为什么我要放弃javaScript数据结构与算法(第五章)—— 链表
这一章你将会学会如何实现和使用链表这种动态的数据结构,这意味着我们可以从中任意添加或移除项,它会按需进行扩张。
本章内容
- 链表数据结构
- 向链表添加元素
- 从链表移除元素
- 使用 LinkedList 类
- 双向链表
- 循环链表
第五章 链表
链表数据结构
要存储多个元素,数组(或列表)可能是最常见的数据结构了。然后这种数据结构有一个缺点:数组的大小是固定的,从数组的起点或中间插入或移除项的成本有点高,因为需要移动元素。
链表存储有序的元素集合,但不同于数组,链表中的元素在内存并不是连续放置的。每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(也称指针或链接)组成,下图展示了一个链表的结构。
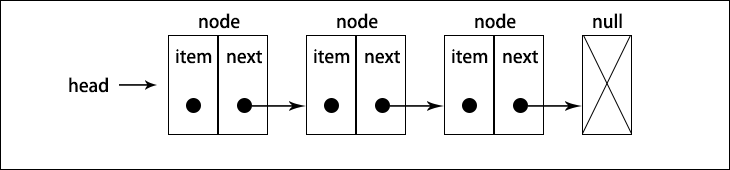
相对于传统的数组,链表的一个好处在于,添加或者移除元素的时候不需要移动其他元素,然后,链表需要使用指针,因为实现链表时需要额外注意。数组的另一个细节是可以直接访问任何位置的任何元素,而想要访问链表中间的一个元素,需要从起点(表头)开始迭代列表直到找到所需的元素。
现实中也有一些链表的例子,第一个例子就是康加舞队,每个人就是一个元素,手就是链向下一个人的指针,可以向队列汇总增加人——只需要找到想加入的点,断开连接,插入一个人,再重新连接起来。
另外一个例子就是寻宝游戏,你有一条线索,这条线索是指向寻找下一个线索的地点的指针,你顺着这条链去下一个地点,得到另一条指向再下一处的线索。得到列表中间的线索的唯一方法,就是从起点(第一个线索)顺着列表寻找。
还有一个可能就是用来说明链表中的最流行的例子,那就是火车。一列火车是由一系列车厢(也称车皮)组成的。每节车厢或车皮都互相连接。可以很容易的分离开一节车皮,改变它的位置,添加或移除它。
创建链表
了解链表是什么之后,就要开始实现我们的数据结构了,一下是我们的 LinkedList 类的骨架:
function LinkedList(){
let Node = function(element){ // 需要一个Node辅助类,表示要加入列表的项,element 代表要添加到列表中的值, next d代表指向列表的下一个节点向的指针
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
let length = 0; // 存储列表项的数量 length 属性
let head = null; // 存储第一个节点的引用在 head 变量
this.append = function(element){};
this.insert = function(position,element){}
this.removeAt = function(position){}
this.remove = function(element){}
this.indexOf = function(position){}
this.isEmpty = function(){}
this.size = function(){}
this.getHead = function(){}
this.toString = function(){}
this.print = function(){}
}
LinkedList 类的方法的功能
- append(element):向列表尾部添加一个新的项
- insert(position,element):向列表的特定位置插入一个新的项
- removeAt(position):从列表的特定位置移除一项
- remove(element):从列表中移除一项
- indexOf(element):返回元素在列表中的索引。如果列表中没有该元素则返回-1
- isEmpty():如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回true,如果链表的长度大于0则返回 false
- size():返回链表包含的元素个数,与数字的 length 属性类似
- toString():由于列表项使用 Node 类,就需要重写继承自 JavaScript 对象默认的 toString 方法,让其只输出元素的值。
向链表尾部追加元素
向 LinkedList 对象尾部添加一个元素时,可能有两种场景,列表为空,添加的是第一个元素,或者列表不为空,向追加元素。
this.append = function(element){
let node = new Node(element),current;
if(head === null){
head = node;
}else{
current = head;
// 循环列表,直到找到最后一项
while(current.next){
current = current.next;
}
// 当current.next元素为null时,找到最后一项,将其 next 赋为 node,建立连接
current.next = node;
}
length++; // 更新列表的长度
};
可以在 append 函数 加上return node ,通过下面的代码来使用和测试目前创建的数据结构
let list = new LinkedList();
console.log(list.append(15)); // Node {element: 15, next: null}
console.log(list.append(10)); // Node {element: 10, next: null}
从链表中移除元素
移除元素也有两种场景:第一种是移除第一个元素,第二种是移除第一个以外的任一元素。我们要实现两种 remove 方法:第一种是从特定位置移除第一个元素,第二种是根据元素的值移除元素。
首先先实现移除特定位置的元素
this.removeAt = function(position){
// 检查越界值
if(position >-1 && position < length){
let current = head,previous,index = 0;
// 移除第一项
if(position === 0){
head = current.next;
