PS Material 漫谈 七: Project Stock
从MRP的角度, 项目有自己的库存. 物料以项目库存的方式进行管理.
每一个WBSe分别有individual stock segment. stock segment是永久性地分配给WBS element,从MRP角度看,其关系是1:1 .用户可以group “stock segments”与"project”. See Grouping for Individual Project Planning
对于项目库存,在做货物移动时,需要输入相关的WBSe.
项目库存可分为:
项目库存可用在make-to-order的生产如果:
- 用户想使用WBS来监测生产品在生产阶段产生的成本
- 从库存管理或物料计划角度看,有必要区别各个不同项目所需的物料.
- 在项目早期阶段,用户需要采购一个交货期很长的物料.
- You want to plan configurable materials, since MRP for configurable is only possible in individual stock.
1. Managing Stocks of Material Components
在network下的物料有以下几种不同的库存方式:
- Plant stock
- Sales order stock
- Project Stock
1.1 Logistical Processing and Project Stock
Activating Requirements
在PS中用户可以为项目库存创建不同类型的物料需求,即Project stock reservations or purchase requisitions.
A distinction is drawn between advance procurement and normal procurement for both non-stock components and stock components.
Material Requirements Planning
对每个拥有项目库存的WBSe,用户可以执行MRP.
当用户给network分配物料时,MRP相关的独立计划需求(Planned independent requirement)被创建. 根据物料主数据是如何维护的,MRP产生计划订单或采购需求. 这些凭证都分配给WBSE.
对于从属需求(Dependent requirement)也是同样的, 他们由多层BOM展开而创建出来,前提是BOM中的物料是以individual库存管理的形式进行维护.
See Material Requirements Planning in BOM Transfer
In-House Production
If planned orders are converted into production orders, the production orders and the components held in stock for them are assigned to the WBS element which is to carry the stock. Subsequent documents, such as material reservations and purchase requisitions, inherit this assignment via MRP-controlled components.
The production orders for semi-finished goods deliver the materials produced into project stock. You can then issue them from project stock to the productions for materials further down the production chain (superior items in the BOM).
External Procurement
You can create purchase requisitions for material components that are accounted to stock in the following ways:
- In the case of non-stock components, directly from the network
- In the case of stock components, in one of the following ways:
- - By converting planned orders
- - Using the MRP planning run
You then assign the purchase orders so generated to the stock-bearing WBS element. In purchasing, the purchase requisitions are then converted into purchase orders.
When you receive materials procured externally, you first post them to project stock. You can then reserve materials for the network or production order. The processing is different to direct procurement for networks (account assignment category F and account assignment object network or network activity).

In the standard system, account assignment category Q is used for items in purchasing documents
The stock-bearing WBS element acts as the account assignment element.
Material Movements
All material movements relating to materials managed as project stock pass through project stock. You post such movements using MM movement types, with special stock indicator Q.
 Material components with a negative quantity represent issues of material from the network activity to stock. The material is delivered to project stock.
Material components with a negative quantity represent issues of material from the network activity to stock. The material is delivered to project stock.
1.2 Costs in Complex Make-To-Order Production
The main feature of complex make-to-order production is that the product to be delivered requires order-specific changes or complete redesign. In such cases, you must plan and monitor costs and revenues at a detailed level.
Various process are available to handle this scenario:
- A: Cost object controlling using projects (Engineer-to-Order) for complex production, in this case, you can work with:
-
- Valuated project stock, in conjunction with cost and revenue bearing WBS elements
- Non-valuated project stock, in conjunction with cost and revenue bearing WBS elements
-
- B: Direct cost monitoring, using the sales order item where there is a connection to a sales order (make-to-order), in this case, you can work with:
-
- Valuated sales order stock, in conjunction with cost and revenue bearing sales order items
- Non-valuated sales order stock, in conjunction with cost and revenue bearing sales order items
-
For detailed information on the role of cost object accounting in complex make-to-order production, see  Product Cost by Sales Order in the Cost Object Controlling (CO-PC-OBJ) component.
Product Cost by Sales Order in the Cost Object Controlling (CO-PC-OBJ) component.
1.3 对于有价项目库存和无价值项目库存的限制
A: Constraints on working with valuated project stock:
- - Not possible to separate quantities and values
Since Release 3.0, it has been possible to use sales order stock in combination with projects (standard account assignment category D in sales order item). The quantities are managed in non-valuated sales order stock and the costs in WBS elements. This scenario cannot be supported for valuated sales order stock.
