PS Material 漫谈 九: Assembly processing in PS (三):
Working with Assembly Processing
Prerequisites
1. Before you can create a network from a sales document using assembly processing, you have to have made the necessary settings, as described in Settings for Assembly Processing.
2. The scheduling line category must permit assembly processing. See,  Schedule Line Categories.
Schedule Line Categories.
3. The order probability in the sales document must be larger then zero.
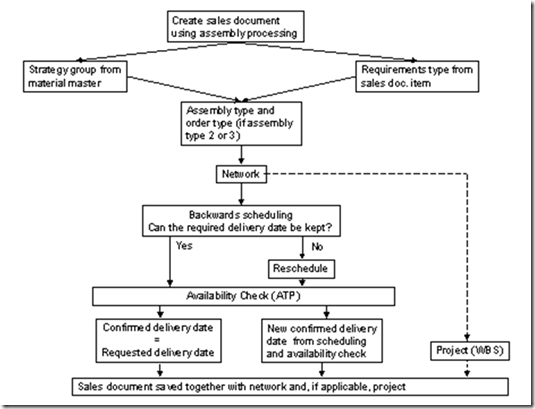
Process Flow
You trigger assembly processing by creating a sales document item for a material, for which the planning strategy is assembly processing. Although it is possible to create an assembly order for an inquiry, this would usually provide too much detail at this stage in the sales process. Consequently you generally only generate networks from quotations and sales orders.
Whether a network is generated when you create a quotation or afterwards when you create the sales order is determined by the requirements class (see Material Requirements in Assembly Processing).

It is not possible to generate two completly defferent projects from one sales document. You cannot enter two materials that lead to two different projects.
The process flow for assembly processing (without configuration) is illustrated in the graphic below.
Configuration
If you are using configuration, the system configures the material before it calls up the network. A dialog box appears, in which you enter values for the characteristics. If the network is also configurable, it uses the characteristic value assignment from the material. If values still have to be assigned, a dialog box appears in which you can enter the necessary data.
Creating a Network
After the material has been configured, the system creates a network using the standard network you have specified. If any necessary entries have not been made in the standard network, you are prompted to make them.
If you enter a quantity of more than 1 for the item quantity in the sales document, the system automatically sets the corresponding execution factor in the network header. For more information, see  Execution factor.
Execution factor.
Note that the sales unit may differ from the unit of measure in the network. Both units can also differ from the base unit of measure. The system takes these differences into account and calculates the execution factor.

If you want to use quantities greater than 1 or if the units of measure can differ as above, make sure you set an execution factor in the activities of the standard network whose values depend on the quantity to be produced. If you leave this field blank, the system assumes that the activity has the same values, for example duration and costs, irrespective of the quantity. This could lead to errors in scheduling and costing.
Scheduling
The network is now scheduled as described in Scheduling in Assembly Processing.
Availability Check
The system uses the results from scheduling to check the material availability on the requirements dates. For more information, see Availability Checks in Assembly Processing.

