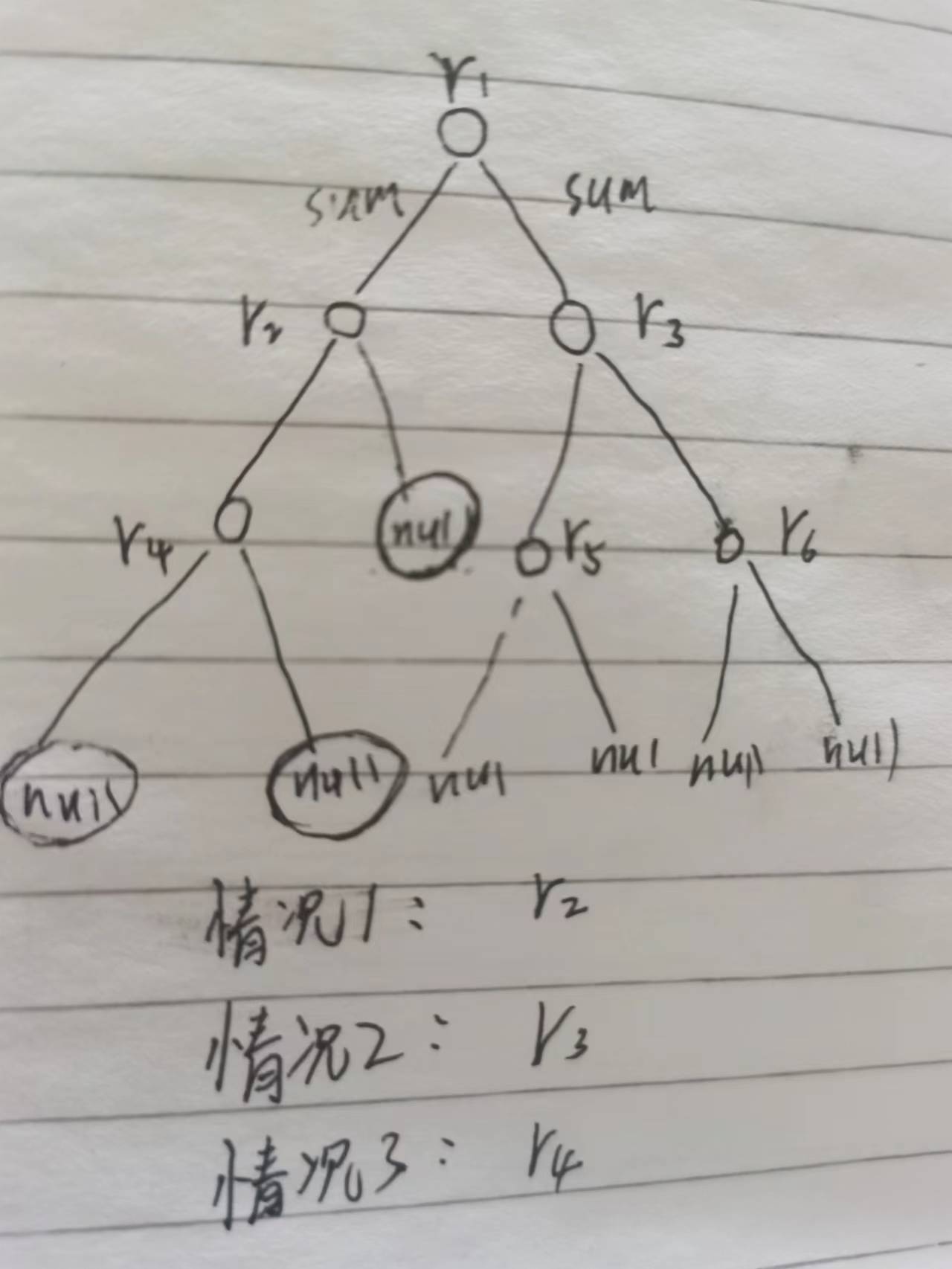
给定一个仅包含数字0-9的二叉树,每一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径都可以用一个数字表示。例如根节点到叶子节点的一条路径是1->2->3,那么这条路径就用123来代替。找出根节点到叶子节点的所有路径表示的数字之和例如:
1↵ / ↵ 2 3
根节点到叶子节点的路径1->2用数字12代替根节点到叶子节点的路径1->3用数字13代替答案为12+13=25
思路:函数传入sum是因为不知道树有多高,即不知道乘以几个10

/** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { private static int res = 0; public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } return compute(root, 0); } public int compute(TreeNode root, int sum) { if (root == null) { return 0; } // 当前节点值是父节点值 * 10 + 当前节点值 sum = sum * 10 + root.val; // 到达子节点 if (root.left = null && root.right == null) { return sum; } // 递归返回左右子树路径和 return compute(root.left, sum) + compute(root.right, sum); } }
- 求给定二叉树的最大深度,最大深度是指树的根结点到最远叶子结点的最长路径上结点的数量。

/** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } return 1 + Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)); } }
- 求给定二叉树的最小深度。最小深度是指树的根结点到最近叶子结点的最短路径上结点的数量。

/** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public int run(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int left = run(root.left); int right = run(root.right); if (left == 0 || right == 0) { return 1 + Math.max(left, right); } else { return 1 + Math.min(left, right); } } }
- 在O(n log n)的时间内使用常数级空间复杂度对链表进行排序

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } ListNode mid = getMid(head); ListNode tmp = mid.next; mid.next = null; return merge(sortList(head), sortList(tmp)); } public ListNode getMid(ListNode head) { if (head == null) { return null; } ListNode slow, fast; slow = fast = head; // 注意只有两个节点的情况 while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } return slow; } // 两个链表合并关键是弄一个头节点 public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { ListNode head = new ListNode(0); ListNode cur = head; while (head1 != null || head2 != null) { if (head2 == null) { cur.next = head1; return head.next; } else if (head1 == null) { cur.next = head2; return head.next; } else if (head1.val > head2.val) { cur.next = head2; head2 = head2.next; } else { cur.next = head1; head1 = head1.next; } // 最后移动cur cur = cur.next; } return head.next; } }
- 递归前序遍历实现二叉树的序列化与反序列化。
例如:给定的二叉树为{1,#,2,3},返回“[1,null,2,null,3]”
1↵ ↵ 2↵ /↵ 3↵
思路:核心思想是递归,序列化直接把左右子树递归结果作为字符串拼接起来,反序列化是利用队列放置序列化后的字符,然后通过递归把队列中元素弹出来,组装成左右子树

public class Codec { // 序列化 public String serialize(TreeNode root) { if(root == null){ return "null"; } return root.val + "," + serialize(root.left) + "," + serialize(root.right); } // 反序列化 public TreeNode deserialize(String data) { // 利用队列先进先出的特性,也可以用list Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(Arrays.asList(data.split(","))); return dfs(queue); } private TreeNode dfs(Queue<String> queue) { String val = queue.poll(); if("null".equals(val)){ return null; } TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val)); root.left = dfs(queue); root.right = dfs(queue); return root; } }
- BFS层次遍历实现二叉树的序列化与反序列化。
例如:给定的二叉树为{1,#,2,3},返回“[1,null,2,null,3]”
1↵ ↵ 2↵ /↵ 3↵

public class Codec { public String serialize(TreeNode root) { if(root == null){ return ""; } StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); res.append("["); Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if(node != null){ res.append(node.val.toString()); queue.offer(node.left); queue.offer(node.right); }else{ res.append("null"); } res.append(","); } res.append("]"); return res.toString(); } public TreeNode deserialize(String data) { if(data == ""){ return null; } // 去掉前后的'['和']' String[] list = data.substring(1, data.length() - 1).split(","); TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(list[0])); Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); int i = 1; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if(!"null".equals(list[i])){ node.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(list[i])); queue.offer(node.left); } i++; if(!"null".equals(list[i])){ node.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(list[i])); queue.offer(node.right); } i++; } return root; } }
-
非递归前序遍历实现二叉树的序列化与反序列化。
1↵ ↵ 2↵ /↵ 3↵

public class Codec { public static String serialize(TreeNode head) { if (head == null) { return "[]"; } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("["); Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(head); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode c = stack.pop(); // 先向栈中压入右节点,再压左节点,出栈就是先左节点再右节点 if (c != null) { sb.append(c.val); stack.push(c.right); stack.push(c.left); } else { sb.append("null"); } sb.append(",") } sb.append("]"); return sb.toString(); } // 反序列化 public TreeNode deserialize(String data) { // 利用队列先进先出的特性,也可以用list Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(Arrays.asList(data.split(","))); return dfs(queue); } private TreeNode dfs(Queue<String> queue) { String val = queue.poll(); if("null".equals(val)){ return null; } TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(val)); root.left = dfs(queue); root.right = dfs(queue); return root; } }
- 给出一棵二叉树,能否使用中序遍历序列化和反序列化这棵树
这是不可能的,因为中序遍历序列化后对应的树不是唯一的
-
对于一个给定的链表,返回环的入口节点,如果没有环,返回null,证明思路见:https://blog.csdn.net/zwwhsxq/article/details/125707465

