linux C 文件操作之fscanf()
描述:
int fscanf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...) 从流 stream 读取格式化输入。
声明:
int fscanf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...)
参数
stream -- 这是指向 FILE 对象的指针,该 FILE 对象标识了流。
format -- 这是 C 字符串,包含了以下各项中的一个或多个:空格字符、非空格字符 和 format 说明符。
功 能:
从一个流中执行格式化输入,fscanf遇到空格和换行时结束,注意空格时也结束。
返回值
如果成功,该函数返回成功匹配和赋值的个数。如果到达文件末尾或发生读错误,则返回 EOF。
1.
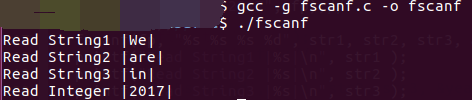
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: fscanf.c 3 > Author: 4 > Mail: 5 > Created Time: Wed 09 Aug 2017 10:08:20 AM CST 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 #include<stdio.h> 8 #include<stdlib.h> 9 int main() 10 { 11 char str1[10], str2[10], str3[10]; 12 int year; 13 FILE * fp; 14 fp = fopen ("file.txt", "w+"); 15 fputs("We are in 2017", fp);// 16 rewind(fp);// 17 fscanf(fp, "%s %s %s %d", str1, str2, str3, &year);// 18 printf("Read String1 |%s|\n", str1 ); 19 printf("Read String2 |%s|\n", str2 ); 20 printf("Read String3 |%s|\n", str3 ); 21 printf("Read Integer |%d|\n", year ); 22 fclose(fp);// 23 return(0); 24 }
2.
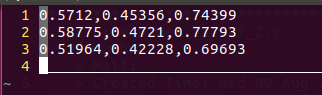
test.txt:将每一列的数据保存在一个double型数组中
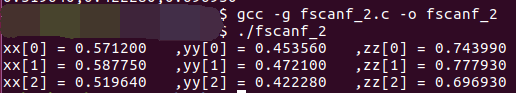
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: fscanf_2.c 3 > Author: 4 > Mail: 5 > Created Time: Wed 09 Aug 2017 10:37:26 AM CST 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 #include<stdio.h> 8 #include<stdlib.h> 9 int main() 10 { 11 FILE *fp = fopen("./test.txt", "r"); 12 if (fp == NULL) 13 { 14 printf("file open error\n"); 15 return -1; 16 } 17 double x; 18 double y; 19 double z; 20 int i = 0; 21 double xx[3]; 22 double yy[3]; 23 double zz[3]; 24 while(fscanf(fp, "%lf,%lf,%lf",&x,&y,&z) != EOF) 25 { 26 xx[i] = x; 27 yy[i] = y; 28 zz[i] = z; 29 i++; 30 } 31 32 for(i = 0; i < 3; i++) 33 { 34 printf("xx[%d] = %lf ,yy[%d] = %lf ,zz[%d] = %lf\n",i,xx[i],i,yy[i],i,zz[i]); 35 } 36 fclose(fp); 37 return 0; 38 }
结果: