CS144-Lab0-networking warmup
lab 地址 :lab0-doc
代码实现:lab0-code
0. ByteStream
1. StreamReassembler
2. TCPReceiver
3. TCPSender
4. TCPConnection
5. ARP
6. IP-Router
1. 目标
1.1 获取网页内容
实现 webget。一个使用操作系统的TCP支持和 Socket 抽象通过 Internet 获取网页的程序。步骤大致如下:
1.从构建目录中,打开文件/文本编辑器或IDE中的 apps/webget.cc。
2.在getURL函数中,找到以 “//Your code here” 开头的注释
3.使用前面使用的HTTP(Web)请求格式实现本文件中描述的简单Web客户端。使用 TCPSocket 和 Address 类。
- HTTP中,每行必须以
“\r\n”结尾- 请求中需要包含“Connection:Close”一行。这告诉服务器,在这一次之后,它不应该等待您的客户端再发送任何请求。相反,服务器将发送一个回复,然后立即结束其输出字节流(从服务器套接字到套接字的字节流)。您将发现传入的字节流已经结束,因为当您读取来自服务器的整个字节流时,套接字将到达“EOF”(文件结尾)。这就是您的客户机如何知道服务器已完成其回复。
- 确保读取并打印服务器的所有输出,直到套接字到达“EOF”(文件结尾)-仅调用一次读取是不够的。
1.2 可靠字节流
为了完成本周的实验,您将在一台计算机的内存中实现一个提供这种抽象的对象:ByteStream。
- 字节写在“输入”端,可以从“输出”端以相同的顺序读取。
ByteStream是有限的:写入器可以结束输入,然后再也不能写入字节。- 当读取器读取到流的末尾时,它将到达“EOF”(文件末尾),无法读取更多字节。
ByteStream被初始化为具有特定的“容量”:在任何给定时间点,它愿意存储在自己的内存中的最大字节数。ByteStream将限制写入器在任何给定时刻的写入量,以确保流不会超过其存储容量。- 当读取器读取字节并将其从流中排出时,写入器可以写入更多字节。
ByteStream用于单个线程,您不必担心并发写入器/读取器、锁定或竞争条件。
2. 实现
2.1 webget
实现上比较简单,主要就是:
- 创建 socket
- 连接目标 host,port 为默认的 http 端口
- write 写入 http header
- read socket 并打印到终端
// should use TCPClient void get_URL(const string &host, const string &path) { // Your code here. // 1. init socket TCPSocket socket; // 2. connect to host socket.connect(Address(host, "http")); // 3. send request path socket.write("GET " + path + " HTTP/1.1\r\n"); socket.write("HOST: " + host + "\r\n"); socket.write("Connection: close\r\n"); socket.write("\r\n"); // 4. read response data while(!socket.eof()) cout << socket.read(); // You will need to connect to the "http" service on // the computer whose name is in the "host" string, // then request the URL path given in the "path" string. // Then you'll need to print out everything the server sends back, // (not just one call to read() -- everything) until you reach // the "eof" (end of file). }