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) { return null; } ListNode slow, fast; slow = fast = head; while(fast != null && fast.next != null){ slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if(slow == fast)//yaofanglibian,fouze diyigejiumanzu slow == fast break; } if (fast == null || fast.next == null) { return null; } fast = head; while (fast != slow) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return fast; } }
- 给定一个字符串s和一组单词dict,判断s是否可以用空格分割成一个单词序列,使得单词序列中所有的单词都是dict中的单词(序列可以包含一个或多个单词)。
例如:
给定s=“leetcode”;
dict=["leet", "code"].
返回true,因为"leetcode"可以被分割成"leet code".
思路:flag[i]代表0~i-1是否在dict中

import java.util.Set; public class Solution { public boolean wordBreak(String s, Set<String> dict) { boolean [] flag = new boolean[s.length() + 1]; flag[0] = true; for (int i = 1;i <= s.length();i ++) { for (int j = 0;j < i;j ++) { if (flag[j] && dict.contains(s.substring(j, i))) { flag[i] = true; break; } } } return flag[s.length()]; } }
-
现在有一个这样的链表:链表的每一个节点都附加了一个随机指针,随机指针可能指向链表中的任意一个节点或者指向空。请对这个链表进行深拷贝。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer. * class RandomListNode { * int label; * RandomListNode next, random; * RandomListNode(int x) { this.label = x; } * }; */ public class Solution { public RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) { if (head == null) { return null; } RandomListNode old_cur; old_cur = head; while (old_cur != null) { RandomListNode new_cur = new RandomListNode(old_cur.label); new_cur.next = old_cur.next; old_cur.next = new_cur; old_cur = old_cur.next.next; } old_cur = head; RandomListNode cur; while (old_cur != null) { cur = old_cur.next; if (old_cur.random != null) { cur.random = old_cur.random.next; } else { cur.random = null; } old_cur = old_cur.next.next; } RandomListNode newHead; old_cur = head; newHead = old_cur.next; while (old_cur != null) { cur = old_cur.next; old_cur.next = cur.next; old_cur = old_cur.next; if (cur.next != null) { cur = cur.next.next; } } return newHead; } }
-
有N个小朋友站在一排,每个小朋友都有一个评分你现在要按以下的规则给孩子们分糖果:
- 每个小朋友至少要分得一颗糖果
- 分数高的小朋友要他比旁边得分低的小朋友分得的糖果多(注意等于)
你最少要分发多少颗糖果?

public class Solution { public int candy(int[] ratings) { int []count = new int [ratings.length]; if (ratings.length == 0) { return 0; } for (int i = 0;i < ratings.length;i ++) { count[i] = 1; } for (int i = 0;i < ratings.length - 1;i ++) { if (ratings[i] < ratings[i + 1]) { count[i + 1] = count[i] + 1; } } for (int i = ratings.length - 1;i > 0;i --) { if (ratings[i - 1] > ratings[i] && count[i] >= count[i - 1]) { count[i - 1] = count[i] + 1; } } int sum = 0; for (int i = 0;i < count.length;i ++) { sum += count[i]; } return sum; } }
-
环形路上有n个加油站,第i个加油站的汽油量是gas[i].你有一辆车,车的油箱可以无限装汽油。从加油站i走到下一个加油站(i+1)花费的油量是cost[i],你从一个加油站出发,刚开始的时候油箱里面没有汽油。求从哪个加油站出发可以在环形路上走一圈。返回加油站的下标,如果没有答案的话返回-1。注意:答案保证唯一。

public class Solution { public int canCompleteCircuit(int[] gas, int[] cost) { if (gas.length == 0 || cost.length == 0) { return 0; } int [] diff = new int [gas.length]; int sum = 0; for (int i = 0;i < gas.length;i ++) { diff[i] = gas[i] - cost[i]; sum += diff[i]; } if (sum < 0) { return -1; } for (int i = 0;i < gas.length;i ++) { sum = diff[i]; if (diff[i] < 0) { continue; } // 从i开始一个一个转圈遍历,如果sum小于0就退出 int j = (i + 1) % gas.length; while (i != j) { sum += diff[j]; if (sum < 0) { break; } else { j = (j + 1) % diff.length; } } if (sum >= 0) { return i; } } return -1; } }
- 找出给出的字符串S中最长的回文子串。假设S的最大长度为1000,并且只存在唯一解。
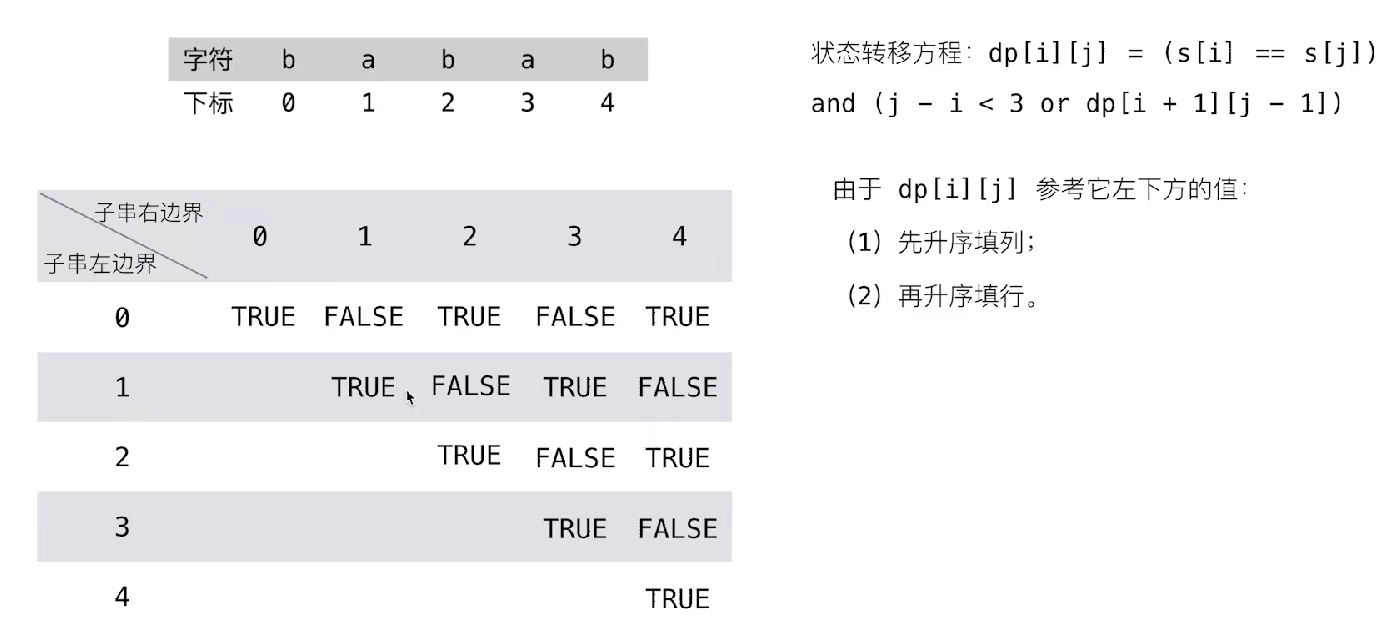
时间复杂度O(n*n)

public class Solution { public String longestPalindrome(String s) { int n = s.length(); if (n < 2) { return s; } // dp[i][j]表示i到j是否是回文串 boolean [][]dp = new boolean[n][n]; // 单个字符是回文串 int max = 1; // 第一个字符 int start = 0; // 初始化,每个字母都是回文串 for (int i = 0;i < n;i ++) { dp[i][i] = true; } // 先一列一列填写,再一行一行填,保证左下角先计算,具体可参见力扣题解 for (int j = 0;j < n;j ++) { for (int i = 0;i < j;i ++) { // 头尾相等 if ((s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) { // 头尾去掉没有字符或者剩一个字符,肯定是回文串 if (j - i < 3) { dp[i][j] = true; } else { dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1]; } } else { // 头尾不相等 dp[i][j] = false; } } // 记录回文串长度和起始位置 if (dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > max) { max = j - i + 1; start = i; } } return s.substring(start, start + max); } }
-
给定一个字符串s,分割s使得s的每一个子串都是回文串返回所有的回文分割结果。(注意:返回结果的顺序需要和输入字符串中的字母顺序一致。)例如:给定字符串s="aab",返回
[↵ ["aa","b"],↵ ["a","a","b"]↵ ]
思路:字符串从前边取0~i的子串判断是否是回文,如果是再递归判断i + 1 ~ len - 1的子串

import java.util.ArrayList; public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> partition(String s) { ArrayList<ArrayList<String>>res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String>>(); ArrayList<String>list = new ArrayList<String>(); if (s == null | s.length() == 0) { return res; } calResult(res, list, s); return res; } public void calResult(ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> res, ArrayList<String> list, String s) { if (s.length() == 0) { res.add(new ArrayList<String> (list)); } for (int i = 1;i <= s.length();i ++) { // 对前边一点一点判断,然后去掉 if (is(s.substring(0, i))) { list.add(s.substring(0, i)); calResult(res, list, s.substring(i)); list.remove(list.size() - 1); } } } public boolean is(String s) { int i = 0; int j = s.length() - 1; while (i < j) { if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) { return false; } i ++; j --; } return true; } }
- 给定一个无序的整数类型数组,求最长的连续元素序列的长度。
例如:给出的数组为[100, 4, 200, 1, 3, 2],最长的连续元素序列为[1, 2, 3, 4]. 返回这个序列的长度:4你需要给出时间复杂度在O(n)之内的算法

import java.util.HashSet; public class Solution { public int longestConsecutive(int[] num) { int max = 1; int count; HashSet<Integer> numSet = new HashSet<>(); for (int i = 0;i < num.length;i ++) { count = 1; numSet.add(num[i]); int a = num[i] - 1; while (numSet.contains(a)) { count ++; a --; } int b = num[i] + 1; while (numSet.contains(b)) { count ++; b ++; } if (count > max) { max = count; } } return max; } }
- 给定两个单词(初始单词和目标单词)和一个单词字典,请找出所有的从初始单词到目标单词的最短转换序列的长度:
- 每一次转换只能改变一个单词
- 每一个中间词都必须存在单词字典当中
例如:给定的初始单词start="hit",目标单词end ="cog"。单词字典dict =["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]一个最短的转换序列为"hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog",返回长度5注意:如果没有符合条件的转换序列,返回0。题目中给出的所有单词的长度都是相同的题目中给出的所有单词都仅包含小写字母
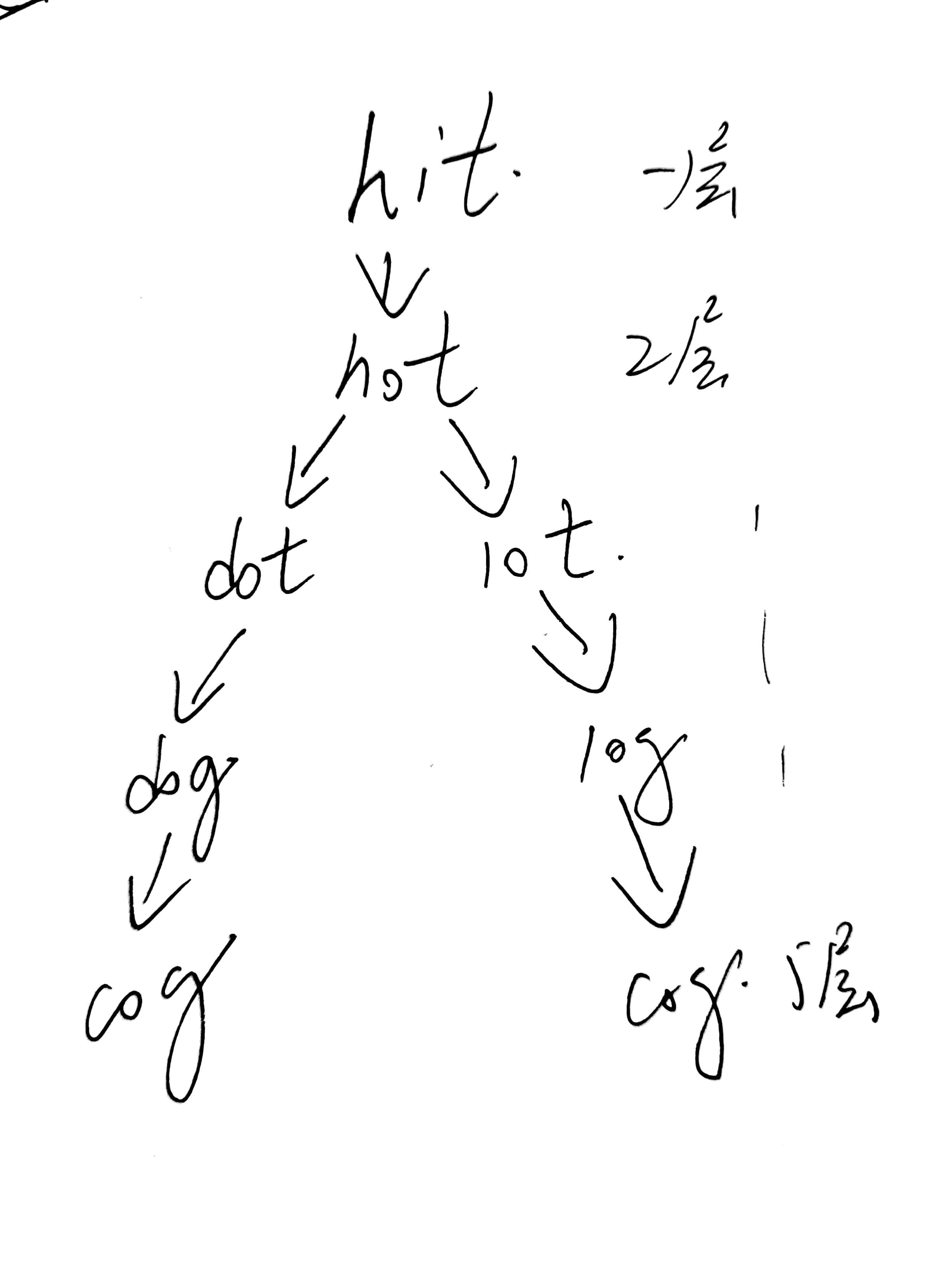

import java.util.Queue; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.LinkedList; public class Solution { public int ladderLength(String start, String end, HashSet<String> dict) { if (start == null || end == null || start.length() == 0 || end.length() == 0) { return 0; } Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<> (); queue.offer(start); String tmp; String s; int res = 1; int size; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0;i < size;i ++) { Iterator<String> it = dict.iterator(); tmp = queue.poll(); if (isDiffOne(tmp, end)) { return res + 1; } while (it.hasNext()) { s = it.next(); if (isDiffOne(tmp, s)) { queue.offer(s); it.remove(); // 注意remove } } } res ++; } return 0; } public boolean isDiffOne(String s1,String s2) { if (s1 == null || s2 == null || s1.length() != s2.length()) { return false; } int count = 0; for (int i = 0;i < s1.length();i ++) { if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(i)) { count ++; } } if (count == 1) { return true; } else { return false; } } }
- 假设你有一个数组,其中第i个元素是某只股票在第i天的价格。
设计一个算法来求最大的利润。你最多可以进行两次交易(两次买,两次卖)。
注意:
你不能同时进行多个交易(即,你必须在再次购买之前出售之前买的股票)

public class Solution { public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { if (prices.length == 0) { return 0; } int len = prices.length; int [] pro = new int[len]; int [] bpro = new int[len]; int min = prices[0]; int tmp = 0; for (int i = 0;i < len;i ++) { if (prices[i] <= min) { min = prices[i]; } else if (tmp < prices[i] - min) { tmp = prices[i] - min; } pro[i] = tmp; // 保存计算的tmp或者之前的tmp } int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; tmp = 0; for (int i = len - 1;i >= 0;i --) { if (prices[i] >= max) { max = prices[i]; } else if (tmp < max - prices[i]) { tmp = max - prices[i]; } bpro[i] = tmp; } max = 0; for (int i = 0;i < len;i ++) { if (pro[i] + bpro[i] > max) { max = pro[i] + bpro[i]; } } return max; } }
- 假设你有一个数组,其中第i个元素是某只股票在第i天的价格。
如果你最多只能完成一笔交易(即买一股和卖一股股票),设计一个算法来求最大利润