- - No complete actual costs from external procurement in projects
If price differences arise on receipt of the goods or during invoice verification, they are managed in Financial Accounting, with no other assignment. There is no additional debit to WBS elements.
B: Constraints on working with non-valuated project stock:
- - Incomplete actual costs in production orders or network activities
As withdrawing materials managed as project stock does not lead to a matching debit to the production order, the actual costs in the production order are not complete. Where production is multi-level, the production order shows only the additional value-added portions from the production level which arise from internal activities or material issues. The material costs for semi-finished goods are not included.
- - Complete actual costs only in the project
Costs from external procurement are posted directly to the stock-keeping WBS element, when the goods or the invoice are received. All the actual costs of manufacture for production are always debited to the project. You cannot use standard price evaluation for materials in individual stock. When the production orders are settled, no price differences are posted. This means that meaningful cost object accounting is only possible at WBS element or overall project level.
- - Incomplete plan costs for production orders and apportioned networks
The only place where you can obtain details on the full planned costs for network components managed in individual stock is in preliminary planning networks.
- - To calculate the WIP in the production orders assigned to the project, you must carry out profitability analysis for projects.
- - You cannot calculate variances in production orders.
- - Results analysis only makes a collective valuation of the different materials managed in project stock.
- - Transferring stocks is complicated because individual material prices do not appear in the stock. You must determine the material price manually and transfer it manually in CO.
- - Cross-company code processing requires corrections in Financial Accounting to be made manually.
2. 有价的项目库存Valuated Project Stock
有价的项目库存是以数量和价值基础进行管理. 每个物料的数量单位货币价值是分别计算的.All goods movements for the make-to-order stock trigger corresponding postings in the stock accounts in Financial Accounting.
从财务角度看,有价的项目库存比起无价的项目库存有如下优点:
· All goods movements are immediately reflected in Financial Accounting.
Viewed from Financial Accounting, the value flow is the same as for make-to-stock production. The system automatically capitalizes stock-relevant costs for finished or semi-finished goods when the goods are actually received. Goods issue postings lead to corresponding reductions in stock.
· Actual costs are complete at all production levels.
As goods issued from project stock lead to actual costs in the order, the system displays the complete actual costs in the order. Variance calculation is possible.
· Materials managed in project stock are valuated separately
Materials that are kept in project stock are valuated separately.
· Cross-company code material issues are possible, as are issues from orders for other projects.
· Simple processes are available for inventory processing and stock revaluation.
· Work in processing is calculated separately for production orders
Production orders for valuated individual stock are treated exactly the same as production orders for normal make-to-stock production, i.e. they are taken into account during results analysis for the project. To capitalize stockable costs from production orders, you may need to initiate a separate WIP calculation. This would not be necessary, for example, if all the costs in the production orders are shown as work in process in the reconciliation ledger and can be posted to Financial Accounting.
· Funds tied up in stock are shown in the WBS elements as statistical actual costs.
· Plan costs for material components managed as make-to-order stock are displayed in the production orders and management networks.
See Logistical Processing When Working with Project Stock and Constraints on Working with Valuated and Non-Valuated Project Stock
2.1 Valuated Project Stock: Scenario
2.1.1前提:
Project Definition
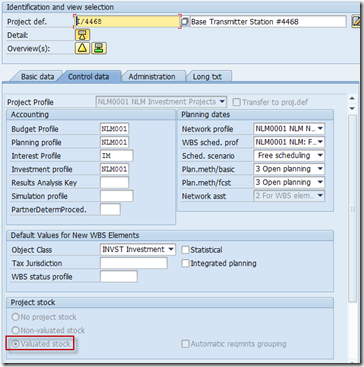
When creating a project, the Valuated project stock indicator must be set in the Project stock section in the project definition.
Material
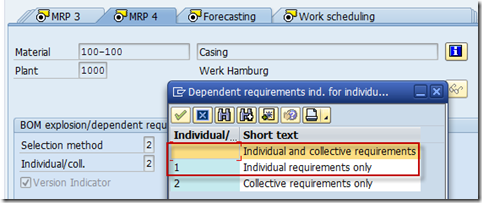
In the material master, the Individual/Collective indicator on the MRP 4 tab page must be set to Individual (1) or Individual/Collective ( ).
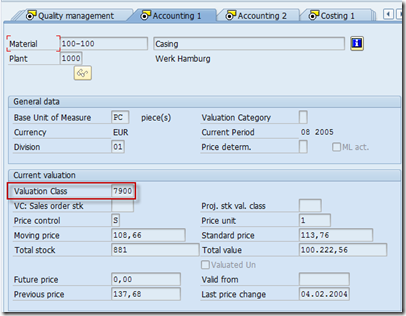
A valuation class for project stock must be entered in the relevant Accounting tab page. If you do not maintain a specific valuation class for the project stock, the system uses the valuation class from plant stock.
Cost Elements for Stock Accounts
In the stock bearing WBS elements, you can post statistical actual costs for the stock movements in and out to the stock accounts in Financial Accounting. You can then use the Project Information System to display the funds committed as stock.
In order for the stock lines from financial accounting documents to be posted as statistical actual costs in CO/PS, statistical cost elements of cost element type 90 for each of the relevant stock accounts have to be created.
2.1.2流程:
The description which follows only covers the special features for valuated individual stock. For a general description of the logistical processes, see 本文1.1 Logistical Processing When Working with Project Stock.
Planning
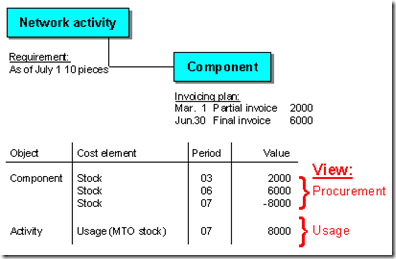
从network的成本计算角度看,在有价项目库存中, 有两种对物料的分配方法:
- From procurement, referencing the stock object (= WBS element)
- From usage, referencing the consumer (= network activity)
You can separate responsibilities for network activities and material components by entering different WBS assignments for them.
Looking at the component from the procurement point of view, it may be a good idea to undertake a cost component split (for example, in the form of a unit costing) if you are producing the component internally. If you are procuring externally, you may want to apportion the procurement costs over time (by, for instance, maintaining an invoicing plan). When the user (network activity, production order) draws the material, the procurement element is credited with the costs. In the period-related view of committed funds, the incurrence of costs is kept chronologically separate from forwarding of costs.
Looking at the component from the use point of view, it is the costs that are of interest; when these are incurred they are displayed, evaluated using a consumption cost element. In such cases, there is no difference between this and direct external procurement/general production, because the user is debited with the material price only.
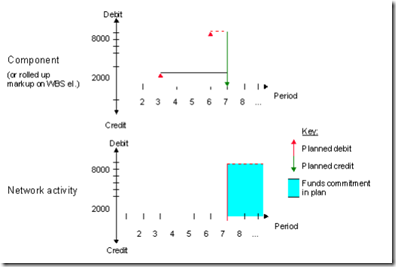
The diagram below shows the funds commitments in plan.
Note the following points relating to planning of components managed in individual stock:
- - Components managed as individual stock are managed as separate objects in the commercial PS object hierarchy and represent the procurement view. They are shown in the hierarchy directly under the relevant WBS element.
The following planned values are recorded directly in the component:
- Planned debits for procurement under an inventory cost element
- Planned credits for issues under an inventory cost element
If there is an invoicing plan for the component, the cost debits are evaluated as of the invoice dates and the credits as for the requirement dates. The planned credits are eliminated in the hierarchy reports in the costs information system as for internal business volume. The planned values for the components are not relevant for MRP In the case of non-stock components, the planned procurement payment flow - possibly based on the invoicing plan- is written to the component. The credit arising from the issue has no payment effect.
- - The consumption of material components managed as individual stock is shown in the relevant network activity or production order. The planned values are not relevant to MRP, regardless of the settings entered in the order type - that is, they are not included in the remaining order plan value in the WBS element. Consumption in the network activity has no payment effect.
- - Components that are procured in advance (preliminary purchase requisitions and planned independent requirements) are of no costing relevance as far as use in the network activity is concerned because they appear at other points in the project where they are used, either directly as network components or in lower BOM levels as components in production orders. Therefore components procured in advance are not valuated with planned costs in the network activity. Plan values in the component are recorded in the same way as for normal components (see first point in this list).
- - In the case of assembly items (network components with negative quantities), a planned credit is charged to the network activity and a planned debit to the network component as of the requirement date and in the amount of the component price. Unlike in components with positive quantities, there are no planned values from procurement in the component.

Planned cost values in the network component and planned payments in network activities and components are only generated using asynchronous network costing.
Valuated and non-valuated project stocks behave in the same way with regard to the MRP planning run.