2.2 ByteSteam
实现一个可靠的字节流类,支持 写入 & 读出,有固定的 capacity,从功能上来说,ByteStream 与 队列的特性非常相似,先进先出,写入的时候顺序排列在字节流后面,读取的时候从头部开始读取并且 pop 出来。
这里选择使用 vector 作为字节流容器(感觉用 queue 就太简单了其次感觉效率没有 vector 高),初始化时直接 reserve 分配好空间,防止 push_back 时 copy 数据造成额外消耗。
读取和写入的接口如下:
// Write a string of bytes into the stream. Write as many // as will fit, and return the number of bytes written. size_t write(const std::string &data); // Returns the number of additional bytes that the stream has space for std::string read(const size_t len);
写入和读取的思路如下,添加 begin 和 end 两个变量用来维护区间,写入时正常 push_back 字符,读取时只需要移动 end 即可,使用 begin 和 end 的时候再对 capacity 取 mod 即可:
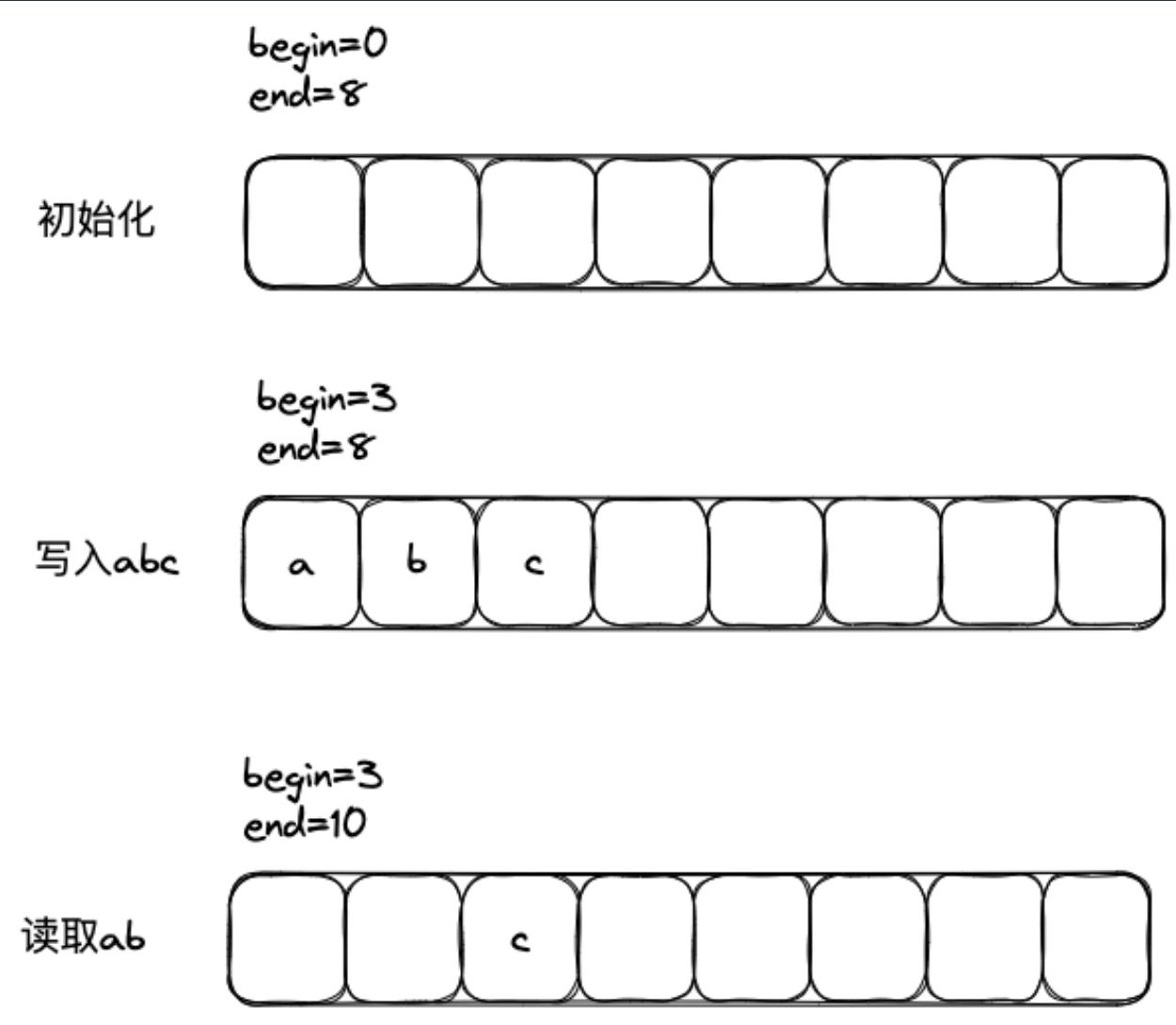
核心代码如下(完整参考 lab0-code)
//! Read (i.e., copy and then pop) the next "len" bytes of the stream //! \param[in] len bytes will be popped and returned //! \returns a string std::string ByteStream::read(const size_t len) { string read_result; int read_size = min(buffer_size(), len); for (int i = _end; i < _end + read_size; i++) { int real_index = i % _capacity; read_result += _data[real_index]; } _total_read += read_size; _end += read_size; return read_result; } size_t ByteStream::write(const string &data) { int write_size = min(data.size(), remaining_capacity()); for (int i = _begin, j = 0; i < _begin + write_size; i++, j++) { int real_index = i % _capacity; _data[real_index] = data[j]; } _begin += write_size; _total_written += write_size; return write_size; }
其次有一点需要注意的是,ByteStream 的 eof 判断条件是需要 不会再有写入(调用了 end_input),且缓存都被读取完毕,才会返回 true。
3. 测试






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本