1. Refactoring Strategy
1.1 Classic Strategy
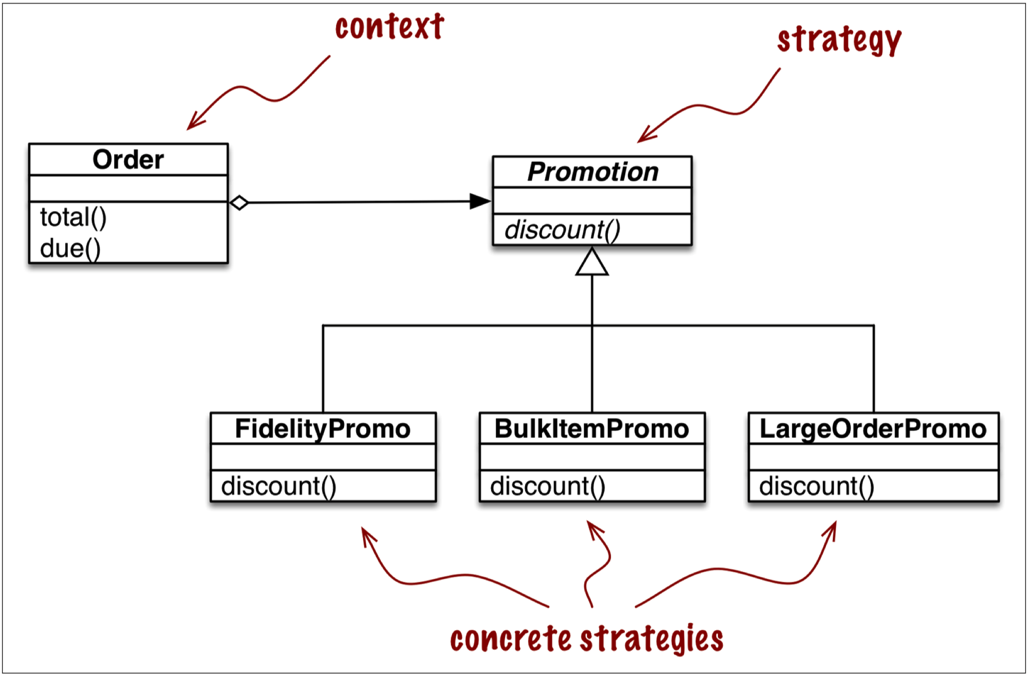
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from collections import namedtuple
Customer = namedtuple('Customer', 'name fidelity')
class LineItem:
def __init__(self, product, quantity, price):
self.product = product # 商品名
self.quantity = quantity # 数量
self.price = price # 单价
def total(self): # 总价
return self.price * self.quantity
class Order:
def __init__(self, customer, cart, promotion=None):
self.customer = customer # 用户名
self.cart = list(cart) # 商品列表
self.promotion = promotion # obj
def total(self): # 总价
if not hasattr(self, '__total'):
self.__total = sum(item.total() for item in self.cart)
return self.__total
def due(self): # 折扣价
if self.promotion is None:
discount = 0
else:
discount = self.promotion.discount(self) # **********
return self.total() - discount
def __repr__(self): # 打印
fmt = '<Order total: {:.2f} due: {:.2f}>'
return fmt.format(self.total(), self.due())
class Promotion(ABC): # an abstract base class
@abstractmethod
def discount(self, order): # 返回折扣的总钱数
pass
class FidelityPromo(Promotion):
"""5% discount for customers with 1000 or more fidelity points"""
def discount(self, order):
return order.total() * .05 if order.customer.fidelity >= 1000 else 0
class BulkItemPromo(Promotion):
"""10% discount for each LineItem with 20 or more units"""
def discount(self, order):
discount = 0
for item in order.cart:
if item.quantity >= 20:
discount += item.total() * .1
return discount
class LargeOrderPromo(Promotion):
"""7% discount for orders with 10 or more distinct items"""
def discount(self, order):
distinct_items = {item.product for item in order.cart}
if len(distinct_items) >= 10:
return order.total() * .07
return 0
joe = Customer('John Doe', 1000)
cart = [LineItem('banana', 4, .5), LineItem('apple', 25, 1.5), LineItem('watermellon', 5, 5.0)]
print(Order(joe, cart, FidelityPromo())) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 61.27>
print(Order(joe, cart, BulkItemPromo())) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 60.75>
print(Order(joe, cart, LargeOrderPromo())) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 64.50>
1.2 Function-Oriented Strategy
- A flyweight is a shared object that can be used in multiple contexts simultaneously. (享元)
from collections import namedtuple
Customer = namedtuple('Customer', 'name fidelity')
class LineItem:
def __init__(self, product, quantity, price):
self.product = product # 商品名
self.quantity = quantity # 数量
self.price = price # 单价
def total(self): # 总价
return self.price * self.quantity
class Order:
def __init__(self, customer, cart, promotion=None):
self.customer = customer # 用户名