public class Solution { public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { int tmp; int res = 0; // 最小就是当天买, 当天卖 int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int i = 0;i < prices.length;i ++) { if (prices[i] < min) { min = prices[i]; } else { tmp = prices[i] - min; if (tmp > res) { res = tmp; } } } return res; } }
-
给出一个三角形,计算从三角形顶部到底部的最小路径和,每一步都可以移动到下面一行相邻的数字,例如,给出的三角形如下:
[↵ [2],↵ [3,4],↵ [6,5,7],↵ [4,1,8,3]↵]
最小的从顶部到底部的路径和是2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11。
思路:倒着看三角,从最后一行遍历,数组中第i个值等于Math.min(下一行中第i个值,下一行中第i + 1个值)

import java.util.ArrayList; public class Solution { public int minimumTotal(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> triangle) { // 注意数组大小 int [] res = new int[triangle.get(triangle.size() - 1).size() + 1]; for (int i = triangle.size() - 1;i >= 0;i --) { for (int j = 0;j < triangle.get(i).size();j ++) { res[j] = triangle.get(i).get(j) + Math.min(res[j], res[j + 1]); } } return res[0]; } }
- 给出一个值numRows,生成杨辉三角的前numRows行,公式res[i][j] = res[i - 1][j - 1] + res[i - 1][j]
例如,给出 numRows = 5,返回
[↵ [1],↵ [1,1],↵ [1,2,1],↵ [1,3,3,1],↵ [1,4,6,4,1]↵]

import java.util.ArrayList; public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> generate(int numRows) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> (); for (int i = 0;i < numRows;i ++) { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer> (); list.add(1); // 因为每次都是新的array,所以要加1 for (int j = 0;j < i - 1;j ++) { list.add(res.get(i - 1).get(j - 1) + res.get(i - 1).get(j)); } if (i != 0) { list.add(1); } res.add(list); } return res; } }
-
给出的二叉树如下:
1↵ / ↵ 2 3↵ / ↵ 4 5 7
调用完你给出的函数之后,这棵树应该变成:1 -> NULL↵ / ↵ 2 -> 3 -> NULL↵ / ↵ 4-> 5 -> 7 -> NULL

import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; /** * Definition for binary tree with next pointer. * public class TreeLinkNode { * int val; * TreeLinkNode left, right, next; * TreeLinkNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public void connect(TreeLinkNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } Queue<TreeLinkNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeLinkNode> (); queue.add(root); int size; TreeLinkNode last = null; TreeLinkNode cur; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0;i < size;i ++) { cur = queue.poll(); if (i != 0) { last.next = cur; } if (cur.left != null) { queue.offer(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null) { queue.offer(cur.right); } last = cur; } last.next = null; } } }
-
给定一个二叉树和一个值sum,请找出所有的根节点到叶子节点的节点值之和等于sum的路径,例如:给出如下的二叉树,sum=22,
5↵ / ↵ 4 8↵ / / ↵ 11 13 4↵ / / ↵ 7 2 5 1
返回[↵ [5,4,11,2],↵ [5,8,4,5]↵]

import java.util.ArrayList; /** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> (); public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) { if (root == null) { return list; } ArrayList<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<Integer> (); find(root, tmp, sum); return list; } public void find(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> tmp, int sum) { if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { if (root.val == sum) { tmp.add(root.val); list.add(new ArrayList(tmp)); tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1); } } else { tmp.add(root.val); if (root.left != null) { find(root.left, tmp, sum - root.val); } if (root.right != null) { find(root.right, tmp, sum - root.val); } tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1); } } }
-
判断给定的二叉树是否是平衡的在这个问题中,定义平衡二叉树为每个节点的左右两个子树高度差的绝对值不超过1的二叉树

/** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return true; } if (judge(root) == -1) { return false; } else { return true; } } public int judge(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int left = judge(root.left); int right = judge(root.right); if (left == -1 || right == -1) { return -1; } else if(Math.abs(left - right) > 1) { return -1; } else { return 1 + Math.max(left, right); } } }
- 给出一个升序排序的数组,将其转化为平衡二叉搜索树(BST).

import java.util.Arrays; /** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] num) { if (num.length == 0) { return null; } int cur = num.length / 2; TreeNode root = new TreeNode(num[cur]); if (cur > 0) { root.left = sortedArrayToBST(Arrays.copyOfRange(num,0, cur)); } else { root.left = null; } if (cur < num.length) { root.right = sortedArrayToBST(Arrays.copyOfRange(num, cur + 1, num.length)); } else { root.right = null; } return root; } }
-
给出一棵树的中序遍历和后序遍历,请构造这颗二叉树注意:保证给出的树中不存在重复的节点

import java.util.Arrays; /** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) { if (inorder.length == 0 || postorder.length == 0 || inorder.length != postorder.length) { return null; } int len = postorder.length; TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[len - 1]); int i = 0; for (;i < inorder.length;i ++) { if (inorder[i] == postorder[len - 1]) { break; } } if (i > 0) { root.left = buildTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, 0, i), Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder, 0, i)); } if (i < len - 1) { root.right = buildTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, i + 1, len), Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder, i, len - 1)); } return root; } }
- 给定一个二叉树,返回该二叉树的之字形层序遍历,(从左向右,下一层从右向左,一直这样交替)

/** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ import java.util.Queue; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); if (root == null) { return res; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); int size; int level = 1; TreeNode tmp; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { size = queue.size(); ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0;i < size;i ++) { tmp = queue.poll(); list.add(tmp.val); if (tmp.left != null) { queue.offer(tmp.left); } if (tmp.right != null) { queue.offer(tmp.right); } } if (level % 2 == 0) { Collections.reverse(list); } res.add(list); level ++; } return res; } }
-
给你一棵二叉树,返回树的最大宽度,将这个二叉树视作与满二叉树结构相同,两端点间会出现一些null节点,这些null节点也计入长度。
因为两端点间的null 节点也需要计入宽度,因此可以对节点进行编号。一个编号为index 的左子节点的编号记为2 * index,右子节点的编号记为2 * index+1,计算每层宽度时,用每层节点的最大编号减去最小编号再加1即为宽度。

public class Solution { public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) { int res = 1; List<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> arr = new ArrayList<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>>(); arr.add(new Pair<TreeNode, Integer>(root, 1)); while (!arr.isEmpty()) { List<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> tmp = new ArrayList<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>>(); for (Pair<TreeNode, Integer> pair : arr) { TreeNode node = pair.getKey(); int index = pair.getValue(); if (node.left != null) { tmp.add(new Pair<TreeNode, Integer>(node.left, index * 2)); } if (node.right != null) { tmp.add(new Pair<TreeNode, Integer>(node.right, index * 2 + 1)); } } res = Math.max(res, arr.get(arr.size() - 1).getValue() - arr.get(0).getValue() + 1); arr = tmp; } return res; } }
-
给定一棵二叉树,判断其是否是自身的镜像(即:是否对称)例如:下面这棵二叉树是对称的

/** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return true; } return equal(root.left, root.right); } public boolean equal(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null && root2 == null) { return true; } if (root1 == null || root2 == null) { return false; } if (root1.val != root2.val) { return false; } return equal(root1.left, root2.right) && equal(root1.right, root2.left); } }
- 给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点p,q的最近公共祖先,时间复杂度O(n)

class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root == p || root == q) { return root; } if (root != null){ TreeNode lNode = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q); TreeNode rNode = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q); if (lNode != null && rNode != null) { return root; } else if(lNode == null) {//两个都在右子树 return rNode; } else { //两个都在左子树里面 return lNode; } } return null; } }
- 给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点p,q的最近公共祖先,时间复杂度O(n)

class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { TreeNode ancestor = root; while (true) { // 如果当前节点的值大于p和q值,说明遍历左子树 if (p.val < ancestor.val && q.val < ancestor.val) { ancestor = ancestor.left; // 如果当前节点的值小于p和q值,说明遍历右子树 } else if (p.val > ancestor.val && q.val > ancestor.val) { ancestor = ancestor.right; // 否则找到根结点 } else { break; } } return ancestor; } }
-
将一个链表m位置到n位置之间的区间反转,要求使用原地算法,并且在一次扫描之内完成反转。例如:给出的链表为1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2 ,n = 4,返回1->4->3->2->5->NULL.注意:给出的m,n满足以下条件:1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) { if (m >= n || n < 1 || m < 1) { return head; } ListNode newHead = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE); ListNode before = newHead; newHead.next = head; ListNode cur = head; for (int i = 1;i < m;i ++) { before = before.next; cur = before.next; } ListNode next; for (int i = m;i < n;i ++) { next = cur.next; // 关键是如何让m之后的链表不断 cur.next = next.next; next.next = before.next; before.next = next; } return newHead.next; } }
-
给出一个可能包含重复元素的整数集合S,返回该整数集合的所有子集。注意:
- 你给出的子集中的元素要按非递增的顺序排列
- 给出的解集中不能包含重复的子集
例如:如果S =[1,2,2], 给出的解集应该是:[[], [1], [1, 2], [1, 2, 2], [2], [2, 2]]

import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] num) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer> (); if (num.length == 0) { return res; } Arrays.sort(num); findSubSet(res, list, 0, num); return res; } public void findSubSet(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res, ArrayList<Integer> list, int start, int []num) { res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list)); for (int i = start;i < num.length;i ++) { // [1, 2, 2]只有一个[1, 2] if (i != start && num[i] == num[i - 1]) { continue; } list.add(num[i]); // 对第一个[1, 2]会产生[1, 2, 2] findSubSet(res, list, i + 1, num); list.remove(list.size() - 1); } } }
- 现在有一个没有重复元素的整数集合S,求S的所有子集
- 你给出的子集中的元素必须按非递增的顺序排列
- 给出的解集中不能出现重复的元素
[↵ [],↵ [1],↵ [2],↵ [3]↵ [1,3],↵ [2,3],↵ [1,2],↵ [1,2,3], ↵]

import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> subsets(int[] S) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer> (); if (S.length == 0) { return res; } Arrays.sort(S); // 控制元素个数 for (int i = 0;i <= S.length;i ++) { findSubSet(res, list, i, 0, S); } return res; } public void findSubSet(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res, ArrayList<Integer> list, int level, int start, int []num) { // level控制元素个数 if (level == 0) { res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list)); return ; } for (int i = start;i < num.length;i ++) { list.add(num[i]); findSubSet(res, list, level - 1, i + 1, num); list.remove(list.size() - 1); } } }
- 从有序数组中找出某个数出现的次数

public int countInArray(int []arr, int size, int target) { int first = search(arr, arr.size, target, 0); int last = search(arr, arr.size, target, 1); if (first == -1) { return 0; } return last - first + 1; } public int search(int []arr, int size, int target, int flag) { int left = 0; int right = size - 1; int mid = 0; int last = -1; while (left < right) { mid = (left + right) / 2; if (arr[mid] < arr[target]) { left = mid + 1; } else if (arr[mid] > arr[target]) { right = mid - 1; } else { last = mid; if (flag = 0) { // 找第一个,在左边找 right = mid - 1; } else if (flag = 1) { // 找最后一个,在右边找 left = mid + 1; } } } return last; }
-
从数组中找出第k个最大元素
第一种解法:通过快速排序(平均时间复杂度为O(n logn)) + 随机化基准数,时间复杂度可达到O(n)

class Solution { public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; return find (nums, 0, n - 1, n - k); } private int find (int[] nums, int low, int high, int k) { if (low > high) { return -1; } // 随机获取基数然后和当前的首位l交换 int index = low + (int) (Math.random() * (high - low + 1)); int tmp = nums[low]; nums[low] = nums[index]; nums[index] = tmp; tmp = nums[low]; int i = low; int j = high; while (i < j) { // 右边找小的 while (i < j && nums[j] >= tmp) { j --; } // 找到了替换 if (i < j) { nums[i ++] = nums[j]; } // 左边找大的 while (i < j && nums[i] < tmp) { i ++; } // 找到了替换 if (i < j) { nums[j --] = nums[i]; } } nums[i] = tmp; if (i == k) { return nums[i]; } else if (i < k) { // 如果i < k,再对右子树排序 return find(nums, i + 1, high, k); } else { // 如果i > k,对左子树排序 return find(nums, low, i - 1, k); } } }
第二种解法:通过最大堆排序获得

class Solution { public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) { int heapSize = nums.length; buildMaxHeap(nums, heapSize); // 输出第k个最大元素 for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= nums.length - k + 1; --i) { // 交换堆顶元素和末尾元素 swap(nums, 0, i); // 堆顶元素脱离二叉树 heapSize --; // 从堆顶元素再开始调整最大堆 adujst(nums, 0, heapSize); } return nums[0]; } public void buildMaxHeap(int[] a, int heapSize) { // 从最后一个非叶子结点开始向上构造最大堆 for (int i = heapSize / 2; i >= 0; --i) { adujst(a, i, heapSize); } } // 调整使之成为最大堆 public void adujst(int[] a, int i, int heapSize) { int left = 2 * i + 1; int right = 2 * (i + 1); int largest = i; // 如果有左子树,且左子树大于父节点 if (left < heapSize && a[left] > a[largest]) { largest = left; } // 如果有右子树,且右子树大于父节点 if (right < heapSize && a[right] > a[largest]) { largest = right; } // 如果父节点不是最大值,将父节点与最大值交换,并递归调整交换后的子树 if (largest != i) { swap(a, i, largest); adujst(a, largest, heapSize); } } public void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) { int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } }
-
给出两个有序的整数数组A和B,请将数组B合并到数组A中,变成一个有序的数组
注意: 可以假设A数组有足够的空间存放B数组的元素,A和B中初始的元素数目分别为m和n

public class Solution { public void merge(int A[], int m, int B[], int n) { if (m == 0) { for (int i = 0;i < B.length;i ++) { A[i] = B[i]; } return ; } if (n == 0) { return ; } int i = m - 1; int j = n - 1; int cur = m + n - 1; while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) { if (A[i] > B[j]) { A[cur --] = A[i --]; } else { A[cur --] = B[j --]; } } while (j >= 0) { // 可能B没有合并完 A[cur --] = B[j --]; } } }
-
给出一个链表和一个值x,以x为参照将链表划分成两部分,使所有小于x的节点都位于大于或等于x的节点之前。 两个部分之内的节点之间要保持的原始相对顺序。 例如: 给出1->4->3->2->5->2和x = 3, 返回1->2->2->4->3->5

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) { ListNode big = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE); ListNode small = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE); ListNode cur = head; ListNode b, s; b = big; s = small; while (cur != null) { if (cur.val < x) { s.next = cur; s = s.next; } else { b.next = cur; b = b.next; } cur = cur.next; } b.next = null; // 不加通不过 if (small.next == null) { return big.next; } else { s.next = big.next; return small.next; } } }
-
给出一个排好序的链表,删除链表中的所有重复出现的元素,只保留原链表中只出现一次的元素。例如:给出的链表为1->2->3->3->4->4->5, 返回1->2->5.给出的链表为1->1->1->2->3, 返回2->3

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0); ListNode p = head; ListNode q = newHead;; while (p != null && p.next != null) { if (p.val == p.next.val) { int tmp = p.val; while (p != null && p.val == tmp) { p = p.next; // 多走一步 } } else { q.next = p; p = p.next; q = q.next; } } q.next = p; return newHead.next; } }
-
删除给出链表中的重复元素(链表中元素从小到大有序),使链表中的所有元素都只出现一次例如:给出的链表为1->1->2,返回1->2.给出的链表为1->1->2->3->3,返回1->2->3

