引入
回顾requests实现数据爬取的流程
- 指定url
- 基于requests模块发起请求
- 获取响应对象中的数据
- 进行持久化存储
其实,在上述流程中还需要较为重要的一步,就是在持久化存储之前需要进行指定数据解析。因为大多数情况下的需求,我们都会指定去使用聚焦爬虫,也就是爬取页面中指定部分的数据值,而不是整个页面的数据。因此,下面会详细介绍讲解三种聚焦爬虫中的数据解析方式。至此,数据爬取的流程可以修改为:
- 指定url
- 基于requests模块发起请求
- 获取响应中的数据
- 数据解析
- 进行持久化存储
目录:
知识点回顾
- requests模块的使用流程
- requests模块请求方法参数的作用
- 抓包工具抓取ajax的数据包
一.正则解析
- 常用正则表达式回顾:
![]() 常用正则表达式
常用正则表达式单字符: . : 除换行以外所有字符 [] :[aoe] [a-w] 匹配集合中任意一个字符 \d :数字 [0-9] \D : 非数字 \w :数字、字母、下划线、中文 \W : 非\w \s :所有的空白字符包,括空格、制表符、换页符等等。等价于 [ \f\n\r\t\v]。 \S : 非空白 数量修饰: * : 任意多次 >=0 + : 至少1次 >=1 ? : 可有可无 0次或者1次 {m} :固定m次 hello{3,} {m,} :至少m次 {m,n} :m-n次 边界: $ : 以某某结尾 ^ : 以某某开头 分组: (ab) 贪婪模式: .* 非贪婪(惰性)模式: .*? re.I : 忽略大小写 re.M :多行匹配 re.S :单行匹配 re.sub(正则表达式, 替换内容, 字符串)
- 回顾练习:
![]() 正则练习
正则练习import re #提取出python key="javapythonc++php" re.findall('python',key)[0] ##################################################################### #提取出hello world key="<html><h1>hello world<h1></html>" re.findall('<h1>(.*)<h1>',key)[0] ##################################################################### #提取170 string = '我喜欢身高为170的女孩' re.findall('\d+',string) ##################################################################### #提取出http://和https:// key='http://www.baidu.com and https://boob.com' re.findall('https?://',key) ##################################################################### #提取出hello key='lalala<hTml>hello</HtMl>hahah' #输出<hTml>hello</HtMl> re.findall('<[Hh][Tt][mM][lL]>(.*)</[Hh][Tt][mM][lL]>',key) ##################################################################### #提取出hit. key='bobo@hit.edu.com'#想要匹配到hit. re.findall('h.*?\.',key) ##################################################################### #匹配sas和saas key='saas and sas and saaas' re.findall('sa{1,2}s',key) ##################################################################### #匹配出i开头的行 string = '''fall in love with you i love you very much i love she i love her''' re.findall('^i.*',string,re.M) ##################################################################### #匹配全部行 string1 = """<div>静夜思 窗前明月光 疑是地上霜 举头望明月 低头思故乡 </div>""" re.findall('.*',string1,re.S)
- 项目需求:爬取糗事百科指定页面的糗图,并将其保存到指定文件夹中
![]() View Code
View Codeimport re import os import time import urllib import requests if not os.path.exists('../qiushi/'): os.mkdir('../qiushi/') headers = { 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_0) AppleWebKit' '/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/69.0.3497.100 Safari/537.36', } url = 'https://www.qiushibaike.com/imgrank/page/%s' # https://www.qiushibaike.com/imgrank/page/2/ # <div class="thumb"> # <a href="/article/123876542" target="_blank"> # <img src="//pic.qiushibaike.com/system/pictures/12387/123876542/medium/JYBSVJJRC960RX8N.jpg" alt="糗事#123876542" class="illustration" width="100%" height="auto"> # </a> # </div> p_s = int(input('enter a start page:')) p_e = int(input('enter a end page:')) for page in range(p_s, p_e + 1): p_url = url % page if page == 1: p_url = url p_res = requests.get(p_url, headers=headers).text img_url_list = re.findall('<div class="thumb">.*?<img src="(.*?)".*?</div>', p_res, re.S) print(img_url_list) for img_url in img_url_list: img_url_n = 'http:' + img_url img_name = img_url.split('/')[-1] img_path = '../qiushi/' + img_name urllib.request.urlretrieve(url=img_url_n, filename=img_path) print(img_name, 'download success') time.sleep(1) print('over')
![]() View Code
View Code#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import requests import re import os if __name__ == "__main__": url = 'https://www.qiushibaike.com/pic/%s/' headers={ 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/69.0.3497.100 Safari/537.36', } #指定起始也结束页码 page_start = int(input('enter start page:')) page_end = int(input('enter end page:')) #创建文件夹 if not os.path.exists('images'): os.mkdir('images') #循环解析且下载指定页码中的图片数据 for page in range(page_start,page_end+1): print('正在下载第%d页图片'%page) new_url = format(url % page) response = requests.get(url=new_url,headers=headers) #解析response中的图片链接 e = '<div class="thumb">.*?<img src="(.*?)".*?>.*?</div>' pa = re.compile(e,re.S) image_urls = pa.findall(response.text) #循环下载该页码下所有的图片数据 for image_url in image_urls: image_url = 'https:' + image_url image_name = image_url.split('/')[-1] image_path = 'images/'+image_name image_data = requests.get(url=image_url,headers=headers).content with open(image_path,'wb') as fp: fp.write(image_data)
二.Xpath解析
Chrome插件:XPath Helper
Firefox插件:Try XPath