console.log(current.element);
}else{
while(index++ < position){
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
// 将 previous 与 current 的下一项连接起来,跳过 current,从移除它
previous.next = current.next;
}
length --;
console.log(current.element);
return current.element;
}else{
return null;
}
}
如果想要移除第一个元素(position=0),要做的就是让 head 指向列表的第二个元素,我们用 current 变量穿甲一个对列表中第一个元素的应用,这样 current 变量就是对列表中第一个元素的引用,如果吧 head 赋值为 current.next 就会移除第一个元素。
如果我们要移除列表的最后一项或者是中间的一项,为此,需要依靠一个细节来迭代列表,知道到达目标位置(index++ < position),使用一个用于内部控制和递增的 index 变量,current 变量总是对所循环列表的当前元素的引用(current = current.next),我们还需要一个对当前元素的前一个元素的引用(previous = current),它被命名为 previous。
因此,要从列表中移除当前元素,要做的就是将 previous.next 和 current.next 链接起来,这样当前元素就会被丢弃在计算机内存中,等着被垃圾回收站清除。
对于最后一个元素,在(while(index++ < position))跳出循环时, current 变量总是对列表中最后一个元素的引用(要移除的元素)。current.next 的值将是 null(因为它是最后一个元素)。由于还保留了对 previous 的引用(当前元素的前一个元素),previous 就指向了 current 。那么要移除 current,要做的就是把 previous.next 的值改变为 current.next 。
在任意位置插入元素
实现 insert 方法,使用这个方法可以在任意位置插入一个元素。
this.insert = function(position,element){
// 检查越界值
if(position >=0 && position <= length){
let node = new Node(element),
current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
if(position === 0 ){ // 在第一个位置添加
node.next = current;
head = node;
}else{
while(index++ < position){
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
}
length++;
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
current 变量是对列表中第一个元素的引用,我们需要做的是把 node.next 的值设为 current (列表中的第一个元素),现在 head 和 node.next 都指向了 current ,接下来要做的就是把 head 的引用改为 node ,这样列表中就有了一个新元素。
现在来处理第二种场景,在列表中间或者末尾添加一个新的元素。首先,循环访问列表,找打目标为位置,当跳出循环的时候, current 变量将是对想要插入新元素的位置之后一个元素的引用,而 previous 将是对想要插入新元素的位置之前的一个元素的引用。在这种情况下,我门要在 previous 和 current 之间添加新项。因此,需要将新项(node)和当前链接起来(node.next = current),然后需要改变 previous 和 current z之间的链接,我们还需要让 previous.next 指向 node。
实现其他方法
toString方法
this.toString = function(){
let current = head,
string = '';
while(current){
string += current.element + (current.next ? '-':'');
current = current.next;
}
return string;
}
赋值current为 head, 循环访问 current,将 current 变量当做索引,初始化用于拼接元素的变量(string)。通过 current 来检查元素是否存在,如果列表为空或是到达列表中最后一个元素的下一位(null),while 循环中的代码就不会执行,就可以得到元素的内容,将其拼接到字符串中,最后,迭代下一个元素。最后,返回列表内容的字符串。
indexOf方法
indexOf方法接受一个元素的值,如果在列表中找到它,就返回元素的位置,否则返回 -1
this.indexOf = function(element){
let current = head,
index = 0;
while(current){
if(element === current.element){
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
循环变量 current,它的初始值是 head ,利用index 来计算位置数。访问元素,检查当前元素是否是我们要找的,如果是,就返回它的位置,不是就继续计数,检查列表中的下一个节点。
如果列表为空,或是到达列表的尾部(current = current.next 将是 null),循环就不会执行。如果没有找到值就返回 -1 。
实现了上面的方法,就可以实现remove等其他方法了
remove方法
this.remove = function(element){
let index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
isEmpty、size 和 getHead方法