When considering which components to include in the availability check, remember that including too many components can adversely affect performance.
When you confirm the delivery date the system transfers data from the network to the sales document. This data includes the billing data (milestone dates), costs and dates.
Costs
The system costs the network and transfers this information to the sales document.
Saving the Sales Document
When you save the sales document, the system assigns the sales document a number within the number range for the sales document type. This number is also used for the project number and subsequently for the numbers of the WBS elements. How the system does this is described in  Determining Project Numbers from Sales Documents. You can decide in the standard WBS that is used as a template whether one structure is generated for the whole sales document or one structure for each item. For more informationm, see Creating one WBS for Each Sales Document Item
Determining Project Numbers from Sales Documents. You can decide in the standard WBS that is used as a template whether one structure is generated for the whole sales document or one structure for each item. For more informationm, see Creating one WBS for Each Sales Document Item
The network is assigned an internal number that is not connected with sales document number.
The sales document, network and project (if applicable) are saved.
Scheduling in Assembly Processing
Use:
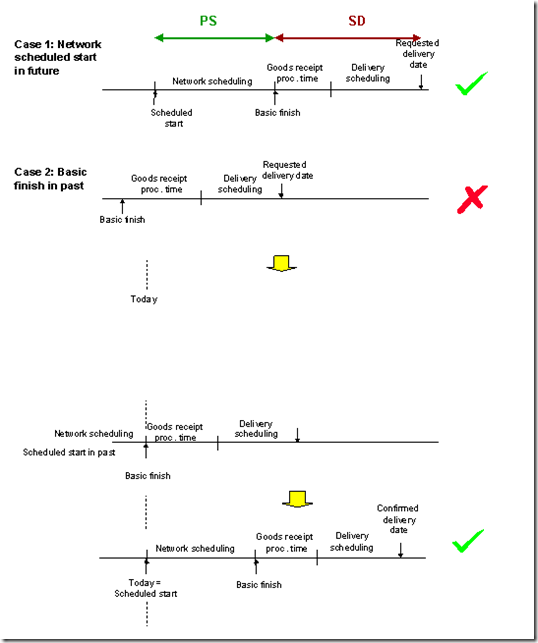
When you create a sales order with assembly processing, scheduling is automatically carried out. The purpose of scheduling is to find out, whether it is possible to meet the requested delivery date entered by the user.If the requested delivery date cannot be met, scheduling automatically determines the earliest date on which the sales order quantity can be confirmed.
During scheduling the system proceeds as illustrated above.
The system starts at the requested delivery date and determines the basic finish date, by carrying out delivery scheduling and subtracting the goods receipt processing time. You maintain the goods receipt processing time in the material master. For information on delivery scheduling, see  Transportation and Delivery Scheduling in the Sales and Distribution - Shipping (SD-SLS) component.
Transportation and Delivery Scheduling in the Sales and Distribution - Shipping (SD-SLS) component.