路径表达式 描述 /bookstore/book[1] 选取bookstore下的第一个子元素 /bookstore/book[last()] 选取bookstore下的倒数第二个book元素。 bookstore/book[position()<3] 选取bookstore下前面两个子元素。 //book[@price] 选取拥有price属性的book元素 //book[@price=10] 选取所有属性price等于10的book元素 通配符 *表示通配符。 通配符 描述 示例 结果 * 匹配任意节点 /bookstore/* 选取bookstore下的所有子元素。 @* 匹配节点中的任何属性 //book[@*] 选取所有带有属性的book元素。 选取多个路径: 通过在路径表达式中使用“|”运算符,可以选取若干个路径。 示例如下: //bookstore/book | //book/title # 选取所有book元素以及book元素下所有的title元素 contains 某个属性包含了多个值,可以用contains函数 //div[contains(@class,'job_detail')] html = ''' <div id='test1'>aaa</div> <div id='test2'>bbb</div> <div id='test3'>ccc</div> ''' div_list = tree.xpath('//div[starts-with(@id,"test")]/text()') # ['aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc'] html = ''' <div id='test'>aaa<span>bbb</span></div> ''' div_str = tree.xpath('string(//div[@id="test"])')[0] # 'aaa bbb'
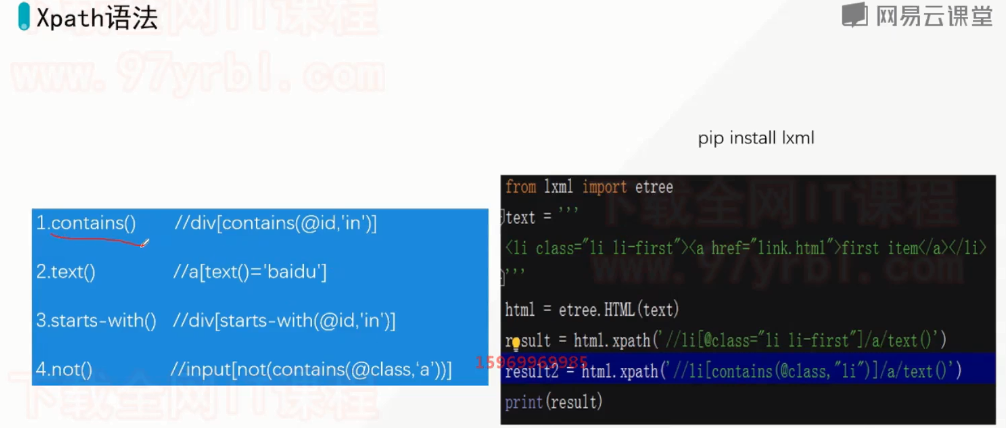