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { ListNode p = head; ListNode q; while (p != null && p.next != null) { q = p.next; while (p != null && q != null && p.val == q.val) { p.next = q.next; q = null; q = p.next; } p = p.next; } return head; } }
- 请写出一个高效的在m*n矩阵中判断目标值是否存在的算法,矩阵具有如下特征:
每一行的数字都从左到右排序每一行的第一个数字都比上一行最后一个数字大例如:对于下面的矩阵:
[↵ [1, 3, 5, 7],↵ [10, 11, 16, 20],↵ [23, 30, 34, 50]↵]
要搜索的目标值为3,返回true;

public class Solution { public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) { if (matrix.length == 0) { return false; } int row = matrix.length - 1; int col = 0; while (row >= 0 && col < matrix[0].length) { if (matrix[row][col] == target) { return true; } else if (matrix[row][col] < target) { col ++; } else { row --; } } return false; } }
- 合并k个已排序的链表并将其作为一个已排序的链表返回。分析并描述其复杂度。

import java.util.ArrayList; /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode mergeKLists(ArrayList<ListNode> lists) { if(lists == null || lists.isEmpty()){ return null; } return mergeKList(lists,0,lists.size()-1); } public ListNode mergeKList(ArrayList<ListNode> lists,int start,int end){ if (end <= start) return lists.get(end); int mid = (start + end) / 2; ListNode left = mergeKList(lists, start, mid); ListNode right = mergeKList(lists, mid+1, end); return merge(left,right); } public ListNode merge(ListNode left, ListNode right) { ListNode h = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE); ListNode tmp = h; while (left != null || right != null) { if (left == null) { tmp.next = right; right = right.next; } else if (right == null) { tmp.next = left; left = left.next; } else { if (left.val > right.val) { tmp.next = right; right = right.next; } else { tmp.next = left; left = left.next; } } tmp = tmp.next; } return h.next; } }
- 给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第n个节点并返回链表的头指针

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) { ListNode first = head; ListNode second = head; // 先走n步 for (int i = n - 1;i > 0;i --) { first = first.next; } ListNode pre = null; // first到尾节点, second到待删除节点 while (first.next != null) { pre = second; first = first.next; second = second.next; } // 删除second节点 if (pre != null) { pre.next = second.next; second = null; } else { // 考虑删除头节点的情况 head = head.next; } return head; } }
- 编写一个函数来查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀。

public class Solution { public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) { if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) { return ""; } String tmp = strs[0]; // 对所有数组元素进行遍历 for (int i = 1;i < strs.length;i ++) { while (strs[i].indexOf(tmp) != 0) { tmp = tmp.substring(0, tmp.length() - 1); if (tmp.length() == 0) { return ""; } } } return tmp; } }
- 求最大连续子序列,最大连续子序列是所有连续子序列中元素和最大的一个,例如给定序列{ -2, 11, -4, 13, -5, -2 },其最大连续子序列为{ 11, -4, 13 }
可用动态规划,状态转移方程如下:dp[i - 1] < 0说明贡献为负
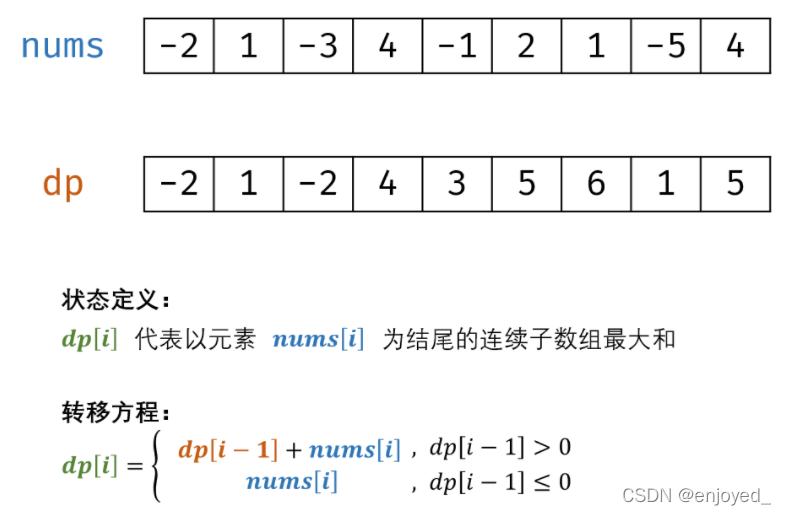

public class Solu { public int maxSubArray(int[] num) { int dp[0] = num[0]; int res = num[0]; for (int i = 1;i < num.length;i ++) { dp[i] = num[i] + Math.max(dp[i - 1], 0); res = Math.max(res, dp[i]); } return res; } }
-
给你一个整数数组
nums和一个整数k,请你统计并返回该数组中和为k的连续子数组的个数 。
输入:nums = [1,2,3], k = 3 输出:2

public class Solution { public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) { int count = 0, pre = 0; Map < Integer, Integer > mp = new HashMap <> (); // 和为0的情况有一个,这样0~i的数据为k mp.put(0, 1); for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { pre += nums[i]; if (mp.containsKey(pre - k)) { // 说明前边有子数组0~某个下标的子数组和为pre-k,map value为这样子数组的个数 count += mp.get(pre - k); } // 和为pre的子数组个数加1 mp.put(pre, mp.getOrDefault(pre, 0) + 1); } return count; } }
- 有两个大小分别为m和n的有序数组A和B。请找出这两个数组的中位数。你需要给出时间复杂度在O(log (m+n))以内的算法。

public class Solution { public double findMedianSortedArrays(int A[], int B[]) { int aLen = A.length; int bLen = B.length; int i = 0; int j = 0; int tmp = 0; int [] res = new int[aLen + bLen]; // 合并A与B两个有序数组到临时数组temp中 while (i < aLen || j < bLen) { if (i >= aLen) { res[tmp ++] = B[j ++]; } else if (j >= bLen) { res[tmp ++] = A[i ++]; } else if (A[i] < B[j]) { res[tmp ++] = A[i ++]; } else { res[tmp ++] = B[j ++]; } } tmp --; if ((tmp + 1) % 2 == 0) { // 如果数组长度为偶数,则返回下标在中间的两个数组元素值的平均值 return (res[tmp / 2] + res[tmp / 2 + 1]) / 2.0; } else { // 如果数组长度为奇数,则返回下标为中间值的数组元素值 return (double) res[tmp / 2]; } } }
-
给出一个整数数组,请在数组中找出两个加起来等于目标值的数。你给出的函数twoSum 需要返回这两个数字的下标(index1,index2),需要满足 index1 小于index2.。注意:下标是从1开始的假设给出的数组中只存在唯一解例如:
给出的数组为 {2, 7, 11, 15},目标值为9
输出 ndex1=1, index2=2

import java.util.HashMap; public class Solution { public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer> (); int [] result = new int[2]; for (int i = 0;i < numbers.length;i ++) { int value = target - numbers[i]; if (map.containsKey(value)) { result[0] = map.get(value) + 1; result[1] = i + 1; break; } else { map.put(numbers[i], i); } } return result; } }
- 给定一个m x n大小的矩阵(m行,n列),按螺旋的顺序返回矩阵中的所有元素。

import java.util.ArrayList; public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) { ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer> (); if (matrix.length == 0) { return res; } int top = 0; int bottom = matrix.length - 1; int left = 0; int right = matrix[0].length - 1; while (top <= bottom && left <= right) { for (int i = left;i <= right;i ++) { res.add(matrix[top][i]); } top ++; for (int j = top;j <= bottom;j ++) { res.add(matrix[j][right]); } right --; if (top <= bottom) { for (int i = right;i >=left;i --) { res.add(matrix[bottom][i]); } } bottom --; if (left <= right) { for (int j = bottom;j >= top;j --) { res.add(matrix[j][left]); } } left ++; } return res; } }
- 求最长摆动子序列的长度

public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) { if(nums.size() == 0) return 0; if(nums.size() == 1) return 1; //dp数组定义为:dp[i][0] = x 表示到第i个元素,以负数差为结尾的最长摆动序列长度为x // dp[i][1] = x 表示到第i个元素,以正数差为结尾的最长摆动序列长度为x int[][] dp = new int[nums.length][2]; dp[0][0] = 1; dp[0][1] = 1 int maxlen = 0; for(int i = 1;i < nums.length;i++){ if(nums[i] < nums[i-1]){ //连续数字之间的差在正数和负数之间交替 dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][1] + 1; dp[i][1] = dp[i-1][1]; }else if(nums[i] > nums[i-1]){ dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0]; //连续数字之间的差在正数和负数之间交替时 dp[i][1] = dp[i-1][0] + 1; } else{ dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0]; dp[i][1] = dp[i-1][1]; } maxlen = Math.max(maxlen, max(dp[i][0],dp[i][1])); } return maxlen; }
- 一个升序不重复元素组成的旋转数组中找到target值得下标,否则返回-1;

public static int find(int [] num, int target) { int pos = -1; int left = 0; int right = num.length - 1; int mid; while (left <= right) { mid = (left + right) / 2; if (num[mid] == target) { pos = mid; break; } if (num[left] <= num[mid]) { // 如果mid(9)左边有序 6 7 8 9 1 2 3 if (target >= num[left] && target <= num[mid]) { right = mid - 1; } else { left = mid + 1; } } else { // 如果mid(2)右边有序 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 if (target >= num[mid] && target <= num[right]) { left = mid + 1; } else { right = mid - 1; } } } return pos; }
- 二分查找