Delivery scheduling is often not carried out for orders connected with projects. However you may want to use it in a make-to-order scenario, if the project management is not responsible for delivery.
- If the basic finish date is in the future,
The system then schedules the network using the network scheduling parameters that have been maintained for the network type and plant in Customizing for the Project System in Dates ® Scheduling ® Specify parameters for network scheduling. If the scheduled start date is in the future or is in the past but within the time margin specified in the scheduling parameters, the requested delivery date can be confirmed.
If the scheduled start date is in the past outside the time margin specified in the material master, the system uses the reduction measures specified in the network scheduling parameters (see  Network Scheduling). If this is not sufficient the system uses today scheduling, determines a new basic finish and consequently a new confirmed delivery date.
Network Scheduling). If this is not sufficient the system uses today scheduling, determines a new basic finish and consequently a new confirmed delivery date.
- If the basic finish date is in the past,
The system also schedules the network according to the scheduling parameters. In the standard system the system moves the basic finish date to the current date, and consequently also moves the delivery date. It then schedules the network as above. Depending on the duration of the network, this could result in the delivery date being moved further into the future. This date can then be confirmed.
Availability Checks in Assembly Processing
Use:
You can use availability checks to make sure that the components you need to carry out the project/network are available when they are required. There is no point in conducting an availability check for the end-product alone, since this is basically the same as scheduling the network.
Prerequisites:
1. The Availability check and the Requirements transfer indicators have been set in the relevant requirements class.
2. You have allocated material components to activities in the standard network.
3. You have assigned checking groups to the material components (in the corresponding material master - MRP view).
Activities:
During network scheduling the system sets requirements dates for the individual components. The availability of these components are then checked.
If the materials are all available on the requirements dates
The system either confirms the requested delivery date, or if the network basic finish date is after the requested delivery date, it informs you so and requires you to confirm the later date.
If one or more materials are not available on the relevant requirements date
The system scans the differences between the requirements date and the confirmed date. It then selects the largest difference and adds this time to the basic finish date of the network to produce the overall commitment date. The system then asks you to confirm this date in the sales document.
Subsequent Changes and Assembly Processing 
Use
One of the advantages of assembly processing is that changes in the sales document are updated in the network and vice versa.
Features
Changes in the Sales Document
Any changes in customer requirements, which are made in the sales document, are passed on to the network until the network header has the status
- DLT (deleted)
- DLFL (deletion flag)
- LKD (locked)
- TECO (technically completed) or
- CLSD (closed).
In the schedule line, you can change the confirmed date but you cannot change the order quantity or the requested delivery date.
If you cancel a sales document item for which a network has been generates using assembly processing, the system automatically sets a deletion flag for the network header and subordinate objects. During this, the system checks whether a deletion flag can be set for the network. If a deletion flag cannot be set, the system issues a corresponding message. For more details, see  System Statuses in Networks.
System Statuses in Networks.
Changes in the Network
Any changes made to dates and quantities in the network are updated in the sales document automatically unless the fixed quantity and date indicator has been set for the item in the sales document.
Any changes to costs in the network are updated in the sales document. However, if required, you can also switch off this link between the network and the sales document. To do this, select the No update indicator in the appropriate requirements class. If you have selected this indicator, any changes in the network are not passed on to the sales document.
Changes to Master Data
Any changes which are made to the master data after you have created the network are not updated automatically in the sales document or the network. If the changes are relevant for the sales document and network, you must update these documents manually.
Accessing the Network from the Sales Document 
- If you are not in the sales document, access it by choosing Logistics ® Sales and Distribution ® Sales, the relevant sales document type andChange. Enter the relevant date on the initial screen.
- Select the item and then choose Schedule lines.
- On the Item data screen choose Procurement.
The Schedule line screen appears. - On this screen there are four buttons, with which you can go to different network functions:
- By choosing Header, you access the network header
- By choosing Gantt chart, you access the Gantt chart for the network, where you can plan dates.
- By choosing Object list, you access the network object overview.
- By choosing Activity Ovw., you access the network activity overview.
Executing Assembly Processing in PS 
Prerequisites
Before you can use assembly processing in the Project System, you must have made the necessary settings as described in Settings for Assembly Processing.
Procedure
- To create a sales document choose Logistics ® Sales and Distribution ® Sales, then the document type you want to create (Inquiry, Quotation orOrder) and Create.
- On the initial screen enter the document type, and if required details of the sales organization. Choose Enter.
- On the next screen enter the sold-to party, the number of the customer's purchase order and the item details. Mandatory entries for the item are the material number and the quantity. Choose Enter.
- The system calls up the standard network, schedules the new network and checks the availability. If necessary, confirm the suggested date or change it as required.
- Save the sales document.
Converting Quotations to Sales Orders 
Use
As with normal quotations, you can convert quotations involving assembly processing to sales orders. This is the case when the customer makes a firm order for the project.
Features
How the system converts one sales document to another, for example a quotation to a sales order, depends on the settings that have been made in Customizing for Sales and Distribution ® Sales. The Pos./neg. quantity indicator in the Copy Control: Sales Document to Sales Document transaction determines how the system reacts, when you convert a quotation to a sales order.
If the Pos./neg. quantity indicator has the value "+"
When you convert a quotation that created a network using assembly processing, the system uses the same network for the sales order. This means that any changes you made to the network during the quotation phase, for example as a result of negotiations with the customer, are automatically transferred to the sales order. This case is described in more detail below.
If the Pos./neg. quantity indicator has the value "0"
The system creates a new network and, if applicable, a new project for the sales order. This new network and the old network, which was created from the quotation, are independent of each other.
For more information, see Copying Documents in the Sales component (SD-SLS).

The Pos./neg. quantity indicator should not have the value "-" in assembly processing. If however it does, the same network is used, as if the value were "+". However the quantity in the quotation would increase, rather than decrease.
Activities
When you create a sales order by converting a quotation, the system updates the network correspondingly. In the network header you can see both the quotation and the sales order. On the activity detail screen you can only see the original document, which is usually the quotation.
The account assignment object remains the same.