(五)Julia并行算法简介:矩阵乘法
在本章中,我们将开始学习一系列专门讨论几种分布算法的设计、分析和实现的会议。这些算法经过精心挑选,以说明分布式内存方法的算法并行化的不同方面和潜在陷阱。本系列的第一部分研究矩阵乘法。
学习目标
在学习完本章节后,我们应该能够:
- 在多个处理器上并行执行矩阵乘法
- 通过复杂度分析和运行代码来研究不同并行化策略的性能
- 在Julia中实施这些策略
- 了解粒度对分布式算法效率的影响(grain size)
- 了解通信开销的概念(communication overhead)
Parallel algorithm overview
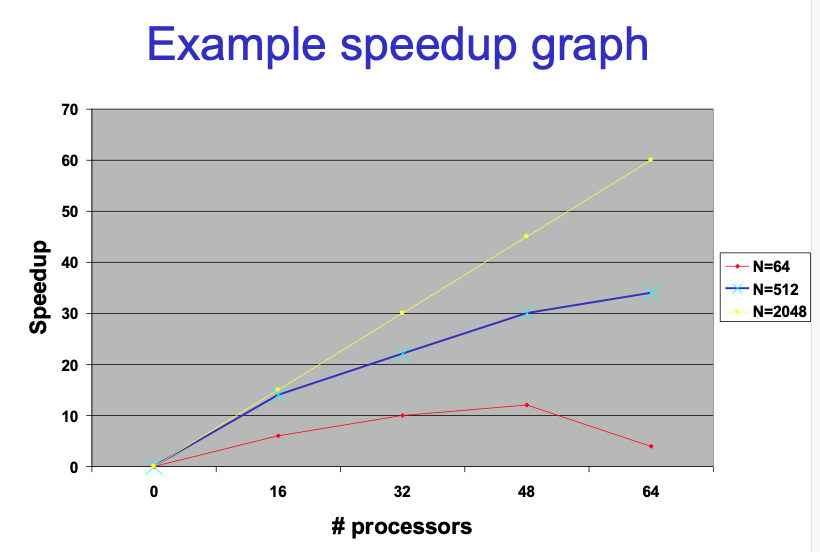
Goal: Design method for developing efficient parallel algorithms that have little communication overhead, load imbalance and search overhead.
We should be able to apply this method to simple cases.