isEmpty和size 和之前章节实现一模一样
this.isEmpty = function(){
return length === 0;
}
this.size = function(){
return length;
}
还有 getHead方法
this.getHead = function(){
return head;
}
head 变量是 LinkedList 类的私有变量,我们如果需要在类的实现外部循环访问列表,就需要提供一种获取类的第一个元素的方法。
整个 LinkedList函数
function LinkedList(){
let Node = function(element){ // 需要一个Node辅助类,表示要加入列表的项,element 代表要添加到列表中的值, next d代表指向列表的下一个节点向的指针
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
let length = 0; // 存储列表项的数量 length 属性
let head = null; // 存储第一个节点的引用在 head 变量
this.append = function(element){
let node = new Node(element),current;
if(head === null){
head = node;
}else{
current = head;
// 循环列表,直到找到最后一项
while(current.next){
current = current.next;
}
// 当current.next元素为null时,找到最后一项,将其 next 赋为 node,建立连接
current.next = node;
}
length++; // 更新列表的长度
};
this.insert = function(position,element){
// 检查越界值
if(position >=0 && position <= length){
let node = new Node(element),
current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
if(position === 0 ){ // 在第一个位置添加
node.next = current;
head = node;
}else{
while(index++ < position){
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
}
length++;
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
this.removeAt = function(position){
// 检查越界值
if(position >-1 && position < length){
let current = head,previous,index = 0;
// 移除第一项
if(position === 0){
head = current.next;
console.log(current.element);
}else{
while(index++ < position){
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
// 将 previous 与 current 的下一项连接起来,跳过 current,从移除它
previous.next = current.next;
}
length --;
return current.element;
}else{
return null;
}
}
this.remove = function(element){
let index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
this.indexOf = function(element){
let current = head,
index = 0;
while(current){
if(element === current.element){
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
this.isEmpty = function(){
return length === 0;
}
this.size = function(){
return length;
}
this.getHead = function(){
return head;
}
this.toString = function(){
let current = head,
string = '';
while(current){
string += current.element + (current.next ? '-':'');
current = current.next;
}
return string;
}
}
双向链表
链表有多种不同的类型,这一节介绍 双向链表,双向链表和普通链表的区别在于,在链表中,一个节点只有链向下一个链接,而在双向链表中,链接是双向的:一个链向下一个元素,另一个链向前一个元素。如下图所示
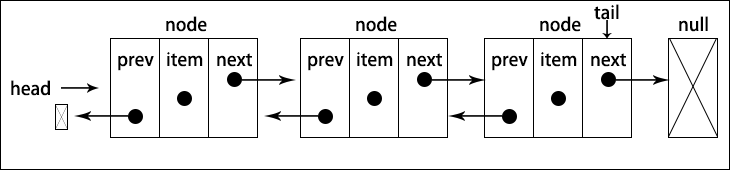
先从实现 DoublyLinkedList 类所需要的变动开始
function DoublyLinkedList(){
let Node = function(elememt){
this.elememt = elememt;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null; // 新增的
}
let length = 0;
let head = null;
let tail = null // 新增的
// 这里是方法
}
可以看出,Node 类中新增了 prev属性(一个新指针),在 DoublyLinkedList 类里也有用来保存对列表最后一项的引用的 tail 属性。
双向链表提供了两种迭代列表的方式:从头到尾,或者从尾到头。我们也可以方位一个特定节点的下一个或者是上一个元素。在单向链表中,如果迭代列表时错过了要找的元素,就需要回到列表起点,重新迭代。这是双向链表的一个优点。