self.cart = list(cart) # 商品列表
self.promotion = promotion # obj
def total(self): # 总价
if not hasattr(self, '__total'):
self.__total = sum(item.total() for item in self.cart)
return self.__total
def due(self): # 折扣价
if self.promotion is None:
discount = 0
else:
discount = self.promotion(self) # **********
return self.total() - discount
def __repr__(self): # 打印
fmt = '<Order total: {:.2f} due: {:.2f}>'
return fmt.format(self.total(), self.due())
def fidelity_promo(order): # created just once
"""5% discount for customers with 1000 or more fidelity points"""
return order.total() * .05 if order.customer.fidelity >= 1000 else 0
def bulk_item_promo(order):
"""10% discount for each LineItem with 20 or more units"""
discount = 0
for item in order.cart:
if item.quantity >= 20:
discount += item.total() * .1
return discount
def large_order_promo(order):
"""7% discount for orders with 10 or more distinct items"""
distinct_items = {item.product for item in order.cart}
if len(distinct_items) >= 10:
return order.total() * .07
return 0
joe = Customer('John Doe', 1000)
cart = [LineItem('banana', 4, .5), LineItem('apple', 25, 1.5), LineItem('watermellon', 5, 5.0)]
print(Order(joe, cart, fidelity_promo)) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 61.27>
print(Order(joe, cart, bulk_item_promo)) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 60.75>
print(Order(joe, cart, large_order_promo)) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 64.50>
1.3 Choosing the Best Strategy
promos = [fidelity_promo, bulk_item_promo, large_order_promo]
# promos = [globals()[name] for name in globals() if name.endswith('_promo') and name != 'best_promo']
# import inspect
# promos = [func for name, func in inspect.getmembers(promotions, inspect.isfunction)] # promotions为自定模块
def best_promo(order):
"""Select best discount available"""
return max(promo(order) for promo in promos)
promos = []
def promotion(promo_func):
promos.append(promo_func)
return promo_func
@promotion
def fidelity_promo(order): # created just once
"""5% discount for customers with 1000 or more fidelity points"""
return order.total() * .05 if order.customer.fidelity >= 1000 else 0
@promotion
def bulk_item_promo(order):
"""10% discount for each LineItem with 20 or more units"""
discount = 0
for item in order.cart:
if item.quantity >= 20:
discount += item.total() * .1
return discount
@promotion
def large_order_promo(order):
"""7% discount for orders with 10 or more distinct items"""
distinct_items = {item.product for item in order.cart}
if len(distinct_items) >= 10:
return order.total() * .07
return 0
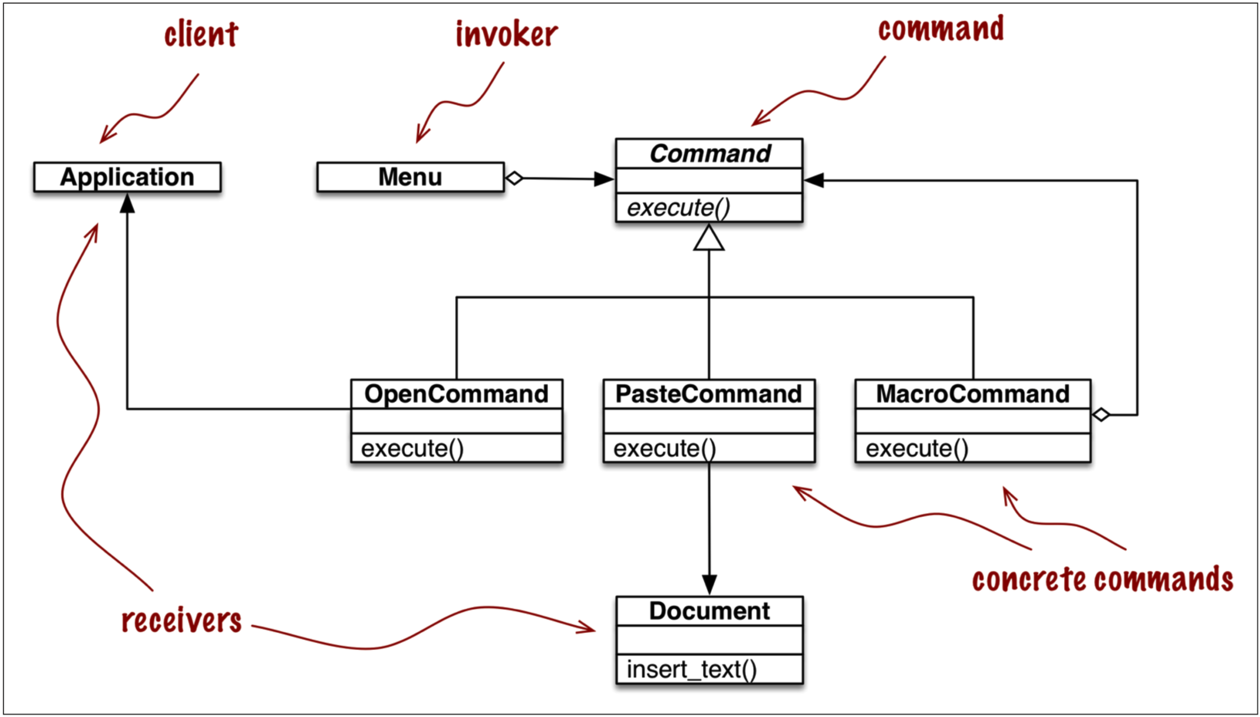
2. Command




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号