Introduction
我们假定非常简单的computer model,Distributed-memory machine:
- All machines are equally fast
- E.g., identical workstations on a network
- We use 1 computation per machine and ignore multicores
- CPU, processor, machine, processing node mean the same
5 parallel algorithms of increasing complexity:
- Matrix multiplication
- Successive overrelaxation
- All-pairs shortest paths
- Linear equations
- Traveling Salesperson problem
We use Message Passing
SEND (destination, message)
- non-blocking: continue immediately (like a mailbox),信息发送是reliable的,当信息发送出去之后,在未来的某一个时刻一定会发出被接收。
RECEIVE (source, message)
RECEIVE-FROM-ANY (message)
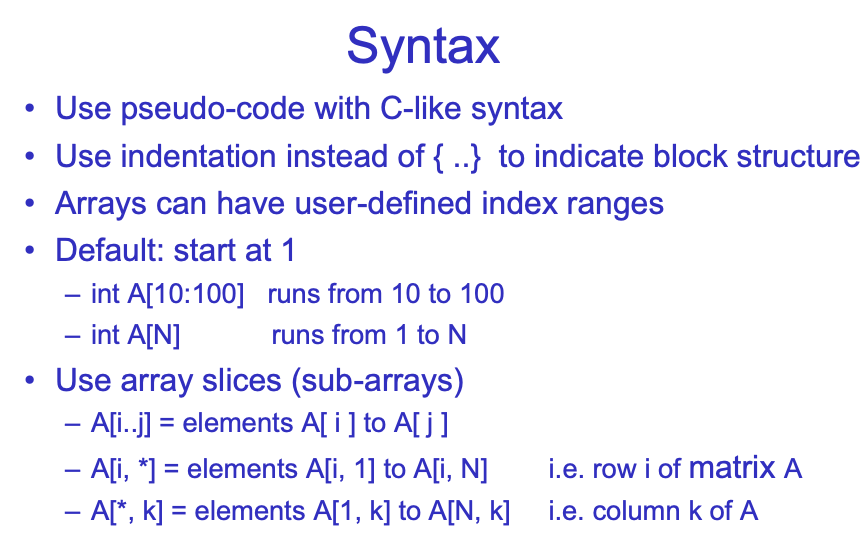
我们使用类似C语法的伪代码,因为实际运行中我们会有很大的array,分区在不同的机器上,所以我们应该可以自己定义array的index。
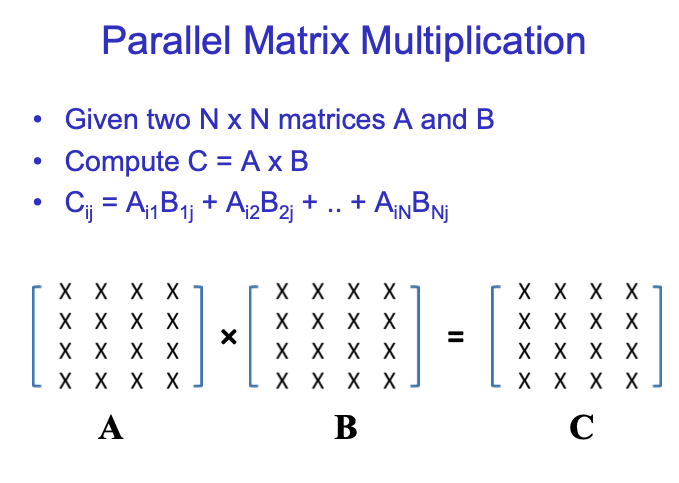
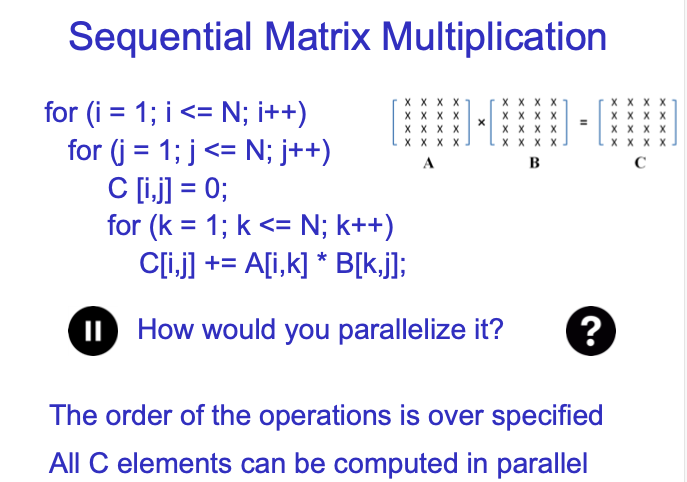
所有C中的元素都是independent的,因此可以并行计算。
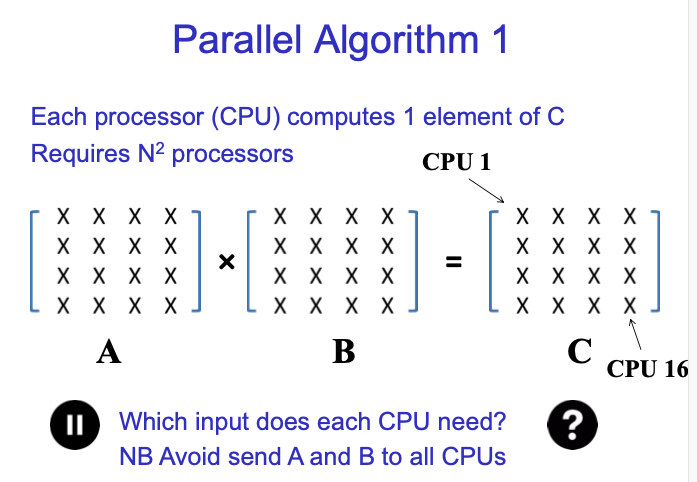
第一种是每个元素的计算都是并行的,我们需要确定每个CPU的input是什么,这被称为data dependency。如果每个CPU都需要整个A和整个B矩阵,那就会做太多的necessary communication。

每个CPU只需要A的一行和B的一列来计算C中的一个元素。

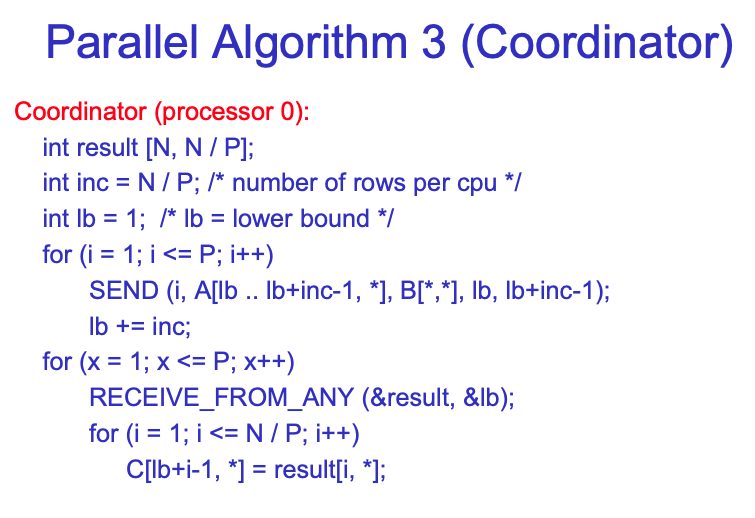
首先我们有一个总体的coordinator来存储所有的initial data,即central computer,这被称为head node。然后我们allocate一些compute node。Head node给所有compute node发送A的一行和B的一列,然后计算出结果后发送回head node。


offload:卸下



我们应该思考一种更好的并行算法,这就引出了第二种算法:
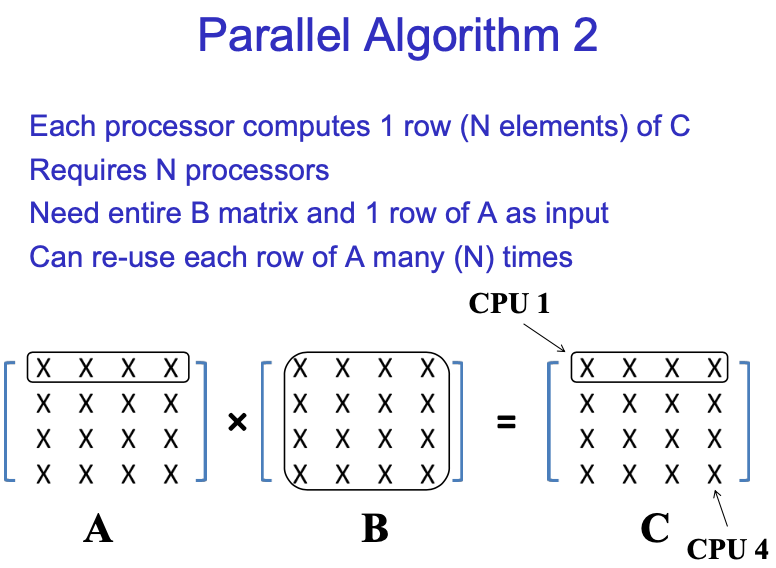
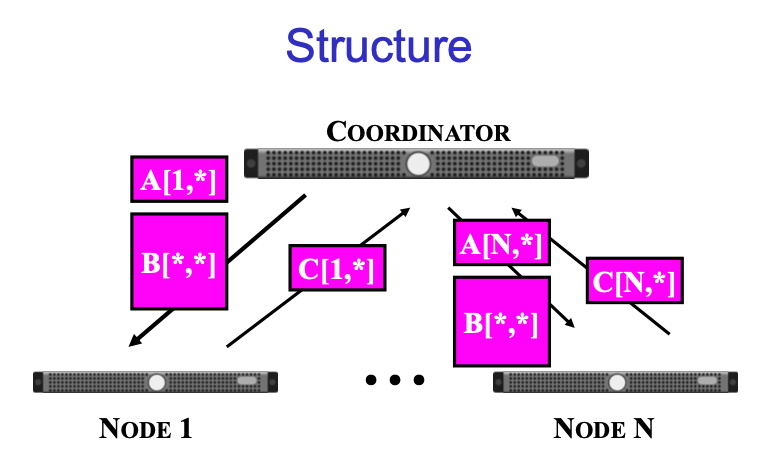


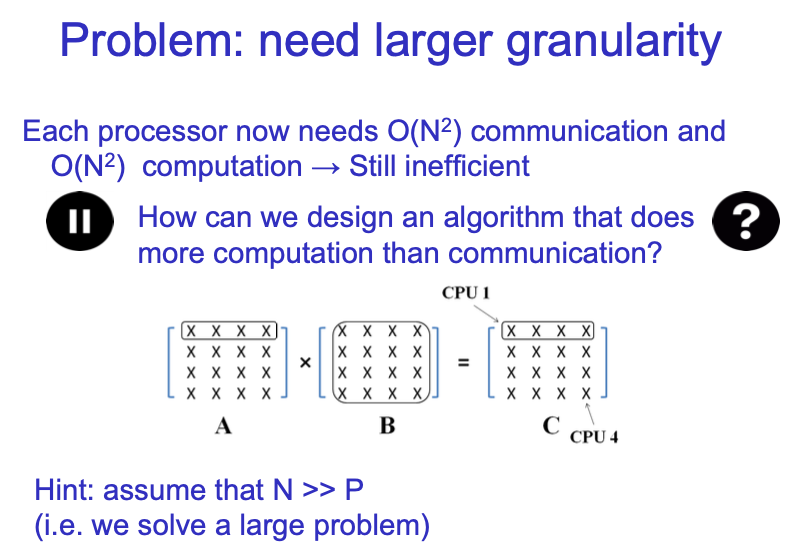
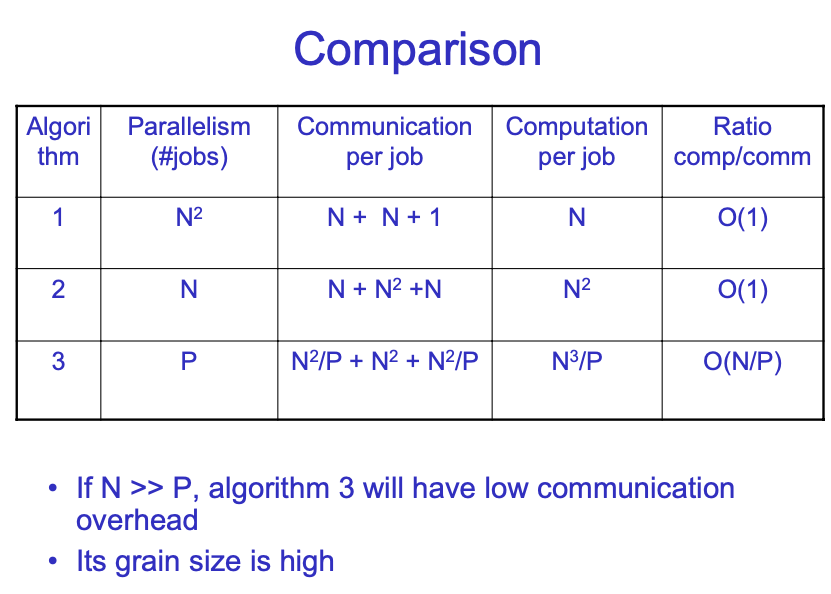
Computation的复杂度变为O(N^2),communication的也变为O(N^2)。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号