第二题,Add Two Numbers
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
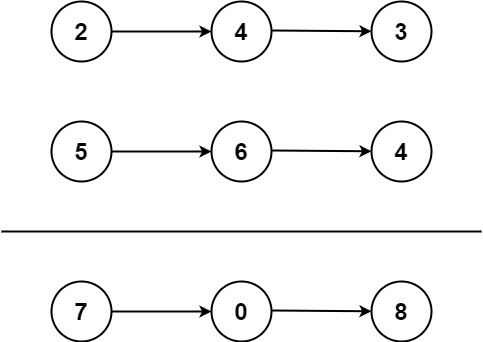
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] Output: [7,0,8] Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0] Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
分析下题目,就是两个链表,从头到尾分别代表从个位到高位的数字,然后输出一个链表,同样是从头到尾,依次是从低位升到高位
我第一次做这个题时候很朴素,就是把链表反转过来,然后相加,在拆分结果做成链表,但是这种方式过于复杂,需要考虑情况过于多,后来转换了思路,也即链表首位是个位的数字,正好符合我们手动计算相加的方式,因此可以按照这种方式来进行计算,另外设置一个flag来表示是否进位即可。
需要注意的点:
1、需要申请两个节点,并且赋值使其相等,这样做的目的是为了保证一个链表节点用于赋值结果,而另外一个相同的节点则负责最终的return返回
ListNode ll = new ListNode(); ListNode lx = ll;
2、判断两个链表为空的情况,直接将其值设置为0
if (l1 == null) { l1 = new ListNode(); l1.val = 0; l1.next = null; } if (l2 == null) { l2 = new ListNode(); l2.val = 0; l2.next = null; }
3、记得申请结果链表的下一个节点对象,思考下什么条件下才会申请节点呢?情况不只下列两种
if(l1 != null || l2 != null ) { ListNode node = new ListNode(); ll.next = node; ll = ll.next; }
// 当两个链表都不为空的时候
if (l1 == null && l2 == null && flag == 1) { flag = 0; ListNode node = new ListNode(1); ll.next = node; ll = ll.next; }
// 当两个链表都都为空且仍然需要进位时
4、处理仅一个链表不为空的情况,类似于两个链表不为空

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号