/** * 循环实现二分查找 * * @param array * @param key * @return */ public static int binarySort(int[] array, int key) { int low = 0; int high = array.length - 1; while (low <= high) { int mid = (low + high) >>> 1; if (key < array[mid]) { high = mid - 1; } else if (key > array[mid]) { low = mid + 1; } else { return mid; } } return -1; } /** * 递归实现二分查找 * * @param array * @param key * @param low * @param high * @return */ public static int binarySortRecursion(int[] array, int key, int low, int high) { if (low <= high) { int mid = (low + high) >>> 1; if (key < array[mid]) { return binarySortRecursion(array, key, low, mid - 1); } else if (key > array[mid]) { return binarySortRecursion(array, key, mid + 1, high); } else { return mid; } } return -1; } }
-
各类排序算法

public void bubbleSort(int [] input) { boolean flag = false; int temp; for (int i = 0;i < input.length;i ++) { flag = false; for (int j = 0;j < input.length - 1 - i;j ++) { if (input[j] < input[j + 1]) { temp = input[j]; input[j] = input[j + 1]; input[j + 1] = temp; flag = true; } } if (flag == false) { return; } } }
- 快速排序(参见快速排序详解)

public int getMid(int [] list, int low, int high) { int temp = list[low]; while (low < high) { while (low < high && list[high] > temp) { high --; } list[low] = list[high]; while(low < high && list[low] < temp) { low ++; } list[high] = list[low]; } list[low] = temp; return low; } public void quickSort(int [] list, int low, int high) { if (low < high) { int middle = getMid(list, low, high); quickSort(list, low, mid - 1); quickSort(list, mid + 1, high); } }
- 归并排序(参见归并排序详解)

public void merge(int []a, int low, int mid, int high) { int []tmp = new int[high - low + 1]; int i = low; int j = mid + 1; int k = 0; while (i <= mid || j <= high) { if (i <= mid && j <= high) { if (a[i] < a[j]) { tmp[k ++] = a[i ++]; } else { tmp[k ++] = a[j ++]; } } else if (i <= mid) { tmp[k ++] = a[i ++]; } else { tmp[k ++] = a[j ++]; } } k = 0; for (k < tmp.length;k ++) { a[low + k] = tmp[k]; } } public void mergeSort(int []a, int low, int high) { int mid = (low +high) / 2; mergeSort(a, low, mid); mergeSort(a, mid + 1, high); merge(a, low, mid, high); }
- 使用插入排序对链表进行排序

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null) { return head; } ListNode newHead = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE); ListNode cur, old, oldNext; old = head; cur = newHead; while (old != null) { oldNext = old.next; cur = newHead; while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val < old.val) { cur = cur.next; } old.next = cur.next; cur.next = old; old = oldNext; } return newHead.next; } }
-
能力提升
给定一个字符串 s ,根据字符出现的频率对其进行降序排序 。一个字符出现的频率是它出现在字符串中的次数。
该方法时间复杂度为O(n + klogk),n是字符串的长度,k是字符串s包含的不同字符的个数。

public String frequencySort(String s) { Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>(); int length = s.length(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { char c = s.charAt(i); int frequency = map.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1; map.put(c, frequency); } List<Character> list = new ArrayList<Character>(map.keySet()); Collections.sort(list, (a, b) -> map.get(b) - map.get(a)); StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); int size = list.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { char c = list.get(i); int frequency = map.get(c); for (int j = 0; j < frequency; j++) { sb.append(c); } } return sb.toString(); } }
- 计算逆波兰式(后缀表达式)的值
["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"] -> ((2 + 1) * 3) -> 9↵ ["4", "13", "5", "/", "+"] -> (4 + (13 / 5)) -> 6

import java.util.Stack; public class Solution { public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) { if (tokens.length == 0) { return 0; } Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); int a; int b; for (int i = 0;i < tokens.length;i ++) { if (tokens[i].equals("+")) { a = stack.pop(); b = stack.pop(); stack.push(a + b); } else if (tokens[i].equals("-")){ a = stack.pop(); b = stack.pop(); stack.push(b - a); } else if (tokens[i].equals("*")) { a = stack.pop(); b = stack.pop(); stack.push(a * b); } else if (tokens[i].equals("/")) { a = stack.pop(); b = stack.pop(); stack.push(b / a); } else { stack.push(Integer.valueOf(tokens[i])); } } return stack.pop(); } }
-
将给定的单链表L: L 0→L 1→…→L n-1→L n,重新排序为: L 0→L n →L 1→L n-1→L 2→L n-2→…要求使用原地算法,并且不改变节点的值例如:对于给定的单链表{1,2,3,4},将其重新排序为{1,4,2,3}.

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public void reorderList(ListNode head) { ListNode slow, fast; slow = head; fast = head; if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) { return ; } // 快慢指针找中点 while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } ListNode cur; cur = slow.next; slow.next = null; ListNode newHead = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE); newHead.next = null; ListNode tmp; // 对slow后面的部分逆序 while (cur != null) { tmp = cur.next; cur.next = newHead.next; newHead.next = cur; cur = tmp; } // 合并前面和后面两部分 ListNode l1 = head; cur = newHead.next; while (cur != null) { tmp = cur.next; cur.next = l1.next; l1.next = cur; l1 = l1.next.next; cur = tmp; } } }
- 假设你有一个数组,其中第i个元素表示某只股票在第i天的价格。
设计一个算法来寻找最大的利润。你可以完成任意数量的交易(例如,多次购买和出售股票的一股)。但是,你不能同时进行多个交易(即,你必须在再次购买之前卖出之前买的股票)。

public class Solution { public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { if (prices.length == 0) { return 0; } int psum = 0; for (int i = 0;i < prices.length - 1;i ++) { if (prices[i] < prices[i + 1]) { psum += prices[i + 1] - prices[i]; } } return psum; } }
- 给定一个二叉树,返回该二叉树由底层到顶层的层序遍历,(从左向右,从叶子节点到根节点,一层一层的遍历)

import java.util.Queue; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.ArrayList; /** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); if (root == null) { return res; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); int size; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { size = queue.size(); ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = 0;i < size;i ++) { TreeNode tmp = queue.poll(); list.add(tmp.val); if (tmp.left != null) { queue.offer(tmp.left); } if (tmp.right != null) { queue.offer(tmp.right); } } res.add(0, list); } return res; } }
- 非递归后序遍历实现二叉树的序列化与反序列化。
1↵ ↵ 2↵ /↵ 3↵

// 序列化 public static String serialize3(TreeNode head) { if (head == null) { return "[]"; } // 为了拿到根结点获取左右子节点,所以用stack1,为了最后访问跟节点,所以用stack2 Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>(); Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>(); stack1.push(head); while (!stack1.isEmpty()) { TreeNode c = stack1.pop(); stack2.push(c); if (c != null) { stack1.push(c.left); stack1.push(c.right); } } // 栈->字符串 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("["); while (!stack2.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack2.pop(); sb.append(node == null ? "null" : node.val).append(","); } sb.append("]"); return sb.toString(); } // 反序列化 public static TreeNode deserialize3(String data) { if ("[]".equals(data)) { return null; } // 去掉前后的'['和']' String[] values = data.substring(1, data.length() - 2).split(","); Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>(); for (String value : values) { stack.push(value); } return posDerial(stack); } private static TreeNode posDerial(Stack<String> stack) { String s = stack.pop(); if ("null".equals(s)) { return null; } TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(s)); root.right = posDerial(stack); root.left = posDerial(stack); return root; }
- 求某个数的开方
因为结果可以是[1, x]范围任意一个数字,所以可以利用二分查找加快执行速率

public class so { public int mySqrt(double x) { if (x <= 1) { return x; } int start = 1, end = x; while (start <= end) { double mid = (start + end) / 2.0; double tmp = mid * mid; if (Math.abs(tmp - x) < 0.00001) { return mid; } else if (tmp < mid) { end = mid; } else { start = mid; } } return end; } }
- 给出两个整数n和k,返回从1到n中取k个数字的所有可能的组合
[↵ [2,4],↵ [3,4],↵ [2,3],↵ [1,2],↵ [1,3],↵ [1,4],↵]

import java.util.ArrayList; public class Solution { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> (); public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { if (n < k) { return res; } ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer> (); // start从1开始 getAllList(n, k, 1, list); return res; } // start控制范围逐渐缩小 public void getAllList(int n, int k, int start, ArrayList<Integer> list) { if (k == 0) { res.add(new ArrayList(list)); return ; } for (int i = start;i <= n;i ++) { list.add(i); getAllList(n, k - 1, i + 1, list); list.remove(list.size() - 1); } } }
- 如果数组中元素最多允许重复两次呢?
例如:给出有序数组 A =[1,1,1,2,2,3],你给出的函数应该返回length =5, A 变为[1,1,2,2,3]

public class Solution { public int removeDuplicates(int[] A) { int n = A.length; if(n == 0) { return 0; } boolean two = false; int k = 0; for (int i = 0;i < n;i ++) { if (i < n - 1 && A[i] == A[i + 1]) { if (!two) { two = true; A[k ++] = A[i]; } } else { two = false; A[k ++] = A[i]; } } return k; } }
- 给定一个二叉树,请计算节点值之和最大的路径的节点值之和是多少。
这个路径的开始节点和结束节点可以是二叉树中的任意节点例如:给出以下的二叉树,
1↵ / ↵ 2 3
返回的结果为6。

/** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { private int sum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } find(root); return sum; } public int find(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } int a = find(root.left); int b = find(root.right); // 以该节点为子树的最大值 int res = root.val; if (a > 0) { res += a; } if (b > 0) { res += b; } if (res > sum) { sum = res; } return Math.max(a, b) > 0 ? Math.max(a, b) + root.val : root.val; // 看左右哪边大取哪边 } }
- 给出两个用字符串表示的数字,将两个数字的乘积作为字符串返回。
备注:数字可以无限大,且是非负数。

import java.util.*; public class Solution { public String multiply(String num1, String num2) { int n1 = num1.length() - 1; int n2 = num2.length() - 1; StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); int [] tmp = new int[n1 + n2 + 2]; for (int i = n1;i >=0;i --) { for (int j = n2;j >= 0;j --) { tmp[i + j + 1] += (num1.charAt(i) - '0') * (num2.charAt(j) - '0'); } } int p = 0; // 从低位开始 for (int i = tmp.length - 1;i >= 0;i --) { tmp[i] = tmp[i] + p; p = tmp[i] / 10; tmp[i] = tmp[i] % 10; } int left = 0; // 高位的零只保留一个 while (left < tmp.length - 1 && tmp[left] == 0) { left ++; } for (;left < tmp.length;left ++) { res.append(tmp[left]); } return res.toString(); } }
-
给出一个字符串s,分割s使得分割出的每一个子串都是回文串计算将字符串s分割成回文分割结果的最小切割数例如:给定字符串s="aab",返回1,因为回文分割结果["aa","b"]是切割一次生成的

import java.util.*; public class Solution { public int minCut(String s) { int n = s.length(); //dp用来保存0...i-1的分割数 int []dp = new int[n]; //m用来表示i...j是不是回文串。 boolean [][]m = new boolean [n][n]; //i从0开始构建dp for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ //每次的dp[i]构建都依赖于dp[0...i-1]的值 //刚开始我们假设这个dp都不是回文串。每个单词构成一个回文串。 dp[i] = i; for(int j = i; j >= 0; j--){ //然后判断i...j是不是回文串。 //如果s[i] == s[j] 并且i== j。单个单词必然是回文串。如‘a' //如果s[i] == s[j] i = j+1; 相邻的两个相同单词必然是回文串。如’aa' //合并前两种情况:s[i] == s[j] && j - i < 2 //如果超过两个单词,s[i] == s[j] && m[i][j] == true。如"a bcb a" // j m[j+1][i-1] i if(s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j) && (i - j <= 2 || m[j+1][i-1])){ //既然走到了这一步,就表明这个i到j是回文串。 //首先m[i][j] = true;表示i...j是回文串。 //然后在计算dp[i]的最小值。 m[j][i] = true; //如果j退到了0,表明0...i整个字符串都是回文串。不需要分割。 if(j == 0){ dp[i] = 0; }else{ //如果退到了j。那就是j...i是回文串。s[j....i]的分割次数是1, // s[0....j-1]的分割次数是dp[j - 1] // 所以dp[i]的值就是dp[i]和 dp[j - 1] + 1两者的最小值 dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[j - 1] + 1); //到这里有人会问,dp[i] 可能会比dp[j - 1]+1小吗? //回答:可能的。因为与其说是min(dp[i], dp[j - 1]+1) //不如说是:min(dp[1]+1, dp[2]+1, dp[3]+1, dp[4] + 1, dp[5]+1,...)的最小值。 // j是从0到i的。所以每都可能会更新。 } } } } return dp[n-1]; } }
- 二叉搜索树(BST)中的两个节点被错误地交换了,请在不改变树的结构的情况下恢复这棵树

/** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { private TreeNode firstMistake = null; private TreeNode secondMistake = null; private TreeNode pre = new TreeNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE); public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return ; } dfs(root); int tmp = firstMistake.val; firstMistake.val = secondMistake.val; secondMistake.val = tmp; } public void dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } dfs(root.left); if (firstMistake == null && pre.val > root.val) { firstMistake = pre; // 第一个错误的是大的点 } if (firstMistake != null && pre.val > root.val) { secondMistake = root; // 第二个错误的是小的点 } pre = root; dfs(root.right); } }
- 一个节点的左子树上节点的值都小于自身的节点值
- 一个节点的右子树上节点的值都小于自身的节点值
- 所有节点的左右子树都必须是二叉搜索树

/** * Definition for binary tree * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return true; } if (isValid(root.left, root.val, 1) && isValid(root.right, root.val, 0)) { return isValidBST(root.left) && isValidBST(root.right); } else { return false; } } public boolean isValid(TreeNode root, int val, int flag) { if (root == null) { return true; } if ((flag == 1 && root.val >= val) || (flag == 0 && root.val <= val)) { return false; } else { return isValid(root.left, val, flag) && isValid(root.right, val, flag); } } }
-
给定一个字符串S和一个字符串T,计算S中的T的不同子序列的个数。字符串的子序列是由原来的字符串删除一些字符(也可以不删除)在不改变相对位置的情况下的剩余字符(例如,"ACE"is a subsequence of"ABCDE"但是"AEC"不是)
例如:S ="rabbbit", T ="rabbit"
返回3
思路:我们需要一个二维数组dp(i)(j)来记录长度为i的字串在长度为j的母串中出现的次数,这里长度都是从头算起的,而且遍历时,保持子串长度相同,先递增母串长度,母串最长时再增加一点子串长度重头开始计算母串。
这里母串有无关字符可以忽略掉的。
首先我们先要初始化矩阵,当子串长度为0时,所有次数都是1,当母串长度为0时,所有次数都是0.当母串子串都是0长度时,次数是1(因为都是空,相等)。接着,如果子串的最后一个字母和母串的最后一个字母不同,说明新加的母串字母没有产生新的可能性,可以沿用该子串在较短母串的出现次数,所以dp(i)(j) = dp(i)(j-1)。如果子串的最后一个字母和母串的最后一个字母相同,说明新加的母串字母带来了新的可能性,我们不仅算上dp(i)(j-1),也要算上新的可能性。那么如何计算新的可能性呢,其实就是在既没有最后这个母串字母也没有最后这个子串字母时,子串出现的次数,我们相当于为所有这些可能性都添加一个新的可能。所以,这时dp(i)(j) = dp(i)(j-1) + dp(i-1)(j-1)。下图是以rabbbit和rabbit为例的矩阵示意图。计算元素值时,当末尾字母一样,实际上是左方数字加左上方数字,当不一样时,就是左方的数字
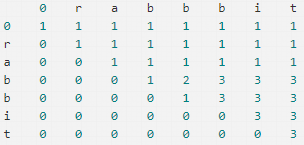

public class Solution { public int numDistinct(String S, String T) { if (S == null || T == null || S.length() < T.length()) { return 0; } int [][]res = new int[T.length() + 1][S.length() + 1]; for (int i = 0;i <= T.length();i ++) { res[i][0] = 0; } for (int j = 0;j <= S.length();j ++) { res[0][j] = 1; } for (int i = 1;i <= T.length();i ++) { for (int j = 1;j <= S.length();j ++) { if (T.charAt(i - 1) != S.charAt(j - 1)) { res[i][j] = res[i][j - 1]; } else { res[i][j] = res[i - 1][j - 1] + res[i][j - 1]; } } } return res[T.length()][S.length()]; } }