在任意位置插入新元素
向双向链表中插入一个新项跟(单向)链表非常相类似。区别在于,链表只要控制一个 next 指针,而双向链表则要同时控制 next 和 prev (previous,前一个)这两个指针。
this.insert = function(position,elememt){
// 检查越界值
if(position >= 0 && position <= length){
let node = new Node(elememt),
current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
if(position === 0){ // 在第一个位置添加
if(!head){
head = node;
tail = node;
}else{
node.next = current;
current.prev = node;
head = node;
}
}else if(position === length){ // 最后一项
current = tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
tail = node;
}else{
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = previous;
}
length++
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
在列表的第一个位置(列表的起点)插入一个新元素,如果列表为空(if(!head)),那只需将 head 和 tail 都指向这个新节点。如果不为空, current 变量将是对列表中的第一个元素的引用。就像我们在链表中所做的,把 node.next 设为 current ,而head 将指针指向 node (它被设为列表中的第一个元素)。不同之处,我们还需要为指向上一个元素的指针设一个值。current.prev 指针将由 指向 null 变成指向 新元素(current.prev = node)。node.prev 指针已经是 null,因此不需要在更新任何东西了。
假如我们要在列表最后添加一个新元素。这是一个特殊情况,因为我们还控制着指向最后一个元素的指针(tail)。current 变量将引用最后一个元素(current = tail)。然后分开建立第一个链接:node.prev 将引用current。current.next 指针(指向null)将指向 node (由于构造函数,node.next 已经指向了 null)。然后只剩下一件事,就是更新 tail ,它将由 指向 current 变成指向 node 。
第三种场景:在列表中插入一个新元素,就像我们在之前方法中所做,迭代列表,知道到达要找的位置(while (index++ < position))。我们将在 current 和 previous 元素之间插入新元素。首先,node.next 将指向 current ,而 previous.next 将指向 node,这样就不会跌势节点之间的链接。然后需要处理所有的链接:current.prev 将指向node ,而 node.prev 将指向 previous
从任意位置移除元素
从双向链表中移除元素跟链表非常类似。唯一区别就是还需要设置一个位置的指针。
this.removeAt = function(position){
// 检查越界值
if(position > -1 && position < length){
let current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
// 移除第一项
if(position === 0){
head = current.next;
// 如果只有一项,更新 tail
if(length === 1){
tail = null;
}else{
head.prev = null;
}
}else if(position === length-1){ // 最后一项
current = tail;
tail = current.prev;
tail.next = null;
}else{
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
// 将 previous 与 current 的下一项连接起来——跳过 current
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous;
}
length --;
return current.elememt;
}else{
return null;
}
}
我们需要处理三种场景,从头部、从中间和从尾部移除一个元素。
移除第一个元素。current 变量是对列表中第一个元素的引用,也就是我们想要移除的远古三。需要做的就是改变 head 的引用,将其从 current 改为下一个元素(head = current.next;),但是我们还需要更新 current.next 指向上一个元素的指针(因为第一个元素的 prev 指针是 null)。因此,把 head.prev 的引用改为 null(因为 head 也指向了列表中的第一个元素,或者也可以用 current.next.prev )。由于还需要控制 tail 的引用,我们可以检测要移除的是否是第一个元素,如果是,只需要把 tail 也设为 null。
移除最后一个位置的元素。既然已经有了对最后一个元素的引用(tail),我们就不需要为找到它而迭代列表。我们可以把 tail 的引用赋给 current 变量。接下来,就需要吧 tail 的引用更新为列表中的倒数第二个元素(current.prev,或者 tail.prev也可以)。既然 tail 指向了倒数第二个元素,我们需要把 next 指针更新为 null (tail.next = null)。
最后一种场景,从列表中移除一个元素。首先需要迭代列表,直到到达要找的位置。current 变量所引用的就是要移除的远古三。那么要移除它,我们可以通过更新 previous.next 和 current.next.prev 的引用,在列表中跳过它。因此,previous.next 将 指向 current.next ,而 current.next.prev 将指向 previous。