- 测试页面数据
![]() View Code
View Code<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>测试bs4</title> </head> <body> <div> <p>百里守约</p> </div> <div class="song"> <p>李清照</p> <p>王安石</p> <p>苏轼</p> <p>柳宗元</p> <a href="http://www.song.com/" title="赵匡胤" target="_self"> <span>this is span</span> 宋朝是最强大的王朝,不是军队的强大,而是经济很强大,国民都很有钱</a> <a href="" class="du">总为浮云能蔽日,长安不见使人愁</a> <img src="http://www.baidu.com/meinv.jpg" alt="" /> </div> <div class="tang"> <ul> <li><a href="http://www.baidu.com" title="qing">清明时节雨纷纷,路上行人欲断魂,借问酒家何处有,牧童遥指杏花村</a></li> <li><a href="http://www.163.com" title="qin">秦时明月汉时关,万里长征人未还,但使龙城飞将在,不教胡马度阴山</a></li> <li><a href="http://www.126.com" alt="qi">岐王宅里寻常见,崔九堂前几度闻,正是江南好风景,落花时节又逢君</a></li> <li><a href="http://www.sina.com" class="du">杜甫</a></li> <li><a href="http://www.dudu.com" class="du">杜牧</a></li> <li><b>杜小月</b></li> <li><i>度蜜月</i></li> <li><a href="http://www.haha.com" id="feng">凤凰台上凤凰游,凤去台空江自流,吴宫花草埋幽径,晋代衣冠成古丘</a></li> </ul> </div> </body> </html>
- 常用xpath表达式
![]() 常用xpath表达式
常用xpath表达式属性定位: #找到class属性值为song的div标签 //div[@class="song"] 层级&索引定位: #找到class属性值为tang的div的直系子标签ul下的第二个子标签li下的直系子标签a //div[@class="tang"]/ul/li[2]/a 逻辑运算: #找到href属性值为空且class属性值为du的a标签 //a[@href="" and @class="du"] #| 或 //li_list = tree.xpath('//div[@class="bottom"]/ul/li | //div[@class="bottom"]/ul/div[2]/li') 模糊匹配: //div[contains(@class, "ng")] //div[starts-with(@class, "ta")] 取文本: # /表示获取某个标签下的文本内容 # //表示获取某个标签下的文本内容和所有子标签下的文本内容 //div[@class="song"]/p[1]/text() //div[@class="tang"]//text() 取属性: //div[@class="tang"]//li[2]/a/@href
- 代码中使用xpath表达式进行数据解析:
1.下载:pip install lxml
2.导包:from lxml import etree
3.将html文档或者xml文档转换成一个etree对象,然后调用对象中的方法查找指定的节点
3.1 本地文件:tree = etree.parse(文件名)
tree.xpath("xpath表达式")
3.2 网络数据:tree = etree.HTML(网页内容字符串)
tree.xpath("xpath表达式")- 安装xpath插件在浏览器中对xpath表达式进行验证:可以在插件中直接执行xpath表达式
-
将xpath插件拖动到谷歌浏览器拓展程序(更多工具)中,安装成功
-
启动和关闭插件 ctrl + shift + x
-
-
项目需求:获取好段子中段子的内容和作者 http://www.haoduanzi.com
![]() View Code
View Codeimport requests from lxml import etree headers = { 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko)Chrome/72.0.3626.119 Safari/537.36', 'Connection': 'close' # 当请求成功后,马上断开该次请求(及时释放请求池中的资源) } url = 'http://www.haoduanzi.com/category/?1-%s.html' page_start = int(input('enter a start num:')) page_end = int(input('enter a end num:')) title_list = [] content_list = [] for page in range(page_start, page_end+1): new_url = url % page page_res_text = requests.get(url=new_url, headers=headers).text tree = etree.HTML(page_res_text) title_list.extend(tree.xpath('//div[@id="LR"]//span[@class="s1"]/text()')) content = tree.xpath('//*[@id="LR"]/div/div[2]/ul/li[1]/div[2]/a//text()') content_list.append(content) print(page, 'download success') print('over') print(title_list) print(content_list)
![]() View Code
View Codefrom lxml import etree import requests url='http://www.haoduanzi.com/category-10_2.html' headers = { 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/66.0.3359.181 Safari/537.36', } url_content=requests.get(url,headers=headers).text #使用xpath对url_conten进行解析 #使用xpath解析从网络上获取的数据 tree=etree.HTML(url_content) #解析获取当页所有段子的标题 title_list=tree.xpath('//div[@class="log cate10 auth1"]/h3/a/text()') ele_div_list=tree.xpath('//div[@class="log cate10 auth1"]') text_list=[] #最终会存储12个段子的文本内容 for ele in ele_div_list: #段子的文本内容(是存放在list列表中) text_list=ele.xpath('./div[@class="cont"]//text()') #list列表中的文本内容全部提取到一个字符串中 text_str=str(text_list) #字符串形式的文本内容防止到all_text列表中 text_list.append(text_str) print(title_list) print(text_list)

import requests from lxml import etree url = 'https://linfen.58.com/lfyicheng/ershoufang/?PGTID=0d30000c-0162-57c4-242c-86665297c246&ClickID=1' headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko)Chrome/72.0.3626.119 Safari/537.36'} page_text = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers).text tree = etree.HTML(page_text) li_list = tree.xpath('//ul[@class="house-list-wrap"]/li') fp = open('58.csv', 'w', encoding='utf-8') for li in li_list: title = li.xpath('./div[2]/h2/a/text()')[0] price = li.xpath('./div[3]//text()') price = ''.join(price) fp.write(title+':'+price+'\n') fp.close() print('over')