In-House Production
The production orders are credited when the orders are delivered to stock. Higher-level production orders are debited as appropriate when semi-finished goods are taken from project stock. If this is the first delivery to project stock for that item, the system calculates a price in line with the price control data and values the quantity delivered accordingly. The goods issue is always valuated at the price in the individual stock segment.
External Procurement
The cost commitment arising from the purchase requisition/purchase order appears in the WBS element under a stock cost element.

For technical reasons, purchase requisitions created by the MRP planning run do not create cost commitments or payment obligations in the WBS elements to which they are assigned. This only happens when the purchase requisitions are converted into purchase orders.
The goods receipt is to project stock and is posted to the stock accounts in Financial Accounting.
When the invoice is received, an additional debit is entered for the material still in stock; or the value is posted to the price difference accounts, depending on price control .
Assembly in Networks
When you begin assembly using networks, goods are issued for the reservations. This leads to a reduction in stock and costs of consumption being posted to the network activity.
If you post a goods receipt to project stock using an assembly item in the network , the price of the component is credited to the relevant network activity and the stock value increases.
Delivery to Customer
When the goods are delivered to the customer, goods are issued for the reservations. Project stock is credited and appropriate cost postings take place to the relevant network activities.
Period-end closing
Commercially speaking, period-end closing for production orders is the same as for normal make-to-stock production.
The production orders have a settlement rule (received when planned orders are converted) where the project stock is entered as the settlement receiver.
You can carry out the following closing operations in the production orders:
- - WIP calculation
- - Variance calculation
- - Order settlement
The balance remaining after actual costs incurred and the delivery create have both been posted is charged to stock or the price different account, depending on the price control data specified. In addition, variances in the production orders are passed on to Profitability Analysis (CO-PA).

Profitability Analysis in WBS elements does not include the values from production orders assigned to the elements.
2.2 Quantities and Values in Valuated Project Stock: Example
The current example illustrates only the special points which affect project stock. For a detailed example illustrating the quantity and value flow in relation to valuated sales order stock, see  Example Customer Project - Controlling with valuated Customer Project stock: Flow of Quantities and Values in the Cost Object Controlling (CO-PC-OBJ) component.
Example Customer Project - Controlling with valuated Customer Project stock: Flow of Quantities and Values in the Cost Object Controlling (CO-PC-OBJ) component.
前提:
The following statements apply only when the sales order item carries costs and revenues:
- The sales order item is charged with actual costs - that is, the functions of Product Cost by Sales Order are used.
- The funds commitment in inventory can be seen on the sales order item.
This example uses a valuated sales order stock.
Planning
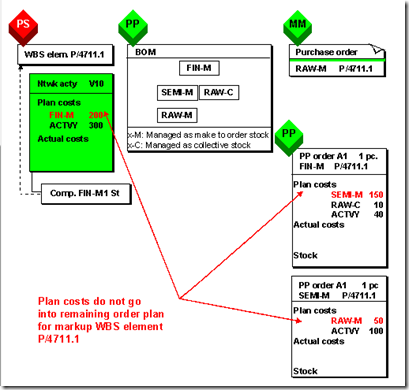
Material FIN-M is assigned to network activity V10 and is managed in the project stock for WBS element P/4711.1.
The network type is flagged as appended and apportioned to the WBS.
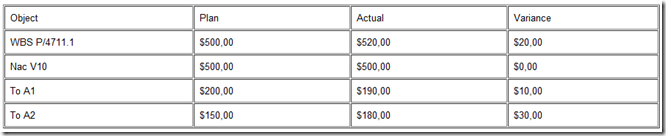
Before the first MRP planning run or before the planned orders are converted into purchase requisitions or production orders, the following amounts appear in WBS element P/4711.1:
- Planned costs of $500,00
- Remaining order plan value of $300,00
The MRP controller begins by converting the planned orders. First, the planned order for the material RAW-M is converted into a purchase requisition and the planned order for the material SEMI-M is converted into production order A2.
The order type is flagged as not appended and apportioned to the WBS.
The remaining order plan value in the WBS element changes by the amount of the internal activities portion of production order A2 to $400,00 (300,00 + 100,00).
After the purchase requisition is converted into a purchase order, a cost commitment of $50,00 also appears in WBS element P/4711.1.
External Procurement
Valuated goods are received for the purchase order, but the price is $10 different at $60. Assuming that material RAW-M is price-controlled, this gives rise to a debit posting of $60,00 in the stock account and credit posting of $60 in the GR/IR clearing account (Financial Accounting).