完整代码
function DoublyLinkedList(){
let Node = function(elememt){
this.elememt = elememt;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null; // 新增的
}
let length = 0;
let head = null;
let tail = null // 新增的
this.append = function(elememt){
let node = new Node(elememt),
current;
if(!head){
head = node;
tail = node;
}else{
current = tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
tail = node;
}
length++;
}
this.insert = function(position,elememt){
// 检查越界值
if(position >= 0 && position <= length){
let node = new Node(elememt),
current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
if(position === 0){ // 在第一个位置添加
if(!head){
head = node;
tail = node;
}else{
node.next = current;
current.prev = node;
head = node;
}
}else if(position === length){ // 最后一项
current = tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
tail = node;
}else{
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = previous;
}
length++
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
this.removeAt = function(position){
// 检查越界值
if(position > -1 && position < length){
let current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
// 移除第一项
if(position === 0){
head = current.next;
// 如果只有一项,更新 tail
if(length === 1){
tail = null;
}else{
head.prev = null;
}
}else if(position === length-1){ // 最后一项
current = tail;
tail = current.prev;
tail.next = null;
}else{
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
// 将 previous 与 current 的下一项连接起来——跳过 current
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous;
}
length --;
return current.elememt;
}else{
return null;
}
}
this.remove = function(elememt){
let index = this.indexOf(elememt);
this.removeAt(index);
}
this.toString = function(){
let current = head,
str = '';
while (current) {
str += current.elememt + (current.next?'-':'');
current = current.next;
}
return str;
}
this.indexOf = function(elememt){
let current = head,
index = 0;
while (current) {
if(current.elememt === elememt){
return index
}
current = current.next;
index++
}
return -1;
}
this.isEmpty = function(){
return length === 0;
}
this.size = function(){
return length;
}
this.getHead = function(){
return head;
}
}
循环链表
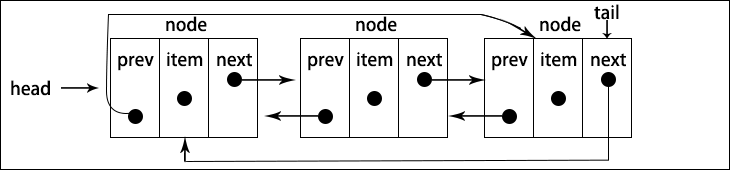
循环链表可以像链表一样只有单向引用,也可以像双向链表一样有双向引用。循环链表和链表之间唯一的区别在于,最后一个元素指向下一个元素的指针(tail.next)不是引用 null,而是指向第一个元素(head),如下图所示
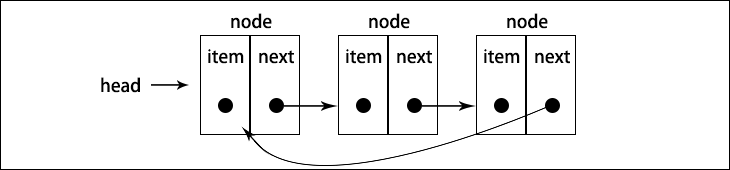
双向链表有指向 head 元素的 tail.next ,和指向 tail 元素的 head.prev
小结
这一章中,学习了链表这种数据结构,及其辩题双向链表和循环链表,知道了如何在任意位置添加和移除元素,已经如何循环访问两边,比数组重要的优点就是,无需移动链表中的元素,就能轻松添加和移除元素。当你需要添加和移除很多元素的时候,最好的选择就是链表,而非数组。下一章将学习集合,最后一种顺序数据结构。
书籍链接: 学习JavaScript数据结构与算法





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号