import random import requests from lxml import etree header_list = [ # 遨游 "Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT 5.1; Maxthon 2.0)", # 火狐 "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv:2.0.1) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/4.0.1", # 谷歌 "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_7_0) AppleWebKit/535.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/17.0.963.56 Safari/535.11" ] url = 'http://iyayatv.net/vodshow/10--------%d---.html' page_start = int(input('enter a start page:')) page_end = int(input('enter a end page:')) # 每行显示电影名个数 line_movie_num = 5 # iyaya.txt中每个电影名+间距 line_member = 13 # 名字过长时限制显示的字数 limit_member = 12 with open('./iyaya.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as fp: for page in range(page_start, page_end+1): page_url = url % page ua = random.choice(header_list) headers = { 'User-Agent': ua, 'Connection': 'close', # 当请求成功后,马上断开该次请求(及时释放请求池中的资源) } page_text = requests.get(url=page_url, headers=headers).text tree = etree.HTML(page_text) li_list = tree.xpath('//div[@class="pannel clearfix"]/ul[@class="vodlist vodlist_wi author*qq3626/95/000 clearfix"]/li') i = 1 fp.write(str(page) + '\n') for li in li_list: movie_name = li.xpath('./div/p/a/text()')[0] # movie_name = movie_name.encode('iso-8859-1').decode('utf-8') if len(movie_name) < line_member: d = 0 for c in movie_name: if c.isdigit() is True or 65 <= ord(c) <= 90 or 97 <= ord(c) <= 122: d += 1 fp.write(movie_name + ' '*(d+2*(line_member-len(movie_name)))) else: w = 0 for e in movie_name[0:limit_member]: if e.isdigit() is True or 65 <= ord(e) <= 90 or 97 <= ord(e) <= 122: w += 1 fp.write(movie_name[0:limit_member] + ' '*((line_member-limit_member)*2+w)) if i % line_movie_num == 0: fp.write('\n') i += 1 fp.write('\n') print('第%d页下载完成' % page) print('over')

import requests import os import urllib from lxml import etree url = 'http://pic.netbian.com/' headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko)Chrome/72.0.3626.119 Safari/537.36'} if not os.path.exists('./4kimgs'): os.mkdir('./4kimgs') response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers) # 解决中文乱码的一般方式,如果不管用,则使用万能方式 # response.encoding = 'utf-8' response_text = response.text tree = etree.HTML(response_text) img_list = tree.xpath('//div[@class="slist"]/ul/li') for img in img_list: img_name = img.xpath('./a/b/text()')[0] + '.jpg' # 解决中文乱码的万能方式 img_name = img_name.encode('iso-8859-1').decode('gbk') img_url = 'http://pic.netbian.com/' + img.xpath('.//img/@src')[0] img_path = './4kimgs/' + img_name print('start download', img_path) urllib.request.urlretrieve(url=img_url, filename=img_path) print('end download', img_path) print('over')

import os import urllib import requests from lxml import etree from fake_useragent import UserAgent if not os.path.exists('./4k'): os.mkdir('./4k') ua = UserAgent(verify_ssl=False,use_cache_server=False).random headers = { 'User-Agent': ua, 'Connection': 'close', # 当请求成功后,马上断开该次请求(及时释放请求池中的资源) } url = 'http://pic.netbian.com/index_%d.html' page_start = int(input('enter a start page:')) page_end = int(input('enter a end page:')) for page in range(page_start, page_end+1): page_url = url % page if page == 1: page_url = 'http://pic.netbian.com/index.html' page_text = requests.get(url=page_url, headers=headers).text tree = etree.HTML(page_text) li_list = tree.xpath('//div[@id="main"]//ul[@class="clearfix"]/li') for li in li_list: img_name = li.xpath('./a/b/text()')[0] + '.jpg' img_name = img_name.encode('iso-8859-1').decode('gbk') img_path = './4k/' + img_name img_url = 'http://pic.netbian.com/' + li.xpath('.//img/@src')[0] urllib.request.urlretrieve(url=img_url, filename=img_path) print(page, 'download success') print('over')