If the inventory accounts was created as a cost element in CO, the following appear in WBS element P/4711.1:
- Statistical actual costs of $60,00 in the stock cost element
- A cost commitment of $0,00
If material RAW-M is price-controlled the standard price is $50,00, the postings in Financial Accounting are: $50,00 debit to a stock account $10,00 debit to a price difference $60,00 credit to the GR/IR clearing account
In this case, the only figure in the WBS element would be statistical actual costs of $50,00.
In-House Production
Production order A2 is released. Material RAW-M is issued from project stock. The costs of $60,00 are debited to production order A2 under a consumption cost element. The credit posting is to WBS element P/4711.1 under the statistical stock cost element. As the production order is assigned to the WBS element, $60,00 in actual costs continue to appear there.
The completion confirmation settles internal activity costs of $120,00. The order plan value caused by production order A2 in WBS element P/4711 is reduced to zero. The production order shows work in progress valued at $180,00.
Material SEMI-M is then delivered into project stock.
If this is the first delivery, the system will valuate the goods based on the production order costing. $150,00 are credited to the production order and debited to the WBS element with statistical actual costs under a stock cost element.
If the planned order for material FIN-E is converted into production order A1, the remaining order plan value in the WBS element rises by $40,00 + $10,00 = $50,00.
Material issues of $150,00 for SEMI-M and $10,00 for RAW-C and internally activity costs of $30,00 lead to WIP of $190,00 in production order A1. These are delivered to project stock at a price of $200,00. An order plan value of $10,00 remains in the WBS element until the production order is completed technically.
Assembly in Networks
If material FIN-M is assembly on the customer’s own premises, a delivery from the project may take place at this point.
For more information, see Delivery from Projects
From the accounting point of view, the delivery is treated in a way similar to that for a "normal" goods issue to the network activity.
This means that $200,00 is credited to the WBS element under the stock cost element and debited to the network activity under a material consumption cost element.
The completion confirmation from assembly activity increases the actual costs in the activity by $300,00.
The hierarchy reports in the PS Information System show the following values in the individual objects:
Period-end closing
After delivery, production order A1 has a negative balance (reserve for missing costs) of $10,00. A2 has a positive balance (WIP) of $30,00. As there is no more project stock, the amounts are settled to price difference accounts. In the case of production order A1, the debit posting is to change of stock and the credit to the price difference account. The reverse is true for A2.
2.3 Valuation of Material Components
Use
The system valuates material components in valuated stock according to the strategy below.
During the first goods receipt, the system saves a standard price in the individual stock segment for a material, plant and WBS element. Afterwards you can only change this price by using Transaction MR21. If the standard price was determined during the first goods receipt, for example by using User-Exit COPCP002, it is not determined during further goods receipts.
In the case of materials with moving average prices, the system also determines the moving average price for each goods movement.

You cannot create segments with Transaction MR21.
Features
For goods movements the system valuates material components in valuated stock according to the following strategy.
- It uses the standard price from the individual stock segment for the combination of WBS element, plant and material. The system determines the standard price for the individual stock segment during the first goods receipt.
- If applicable, it uses the valuation from User-Exit COPCP002.
- If a sales order item is account assigned to the WBS element and there is a product costing for the sales order item, the system looks for the corresponding costing item and uses this for the valuation, if the costing allows this. Only those costs are copied that are relevant for stock valuation.
- It uses the value from the unit costing for the material component in the network or from the Seiban product costing. You must have previously activated Seiban product costing with Transaction CKW4.
- The system uses the production order costing for material, plant and WBS element. The production order must have been costed without any errors.
- The system uses the price from the material master.
The strategy is determined in the above sequence in the following cases:
- For valuating the first goods receipt, whereby strategy 1 cannot be used.
- For valuating components for the preliminary costing of production orders or networks (only item category L)
- For valuating planned and actual credits to a production order

You can use unit costing for a material component in a network to define a price for valuation. Since only one standard price is saved for each combination of material plant and WBS element, it is pointless to execute another unit costing for the same combination, for example for another network. The system always uses the value it determined first.
3. Non-valuated project stock
Definition
Project stock where each material is managed on a quantity basis only, without being valuated directly in terms of money. Goods movements to individual stock are not valuated and do not give rise to postings in Financial Accounting. In general you calculate the value of the project stock in total at the period end by results analysis; the values are then transferred to Financial Accounting.
