第13周作业集
题目1:
创建两个线性表,分别存储{“chen”,“wang”,“liu”,“zhang”}和{“chen”,“hu”,“zhang”},求这两个线性表的交集和并集。
代码:
1 package 交集并集; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 5 /** 6 * 7 * 利用retainAll方法求交集,将两个字符集合在一起去掉相同的元素,然后添加上交集求并集。 8 */ 9 public class Test { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 ArrayList<String> array1 = new ArrayList<String>(); 12 ArrayList<String> array2 = new ArrayList<String>(); 13 ArrayList<String> intersection = new ArrayList<String>(); 14 ArrayList<String> unionsection = new ArrayList<String>(); 15 array1.add("chen"); 16 array1.add("wang"); 17 array1.add("liu"); 18 array1.add("zhang"); 19 array2.add("chen"); 20 array2.add("hu"); 21 array2.add("zhang"); 22 // 求交集 23 intersection = array1.size() > array2.size() ? new ArrayList<String>(array1) : new ArrayList<String>(array2); 24 intersection.retainAll(array1.size() < array2.size() ? array1 : array2); 25 System.out.println("交集:" + intersection); 26 // 求并集 27 unionsection.addAll(array1); 28 unionsection.addAll(array2); 29 unionsection.removeAll(intersection); 30 unionsection.addAll(intersection); 31 32 System.out.println("并集:" + unionsection); 33 34 } 35 }
截图:

题目2:
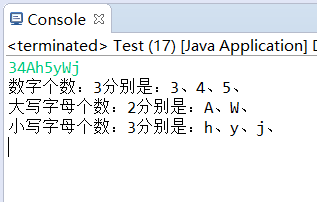
编写一个应用程序,输入一个字符串,该串至少由数字、大写字母和小写字母三种字符中的一种构成,如“123”、“a23”、“56aD”、“DLd”、“wq”、“SSS”、“4NA20”,对输入内容进行分析,统计每一种字符的个数,并将该个数和每种字符分别输出显示。如:输入内容为“34Ah5yWj”,则输出结果为:数字——共3个,分别为3,4,5;小写字母——共3个,分别为h,y,j;大写字母——共2个,分别为A,W。
代码:
1 package 统计; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.Map; 6 import java.util.Scanner; 7 import java.util.Set; 8 9 /** 10 * 11 * 将字符串拆分成字符数组放入哈希表key上,并在value上表示该字符个数。 利用迭代器遍历哈希表,并判断记录下来,最后输出。 12 * 13 */ 14 public class Test { 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 HashMap<Character, Integer> hm = new HashMap<>(); 17 String s = new Scanner(System.in).next(); 18 char[] ch = s.toCharArray(); 19 for (char c : ch) { 20 if (!hm.containsKey(c)) { 21 hm.put(c, 1); 22 } else { 23 hm.put(c, hm.get(c) + 1); 24 } 25 } 26 int[] num = new int[4]; 27 Set set = hm.entrySet(); 28 Iterator i = set.iterator(); 29 StringBuffer n = new StringBuffer(); 30 StringBuffer d = new StringBuffer(); 31 StringBuffer x = new StringBuffer(); 32 while (i.hasNext()) { 33 Map.Entry me = (Map.Entry) i.next(); 34 35 if (me.getKey().toString().charAt(0) >= '0' && me.getKey().toString().charAt(0) <= '9') { 36 num[0] += Integer.parseInt(me.getValue().toString()); 37 n.append(me.getKey().toString().charAt(0)); 38 n.append("、"); 39 } 40 if (me.getKey().toString().charAt(0) >= 'A' && me.getKey().toString().charAt(0) <= 'Z') { 41 num[1] += Integer.parseInt(me.getValue().toString()); 42 d.append(me.getKey().toString().charAt(0)); 43 d.append("、"); 44 } 45 if (me.getKey().toString().charAt(0) >= 'a' && me.getKey().toString().charAt(0) <= 'z') { 46 num[2] += Integer.parseInt(me.getValue().toString()); 47 x.append(me.getKey().toString().charAt(0)); 48 x.append("、"); 49 } 50 } 51 System.out.println("数字个数:" + num[0] + "分别是:" + n); 52 System.out.println("大写字母个数:" + num[1] + "分别是:" + d); 53 System.out.println("小写字母个数:" + num[2] + "分别是:" + x); 54 55 } 56 }
截图:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号