一般方式(如果不管用,则用万能方式): response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers) response.encoding = 'utf-8' # 一般方式 response_text = response.text 万能方式: img_name = img.xpath('./a/b/text()')[0] + '.jpg' img_name = img_name.encode('iso-8859-1').decode('gbk') # 万能方式
【重点】下载煎蛋网中的图片数据:http://jandan.net/ooxx

import requests from lxml import etree from fake_useragent import UserAgent import base64 import urllib.request url = 'http://jandan.net/ooxx' ua = UserAgent(verify_ssl=False,use_cache_server=False).random headers = { 'User-Agent':ua } page_text = requests.get(url=url,headers=headers).text #查看页面源码:发现所有图片的src值都是一样的。 #简单观察会发现每张图片加载都是通过jandan_load_img(this)这个js函数实现的。 #在该函数后面还有一个class值为img-hash的标签,里面存储的是一组hash值,该值就是加密后的img地址 #加密就是通过js函数实现的,所以分析js函数,获知加密方式,然后进行解密。 #通过抓包工具抓取起始url的数据包,在数据包中全局搜索js函数名(jandan_load_img),然后分析该函数实现加密的方式。 #在该js函数中发现有一个方法调用,该方法就是加密方式,对该方法进行搜索 #搜索到的方法中会发现base64和md5等字样,md5是不可逆的所以优先考虑使用base64解密 #print(page_text) tree = etree.HTML(page_text) #在抓包工具的数据包响应对象对应的页面中进行xpath的编写,而不是在浏览器页面中。 #获取了加密的图片url数据 imgCode_list = tree.xpath('//span[@class="img-hash"]/text()') imgUrl_list = [] for url in imgCode_list: #base64.b64decode(url)为byte类型,需要转成str img_url = 'http:'+base64.b64decode(url).decode() imgUrl_list.append(img_url) for url in imgUrl_list: filePath = url.split('/')[-1] urllib.request.urlretrieve(url=url,filename=filePath) print(filePath+'下载成功')

import requests import os import urllib from lxml import etree url = 'http://jandan.net/ooxx' headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko)Chrome/72.0.3626.119 Safari/537.36'} if not os.path.exists('./jandanimgs'): os.mkdir('./jandanimgs') response_text = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers).text tree = etree.HTML(response_text) img_src_list = tree.xpath('//div[@id="comments"]/ol/li/div/div/div[2]/p/img/@src') for img_src in img_src_list: img_name = img_src.split('/')[-1] img_path = './jandanimgs/' + img_name + '.jpg' img_url = 'http:' + img_src urllib.request.urlretrieve(url=img_url, filename=img_path) print('success download', img_path) print('over')

import requests from lxml import etree import base64 page_text = requests.get(url=url,headers=headers).text tree = etree.HTML(page_text) imgCode_list = tree.xpath('//span[@class="img-hash"]/text()') imgUrl_list = [] for url in imgCode_list: #base64.b64decode(url)为byte类型,需要转成str img_url = 'http:' + base64.b64decode(url).decode() # base64加密 破解方法 imgUrl_list.append(img_url)
爬取 https://www.aqistudy.cn/historydata/ 中 所有的城市名称(注意:xpath 管道符| 的使用):

# 解析所有的城市名称 import requests import os import random from lxml import etree headers = { 'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko)Chrome/72.0.3626.119 Safari/537.36', 'Connection':'close' # 当请求成功后,马上断开该次请求(及时释放请求池中的资源) } url = 'https://www.aqistudy.cn/historydata/' page_text = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers).text tree = etree.HTML(page_text) li_list = tree.xpath('//div[@class="bottom"]/ul/li | //div[@class="bottom"]/ul/div[2]/li') fp = open('./allcityss.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') for li in li_list: city_name = li.xpath('./a/text()')[0] fp.write(city_name+' ') fp.close() print('over')

import requests from lxml import etree from fake_useragent import UserAgent ua = UserAgent(verify_ssl=False,use_cache_server=False).random headers = { 'User-Agent': ua, 'Connection': 'close', # 当请求成功后,马上断开该次请求(及时释放请求池中的资源) } url = 'https://www.aqistudy.cn/historydata/' res_text = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers).text tree = etree.HTML(res_text) ul_list = tree.xpath('//div[@class="all"]/div[@class="bottom"]/ul') with open('./citys.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: for ul in ul_list: city_cap = ul.xpath('./div/b/text()')[0] city_list = [] li_list = ul.xpath('./div[2]/li') for li in li_list: city_list.append(li.xpath('./a/text()')[0]) city_str = ','.join(city_list) f.write(city_cap + '\n' + city_str + '\n') print('over')
爬取 站长素材 中的 高清图片(注意:图片懒加载,注意懒加载的img标签的src名字):