Use
From the accounting point of view, working with valuated project stock offers the following advantages over working with non-valuated project stock:
- Compatibility with data in releases prior to 4.0A.
- All the actual production costs appear in the project because no price variances can occur and all external procurement follow-up costs are debited to the WBS element.
- You can use project resource-related billing and show the goods receipt as an expense to be billed.
- There are view line items relevant to billing because there are no CO documents for goods movements between project and production orders/networks.

Unless you are compelled by the need for compatibility with earlier data to use non-valuated project stock, we recommend that you use valuated project stock because future program development will extend this functionality.
You cannot convert existing projects with non-valuated individual stock.
3.1 Non-Valuated Project Stock: Scenario
Prerequisites
The Non-valuated project stock indicator must be set in the project definition.
In the material master, the Individual/Collective indicator on the MRP 4 tab page must be set to Individual (1) or Individual/Collective ().
Process Flow
The text which follows describes only the special features of non-valuated make-to-order stock. For a general description of the logistical processes, seeLogistical Processing When Working with Project Stock.
Planning
You only obtain complete planned costs for network components managed in individual stock in planning networks because these networks are only intended for use in planning and never carry actual costs. The planned costs for these components do not appear in apportioned orders because no actual costs arise on the non-valuated goods issues arising when these are used; this is the only way that a meaningful plan/actual comparison can be guaranteed.
Additional planning of production costs - using, for example, a unit costing in the WBS - may be necessary because results analysis requires complete cost planning.
No planned value flow is updated to non-stock components.
Valuated and non-valuated project stocks behave in the same way with regard to the MRP planning run.
In-House Production
The production orders created when planned orders are converted have a settlement rule, which stipulates the stock-bearing WBS element as the settlement receiver.
The production orders are not credited when the material is delivered to stock. Only the quantity is posted as a receipt to stock. Similarly, no costs are debited to the production order when you draw semi-finished goods from project stock.
All internal activity/material costs arising when you draw on general plant stock are settled to the WBS element.
External Procurement
External procurement via project stock follows the same cost procedure as direct procurement for the project.
The cost commitment arising from the purchase requisition or purchase order appears under a material consumption cost element in the WBS element.

For technical reasons, purchase requisitions created by the MRP planning run do not create cost commitments or payment obligations in the WBS elements to which they are assigned. This only happens when the purchase requisitions are converted into purchase orders.
Goods received are posted on a quantity basis to project stock. When valuated goods are received, the costs are posted to the WBS element as an expense, under a material consumption cost element.
When the invoice is received, an additional debit is entered (or a first debit if the goods receipt was not valuated) to the WBS element, under an material consumption cost element.
Assembly in Networks
When you begin assembly using networks, goods are issued from goods reservations. This leads only to quantity-based stock reductions. No consumption costs are debited to the network activity, meaning that the actual costs remain in the WBS element.
If you use an assembly item in the network to post an addition to project stock, there is no credit posting to the relevant network activity. The project stock managed on a quantity-basis is increased; no debit posting is made to the WBS element.
Delivery to Customer
When you deliver to your customer, non-valuated goods are issued from reservations. The project stock is credited on a quantity basis only. No cost postings are made in the affected WBS elements or network activities.
Period-end closing
The values of assigned production orders are included in results analysis for WBS elements because the incompleteness of the actual costs in the production orders makes it impossible to determine separate values for WIP and variances in these production orders.
For a complete example illustrating the quantity and value flow using non-valuated sales order stock, see  Example: Non-Valuated Sales Order Stock in the Product Cost Controlling (CO-PC) component.
Example: Non-Valuated Sales Order Stock in the Product Cost Controlling (CO-PC) component.
3.2 Non-Valuated Sales Order Stock Assigned to Projects: Scenario
Purpose
There are various ways of processing complex make-to-order production. If you want to process customer projects using the Project System, you can either use project stock or non-valuated sales order stock, with account assignment to your project.
This scenario has quantity-based inventory management being processed using the sales document item. The values for all the relevant postings are assigned to the non-valuated project stock.
To be able to use this scenario, use a requirement class with account assignment category D (standard customizing) for your sales document item. This account assignment category controls the following:
- The quantities for the sales document item by means of special stock indicator E
- The values in the WBS elements, by means of consumption indicator P
The advantage of this scenario is that there is only one stock (as viewed from MRP). The MRP planning run can simply assign the elements, triggering and covering material requirements in this stock.
There are also disadvantages to this scenario, arising from the use of non-valuated project stock.