| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | c语言程序设计 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/software-engineering-class1-2018/homework/3235 |
| 我在这个课程的目标是 | 链表,指针数组 |
| 这个作业在那个具体方面帮助我实现目标 | 链表的使用,指针数组的概念和使用 |
| 参考文献 | c语言程序设计 |
-1 计算最长的字符串长度 (15 分)
本题要求实现一个函数,用于计算有n个元素的指针数组s中最长的字符串的长度。
函数接口定义:
int max_len( char *s[], int n ); 其中n个字符串存储在s[]中,函数max_len应返回其中最长字符串的长度。
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXN 10
#define MAXS 20
int max_len( char *s[], int n );
int main()
{
int i, n;
char *string[MAXN] = {NULL};
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string[i] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*MAXS);
scanf("%s", string[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", max_len(string, n));
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例:
4
blue
yellow
red
green
输出样例:
6
实验代码:
int max_len( char *s[],int n )
{
int i,len,max=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
len=strlen(s[i]);
if(len>max)
{
max=len;
}
}
return max;
}
实验结果:
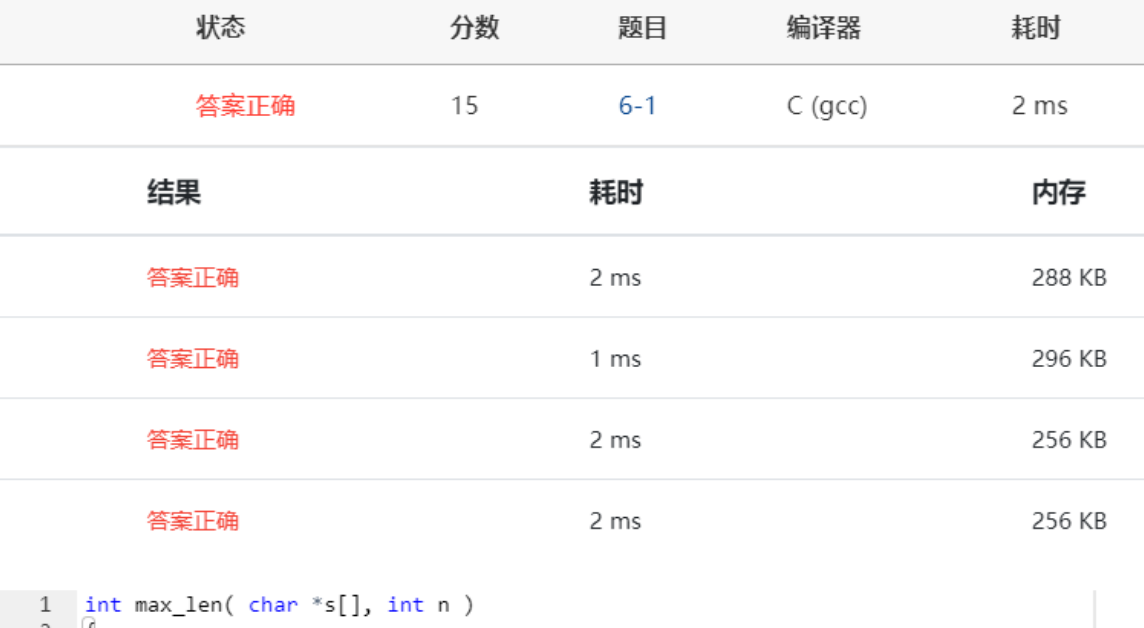
6-2 统计专业人数 (15 分)
本题要求实现一个函数,统计学生学号链表中专业为计算机的学生人数。链表结点定义如下:
struct ListNode {
char code[8];
struct ListNode *next;
};
这里学生的学号共7位数字,其中第2、3位是专业编号。计算机专业的编号为02。
函数接口定义:
int countcs( struct ListNode *head );
其中head是用户传入的学生学号链表的头指针;函数countcs统计并返回head链表中专业为计算机的学生人数。
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct ListNode {
char code[8];
struct ListNode *next;
};
struct ListNode *createlist(); /*裁判实现,细节不表*/
int countcs( struct ListNode *head );
int main()
{
struct ListNode *head;
head = createlist();
printf("%d\n", countcs(head));
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例:
1021202
2022310
8102134
1030912
3110203
4021205
#
输出样例:
3
实验代码:
int countcs(struct ListNode *head)
{
int count=0;
while(head)
{
if(head->code[1]=='0'&&head->code[2]=='2')
{
count++;
}
head=head->next;
}
return count;
}
实验结果:

6-3 删除单链表偶数节点 (20 分)
本题要求实现两个函数,分别将读入的数据存储为单链表、将链表中偶数值的结点删除。链表结点定义如下:
struct ListNode {
int data;
struct ListNode *next;
};
函数接口定义:
struct ListNode *createlist();
struct ListNode *deleteeven( struct ListNode *head );
函数createlist从标准输入读入一系列正整数,按照读入顺序建立单链表。当读到−1时表示输入结束,函数应返回指向单链表头结点的指针。
函数deleteeven将单链表head中偶数值的结点删除,返回结果链表的头指针。
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct ListNode {
int data;
struct ListNode *next;
};
struct ListNode *createlist();
struct ListNode *deleteeven( struct ListNode *head );
void printlist( struct ListNode *head )
{
struct ListNode *p = head;
while (p) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
struct ListNode *head;
head = createlist();
head = deleteeven(head);
printlist(head);
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例:
1 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 -1
输出样例:
1 3 5 7
实验代码:
struct ListNode *createlist()
{
struct ListNode *head,*p;
int n;
head=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
p=head;
head->next=NULL;
while(1)
{
p->next=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n==-1)
{
break;
}
p=p->next;
p-> data=n;
p->next=NULL;
}
head=head->next;
return (head);
}
struct ListNode *deleteeven(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode *p,*q;
if(head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
p=head;
q=p->next;
while(q!=NULL)
{
if(q->data%2==0)
{
p->next=q->next;
free(q);
q=p->next;
}
else
{
p=p->next;
q=p->next;
}
}
if(head->data%2==0)
{
head=head->next;
}
return (head);
}
实验结果:
学习总结:
| 周/日期 | 这周所花的时间 | 代码行 | 学到的知识点简介 | 目前比较迷惑的问题 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3-3.9 | 3h | 32 | 如何在Dev | C++中写入文件并打开执行命令 |
| 3.10-3.16 | 5h | 75 | 用指针打开文件 | 二维数组 |
| 3.17-3.23 | 6h | 112 | 选择排序 | 冒泡排序的方法 |
| 3.24-3.30 | 5h | 97 | 冒泡排序以及字符串使用 | 冒泡排序与选择排序的区 |
| 4.2-4.6 | 3h | 40 | 指针返回多个函数的值 | *和&的变化和指针传变量地址的问题 |
| 4.6-4.14 | 5h | 201 | 冒泡排顺序 | 指针和数组之间的关系 |
| 4.14-4.19 | 9h | 311 | 字符串 | 字符串使用 |
| 4.19-4.26 | 3h | 154 | 结构体 | 结构体的使用 |
| 5.3-5.10 | 2h | 52 | 递归函数 | 递归函数的使用 |
| 5.10-5.17 | 2h | 205 | 链表,指针数组 | 链表,指针数组使用 |
结对经验:
懵逼树下又多了一个人
心德:
感觉学的东西好像处理一些难的东西派不上用场