# 爬取 站长素材 的高清图片(图片懒加载) import requests import os import urllib from lxml import etree url = 'http://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/ribenmeinv.html' headers = { 'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko)Chrome/72.0.3626.119 Safari/537.36', 'Connection':'close' # 当请求成功后,马上断开该次请求(及时释放请求池中的资源) } if not os.path.exists('./zhanzhangimgs'): os.mkdir('./zhanzhangimgs') response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers) response.encoding = 'utf8' response_text = response.text tree = etree.HTML(response_text) img_list = tree.xpath('//div[@id="container"]/div/div/a/img') for img in img_list: img_name = img.xpath('./@alt')[0] img_path = './zhanzhangimgs/' + img_name + '.jpg' img_url = img.xpath('./@src2')[0] urllib.request.urlretrieve(url=img_url, filename=img_path) print('success download', img_path) print('over')
爬取 站长素材中 的 免费简历模板(注意:1、解决中文乱码问题; 2、设置请求头'Connection':'close' 及时释放请求资源 3、在新的页面创建新的tree来使用):

import requests import os import random from lxml import etree headers = { 'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko)Chrome/72.0.3626.119 Safari/537.36', 'Connection':'close' # 当请求成功后,马上断开该次请求(及时释放请求池中的资源) } if not os.path.exists('./jianli'): os.mkdir('./jianli') url = 'http://sc.chinaz.com/jianli/free_%d.html' for page in range(2, 5): if page == 1: new_url = 'http://sc.chinaz.com/jianli/free.html' else: new_url = format(url % page) response = requests.get(url=new_url, headers=headers) response.encoding = 'utf-8' page_text = response.text tree = etree.HTML(page_text) div_list = tree.xpath('//div[@id="container"]/div') for div in div_list: detail_url = div.xpath('./a/@href')[0] name = div.xpath('./a/img/@alt')[0] detail_page = requests.get(url=detail_url, headers=headers).text detail_tree = etree.HTML(detail_page) download_list = detail_tree.xpath('//div[@class="clearfix mt20 downlist"]/ul/li/a/@href') download_url = random.choice(download_list) path = './jianli/' + name + '.rar' data = requests.get(url=download_url, headers=headers).content with open(path, 'wb') as fp: fp.write(data) print(path, 'download success') print('over')

import os import random import requests from lxml import etree from fake_useragent import UserAgent if not os.path.exists('./jianli'): os.mkdir('./jianli') ua = UserAgent(verify_ssl=False,use_cache_server=False).random headers = { 'User-Agent': ua, 'Connection': 'close', # 当请求成功后,马上断开该次请求(及时释放请求池中的资源) } url = 'https://sc.chinaz.com/jianli/index_%d.html' page_start = int(input('enter a start page:')) page_end = int(input('enter a end page:')) num = 1 for page in range(page_start, page_end+1): page_url = url % page if page == 1: page_url = 'https://sc.chinaz.com/jianli/index.html' page_text = requests.get(url=page_url, headers=headers).text tree = etree.HTML(page_text) a_list = tree.xpath('//div[@id="main"]//p/a') for a in a_list: a_name = a.xpath('./text()')[0] + '.rar' a_name = a_name.encode('iso-8859-1').decode('utf-8') # 解决中文乱码问题 a_path = './jianli/' + a_name a_url = 'https:' + a.xpath('./@href')[0] a_page_text = requests.get(url=a_url, headers=headers).text a_tree = etree.HTML(a_page_text) # 跳过付费模板,选择免费模板下载 if a_tree.xpath('//div[@id="down"]'): download_list = a_tree.xpath('//div[@id="down"]//ul/li/a/@href') download_choice = random.choice(download_list) file_content = requests.get(url=download_choice, headers=headers).content with open(a_path, 'wb') as f: f.write(file_content) print(a_path, 'download success') print('page ' + str(num) + ' download success') num += 1 print('over')

