嵌套类的作用:
被包含的类可以就是为其外层类服务而存在的,因此它不必向外界暴露。(说得简单点儿,被包含类只是一个辅助类)可以在外层类的定义中定义辅助类。这种被包含的内部类我们称之为嵌套类(nested class),而包含它的类我们直接称为外层类(outer class)。从面向对象的方式来思考,嵌套类所面向的对象就是外层类,它主要就是给外层类服务的。
嵌套类的好处:
嵌套类的好处是可以对外层类的所有成员进行访问。嵌套类的方法可以访问外层类的私有成员。如果嵌套类声明的是private的,那么它对除了它的外部类之外的所有类隐藏,如果嵌套类声明是public的,那么可以使用外层类.嵌套类的方式来访问嵌套类。
下面看个例子:
| using System; |
| using System.Collections.Generic; |
| using System.Linq; |
| using System.Text; |
| namespace NestedClass |
| { |
| class InnerAndOuter |
| { |
| public static int _Aint; |
| private int _instanceInt; |
| private static void Amethod() |
| { |
| Console.WriteLine(_Aint); |
| } |
| private void ShowInstanceInt() |
| { |
| Console.WriteLine(this._instanceInt); |
| } |
| public void SayIt() |
| { |
| InnerClass.Method(this); |
| } |
| #region 嵌套类定义 |
| private class InnerClass |
| { |
| public static void Method(InnerAndOuter io) |
| { |
| _Aint = 100; |
| Amethod(); |
| io._instanceInt = 10; |
| io.ShowInstanceInt(); |
| } |
| } |
| #endregion |
| } |
| } |
从上面可以看出,嵌套类可以访问外部类的所有字段和方法,包括私有的。
但是外部类只能够访问修饰符为public、internal嵌套类的字段、方法、属性。示例如下:
| public class A |
| { |
| public static void AMethod() |
| { |
| //成功 |
| NestedA.StaticMethod(); |
| //编译报错 |
| NestedA._Int = 100; |
| NestedA ins=new NestedA(); |
| //成功 |
| ins.Method(); |
| //编译报错 |
| ins._instanceInt = 100; |
| } |
| /*嵌套类 定义*/ |
| private class NestedA |
| { |
| private static int _Int; |
| private int _instanceInt; |
| public static void StaticMethod() { } |
| public void Method(){} |
| } |
| } |
嵌套类与外部类的沟通方法:
嵌套类访问外部类实例的方法、字段、属性时候。一般在采取构造函数输入外部类,或者外部类的实例作为嵌套类方法的参数。如下:
| public class A |
| { |
| private int _a; |
| /*嵌套类 定义*/ |
| private class NestedA |
| { |
| public NestedA(A a) |
| { |
| a._a = 9; |
| } |
| } |
| } |
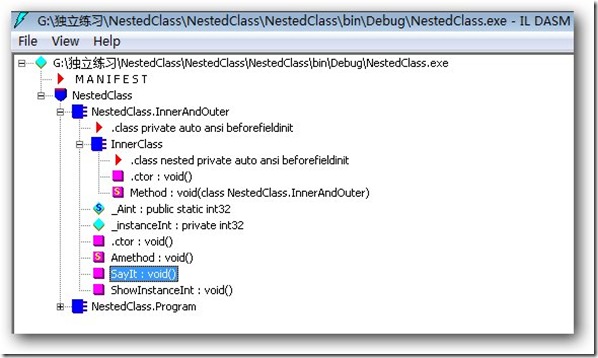
下面我们来看看第一段代码的反编译面目:
从上图中可以看出,在InnerAndOuter类中包含InnerClass类的定义,嵌套类看起来跟其他类内部的成员一么一样。
接着我们来看看外部类的SayIt方法:
| .method public hidebysig instance void SayIt() cil managed |
| { |
| // Code size 9 (0x9) |
| .maxstack 8 |
| IL_0000: nop |
| IL_0001: ldarg.0 |
| IL_0002: call void NestedClass.InnerAndOuter/InnerClass::Method(class NestedClass.InnerAndOuter) |
| IL_0007: nop |
| IL_0008: ret |
| } // end of method InnerAndOuter::SayIt |
注意看调用嵌套类的方法时,il不是使用.操作符,而是使用了/操作符。
嵌套类的继承:
继承类,也就是继承类外部类的类,只能使用父类中嵌套类的public或者internal(同一个程序集合)方法。但是继承类可以再定义一个内嵌类并从继承父类中嵌套类。如:
| public class A |
| { |
| /*嵌套类 定义*/ |
| protected class Nested |
| { |
| protected virtual void BaseNested_Method(){} |
| } |
| } |
| public class C : A |
| { |
| /*内嵌类 定义*/ |
| protected class C_Nested:Nested |
| { |
| protected override void BaseNested_Method() |
| { |
| //重写部分 |
| } |
| } |
| } |
因为C中A中继承,因此C_Nested可以继承Nested类,从而获取重写父嵌套类的机会。但是Nested必须是可继承类及可访问的(非private 、sealed、static)。
嵌套类可以随意外部类的任何数据属性,而外部类访问嵌套类就只能遵守访问修饰符。从这个角度看,嵌套类是外部类的补充,通过嵌套类可以获取更好的封装性,增加外部类的可维护性和可读性。
从程序结构看,嵌套类在逻辑上更加接近使用类。可以更有效地表示类与类之间的紧密程度。为类管理提供除命名空间外的另一种方法。
懒加载:
嵌套类的静态构造函数不会随着外部类的触发而初始化。因此可以有效地避免创建时候初始化时间,当需要使用内嵌类的时候,嵌套类才开始初始化才开始初始化。
| public class Outside |
| { |
| static Outside() |
| { |
| Console.WriteLine("Outside Inilizlized"); |
| } |
| public void SayIt() |
| { |
| Nested.Run(); |
| } |
| private class Nested |
| { |
| static Nested() |
| { |
| Console.WriteLine("Nested initilized"); |
| } |
| public static void Run() |
| { |
| Console.WriteLine("Nested Run"); |
| } |
| } |
| } |
执行结果:
| Outside o = new Outside();//打印"Outside Inilizlized" |
| Console.ReadLine(); |
| o.SayIt();//首先打印"Nested initilized" 再打印 "Nested Run" |
| Console.ReadLine(); |
一般应用这个特性会在一些C#单例模式中找到,而这种模式可以被称为Fully lazy singleton模式。
| public class Singleton |
| { |
| public static Singleton Instance |
| { |
| get |
| { |
| return Nested.instance; |
| } |
| } |
| private class Nested |
| { |
| public readonly static Singleton instance=new Singleton(); |
| } |
| } |
嵌套类的反射:
类定义:
| namespace InsideClass |
| { |
| public class A |
| { |
| public class Nested |
| { |
| protected void BaseNested_Method() |
| { |
| } |
| } |
| } |
| } |
反射:
| //如果嵌套类在外部类中声明为private的,即外部不可见的,那么下面这种方法可以实例化它 |
| object o = System.Activator.CreateInstance("NestedClass", "NestedClass.InnerAndOuter+InnerClass"); |
| //如果嵌套类在外部类中声明为public或者internal的,即外部可见的,那么下面这种方法也行 |
| object o2 = Activator.CreateInstance( typeof(NestedClass.InnerAndOuter.InnerClass), new string[] { }); |