三.BeautifulSoup解析

BeautifulSoup4库 和 lxml 一样,Beautiful Soup 也是一个HTML/XML的解析器,主要的功能也是如何解析和提取 HTML/XML 数据。 lxml 只会局部遍历,而Beautiful Soup 是基于HTML DOM(Document Object Model)的,会载入整个文档,解析整个DOM树,因此时间和内存开销都会大很多,所以性能要低于lxml。 BeautifulSoup 用来解析 HTML 比较简单,API非常人性化,支持CSS选择器、Python标准库中的HTML解析器,也支持 lxml 的 XML解析器。 Beautiful Soup 3 目前已经停止开发,推荐现在的项目使用Beautiful Soup 4。 安装和文档: 安装:pip install bs4。 中文文档:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/index.zh.html 几大解析工具对比: 解析工具 解析速度 使用难度 BeautifulSoup 最慢 最简单 lxml 快 简单 正则 最快 最难 简单使用: from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ #创建 Beautiful Soup 对象 # 使用lxml来进行解析 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"lxml") print(soup.prettify()) 四个常用的对象: Beautiful Soup将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是Python对象,所有对象可以归纳为4种: Tag NavigatableString BeautifulSoup Comment 1. Tag: Tag 通俗点讲就是 HTML 中的一个个标签。示例代码如下: from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ #创建 Beautiful Soup 对象 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') print soup.title # <title>The Dormouse's story</title> print soup.head # <head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> print soup.a # <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a> print soup.p # <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> print type(soup.p) # <class 'bs4.element.Tag'> 我们可以利用 soup 加标签名轻松地获取这些标签的内容,这些对象的类型是bs4.element.Tag。但是注意,它查找的是在所有内容中的第一个符合要求的标签。如果要查询所有的标签,后面会进行介绍。 对于Tag,它有两个重要的属性,分别是name和attrs。示例代码如下: print soup.name # [document] #soup 对象本身比较特殊,它的 name 即为 [document] print soup.head.name # head #对于其他内部标签,输出的值便为标签本身的名称 print soup.p.attrs # {'class': ['title'], 'name': 'dromouse'} # 在这里,我们把 p 标签的所有属性打印输出了出来,得到的类型是一个字典。 print soup.p['class'] # soup.p.get('class') # ['title'] #还可以利用get方法,传入属性的名称,二者是等价的 soup.p['class'] = "newClass" print soup.p # 可以对这些属性和内容等等进行修改 # <p class="newClass" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> 2. NavigableString: 如果拿到标签后,还想获取标签中的内容。那么可以通过tag.string获取标签中的文字。示例代码如下: print soup.p.string # The Dormouse's story print type(soup.p.string) # <class 'bs4.element.NavigableString'>thon 3. BeautifulSoup: BeautifulSoup 对象表示的是一个文档的全部内容.大部分时候,可以把它当作 Tag 对象,它支持 遍历文档树 和 搜索文档树 中描述的大部分的方法. 因为 BeautifulSoup 对象并不是真正的HTML或XML的tag,所以它没有name和attribute属性.但有时查看它的 .name 属性是很方便的,所以 BeautifulSoup 对象包含了一个值为 “[document]” 的特殊属性 .name soup.name # '[document]' 4. Comment: Tag , NavigableString , BeautifulSoup 几乎覆盖了html和xml中的所有内容,但是还有一些特殊对象.容易让人担心的内容是文档的注释部分: markup = "<b><!--Hey, buddy. Want to buy a used parser?--></b>" soup = BeautifulSoup(markup) comment = soup.b.string type(comment) # <class 'bs4.element.Comment'> Comment 对象是一个特殊类型的 NavigableString 对象: comment # 'Hey, buddy. Want to buy a used parser' 遍历文档树: 1. contents和children: html_doc = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'lxml') head_tag = soup.head # 返回所有子节点的列表 print(head_tag.contents) # 返回所有子节点的迭代器 for child in head_tag.children: print(child) 2. strings 和 stripped_strings 如果tag中包含多个字符串 [2] ,可以使用 .strings 来循环获取: for string in soup.strings: print(repr(string)) # u"The Dormouse's story" # u'\n\n' # u"The Dormouse's story" # u'\n\n' # u'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n' # u'Elsie' # u',\n' # u'Lacie' # u' and\n' # u'Tillie' # u';\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.' # u'\n\n' # u'...' # u'\n' 输出的字符串中可能包含了很多空格或空行,使用 .stripped_strings 可以去除多余空白内容: for string in soup.stripped_strings: print(repr(string)) # u"The Dormouse's story" # u"The Dormouse's story" # u'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were' # u'Elsie' # u',' # u'Lacie' # u'and' # u'Tillie' # u';\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.' # u'...' 搜索文档树: 1. find和find_all方法: 搜索文档树,一般用得比较多的就是两个方法,一个是find,一个是find_all。find方法是找到第一个满足条件的标签后就立即返回,只返回一个元素。find_all方法是把所有满足条件的标签都选到,然后返回回去。使用这两个方法,最常用的用法是出入name以及attr参数找出符合要求的标签。 soup.find_all("a",attrs={"id":"link2"}) 或者是直接传入属性的的名字作为关键字参数: soup.find_all("a",id='link2') 2. select方法: 使用以上方法可以方便的找出元素。但有时候使用css选择器的方式可以更加的方便。使用css选择器的语法,应该使用select方法。以下列出几种常用的css选择器方法: (1)通过标签名查找: print(soup.select('a')) (2)通过类名查找: 通过类名,则应该在类的前面加一个.。比如要查找class=sister的标签。示例代码如下: print(soup.select('.sister')) (3)通过id查找: 通过id查找,应该在id的名字前面加一个#号。示例代码如下: print(soup.select("#link1")) (4)组合查找: 组合查找即和写 class 文件时,标签名与类名、id名进行的组合原理是一样的,例如查找 p 标签中,id 等于 link1的内容,二者需要用空格分开: print(soup.select("p #link1")) 直接子标签查找,则使用 > 分隔: print(soup.select("head > title")) (5)通过属性查找: 查找时还可以加入属性元素,属性需要用中括号括起来,注意属性和标签属于同一节点,所以中间不能加空格,否则会无法匹配到。示例代码如下: print(soup.select('a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]')) (6)获取内容 以上的 select 方法返回的结果都是列表形式,可以遍历形式输出,然后用 get_text() 方法来获取它的内容。 soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print type(soup.select('title')) print soup.select('title')[0].get_text() for title in soup.select('title'): print title.get_text()

解析原理: 1.将即将要进行解析的源码加载到bs对象 2.调用bs对象中相关的方法或属性进行源码中的相关标签的定位 3.将定位到的标签之间存在的文本或者属性值获取
- 环境安装
![]() 环境安装
环境安装- 需要将pip源设置为国内源,阿里源、豆瓣源、网易源等 - windows (1)打开文件资源管理器(文件夹地址栏中) (2)地址栏上面输入 %appdata% (3)在这里面新建一个文件夹 pip (4)在pip文件夹里面新建一个文件叫做 pip.ini ,内容写如下即可 [global] timeout = 6000 index-url = https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ trusted-host = mirrors.aliyun.com - linux (1)cd ~ (2)mkdir ~/.pip (3)vi ~/.pip/pip.conf (4)编辑内容,和windows一模一样 - 需要安装:pip install bs4 bs4在使用时候需要一个第三方库,把这个库也安装一下 pip install lxml
- 基础使用
![]() 基础使用
基础使用使用流程: - 导包:from bs4 import BeautifulSoup - 使用方式:可以将一个html文档,转化为BeautifulSoup对象,然后通过对象的方法或者属性去查找指定的节点内容 (1)转化本地文件: - soup = BeautifulSoup(open('本地文件'), 'lxml') (2)转化网络文件: - soup = BeautifulSoup('字符串类型或者字节类型', 'lxml') (3)打印soup对象显示内容为html文件中的内容 soup.prettify() # 格式化输出 基础巩固: (1)根据标签名查找 - soup.a 只能找到第一个符合要求的标签 (2)获取属性 - soup.a.attrs 获取a所有的属性和属性值,返回一个字典 - soup.a.attrs['href'] 获取href属性 - soup.a['href'] 也可简写为这种形式 (3)获取内容 - soup.a.string - soup.a.text - soup.a.get_text() 【注意】如果标签还有标签,那么string获取到的结果为None,而其它两个,可以获取文本内容 (4)find:找到第一个符合要求的标签 - soup.find('a') 找到第一个符合要求的 - soup.find('a', title="xxx") - soup.find('a', alt="xxx") - soup.find('a', class_="xxx") - soup.find('a', id="xxx") (5)find_all:找到所有符合要求的标签 - soup.find_all('a') - soup.find_all(['a','b']) 找到所有的a和b标签 - soup.find_all('a', limit=2) 限制前两个 (6)根据选择器选择指定的内容 select:soup.select('#feng') - 常见的选择器:标签选择器(a)、类选择器(.)、id选择器(#)、层级选择器 - 层级选择器: div .dudu #lala .meme .xixi 下面好多级 div > p > a > .lala 只能是下面一级 【注意】select选择器返回永远是列表,需要通过下标提取指定的对象
- 需求:使用bs4实现将诗词名句网站中三国演义小说的每一章的内容爬去到本地磁盘进行存储 http://www.shicimingju.com/book/sanguoyanyi.html
![]() View Code
View Code#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup headers={ 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/69.0.3497.100 Safari/537.36', } def parse_content(url): # 获取标题正文页数据 page_text = requests.get(url,headers=headers).text soup = BeautifulSoup(page_text,'lxml') # 解析获得标签 ele = soup.find('div',class_='chapter_content') content = ele.text # 获取标签中的数据值 return content if __name__ == "__main__": url = 'http://www.shicimingju.com/book/sanguoyanyi.html' reponse = requests.get(url=url,headers=headers) page_text = reponse.text # 创建soup对象 soup = BeautifulSoup(page_text,'lxml') # 解析数据 a_eles = soup.select('.book-mulu > ul > li > a') # print(a_eles) cap = 1 fp = open('./sanguo.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') for ele in a_eles: print('开始下载第%d章节' % cap) cap+=1 title = ele.string content_url = 'http://www.shicimingju.com'+ele['href'] content = parse_content(content_url) fp.write(title+":"+content+'\n\n\n\n\n') print('结束下载第%d章节' % cap) fp.close() print('download over')
![]()
![]()





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号