【树】二叉树的应用 I
1. 题目列表
| 序号 | 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 226. 翻转二叉树 | 简单 |
| 2 | 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 | 中等 |
| 3 | 114. 二叉树展开为链表 | 中等 |
| 4 | 652. 寻找重复的子树 | 中等 |
2. 应用
2.1. Leetcode 226. 翻转二叉树
2.1.1. 题目
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
2.1.2. 解题思路
2.1.2.1. 方法一:前序遍历
我们可以考虑在进入每个节点之前,在前序的位置交换每个节点的左右子树。
2.1.2.2. 方法二:后序遍历
我们也可以考虑在离开每个节点之后,在后序的位置交换每个节点的左右子树。
2.1.3. 代码实现
- 方法一:前序遍历
class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) { return dfs(root); } private TreeNode dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return null; } TreeNode temp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = temp; dfs(root.right); dfs(root.left); return root; } }
- 方法二:后序遍历
class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) { return dfs(root); } private TreeNode dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return null; } TreeNode right = dfs(root.right); TreeNode left = dfs(root.left); root.left = right; root.right = left; return root; } }
2.2. Leetcode 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
2.2.1. 题目
给定一个 完美二叉树 ,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node { int val; Node *left; Node *right; Node *next; } 填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
输出:[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
解释:给定二叉树如图 A 所示,你的函数应该填充它的每个 next 指针,以指向其下一个右侧节点,如图 B 所示。序列化的输出按层序遍历排列,同一层节点由 next 指针连接,'#' 标志着每一层的结束。
2.2.2. 解题思路
2.2.2.1. 方法一:广度优先搜索
我们可以使用广度优先搜索的思路,将每一层的元素依次指向右侧的元素即可。
2.2.2.2. 方法二:深度优先搜索
我们使用深度优先搜索的思路,同时搜索一个节点的左右子树,将每一个左子树的根节点指向,右子树的根节点即可。
同时,我们还需要将当前节点的右子树,与同层的相邻节点的左子树相连。
2.2.3. 代码实现
- 方法一:广度优先搜索
class Solution { public Node connect(Node root) { if (root == null) { return null; } bfs(root); return root; } private void bfs(Node root) { Deque<Node> queue = new ArrayDeque<>(); queue.offer(root); root.next = null; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); Node last = null; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { Node candidate = queue.poll(); if (candidate.left != null) { queue.offer(candidate.left); } if (candidate.right != null) { queue.offer(candidate.right); } if (last != null) { last.next = candidate; } last = candidate; } last.next = null; } } }
- 方法二:深度优先搜索
class Solution { public Node connect(Node root) { if (root == null) { return null; } dfs(root.left, root.right); return root; } private void dfs(Node p, Node q) { if (p == null || q == null) { return ; } p.next = q; dfs(p.left, p.right); dfs(p.right, q.left); dfs(q.left, q.right); } }
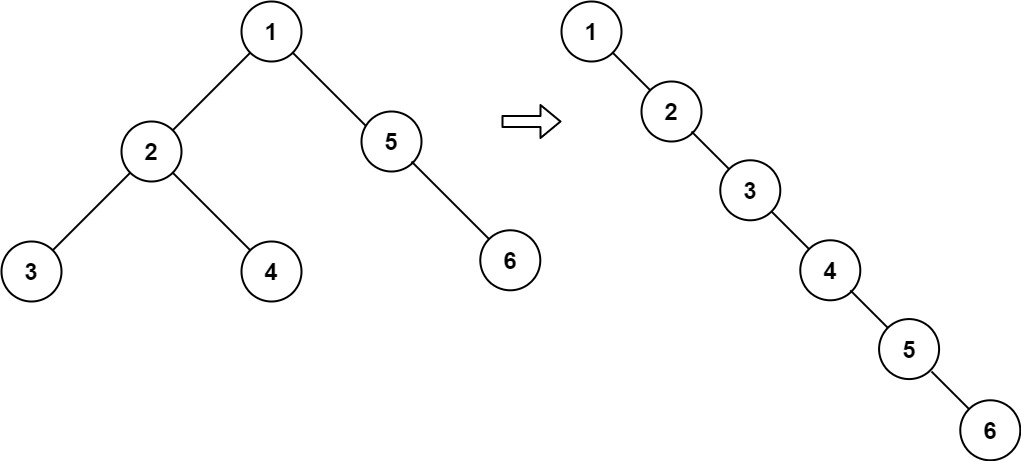
2.3. Leetcode 114. 二叉树展开为链表
2.3.1. 题目
给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你将它展开为一个单链表:
- 展开后的单链表应该同样使用 TreeNode ,其中 right 子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为 null 。
- 展开后的单链表应该与二叉树 先序遍历 顺序相同。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6]
输出:[1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
2.3.2. 解题思路
比较直观的思路,是在每一个节点的后序遍历的位置,将它的左子树插入到它的右子树的位置,然后将原始的右子树连接到新的右子树尾部。
2.3.3. 代码实现
class Solution { public void flatten(TreeNode root) { dfs(root); } private TreeNode dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return null; } TreeNode left = dfs(root.left); TreeNode right = dfs(root.right); // 将左子树插入到右子树的位置 root.left = null; root.right = left; // 将原始的右子树接到新的右子树尾部 TreeNode node = root; while (node.right != null) { node = node.right; } node.right = right; return root; } }
2.4. Leetcode 652. 寻找重复的子树
2.4.1. 题目
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回所有 重复的子树 。对于同一类的重复子树,你只需要返回其中任意 一棵 的根结点即可。如果两棵树具有 相同的结构 和 相同的结点值 ,则认为二者是 重复 的。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,null,2,4,null,null,4]
输出:[[2,4],[4]]
2.4.2. 解题思路
这里是在求相同的子树,所以,我们很容易想到在后序遍历的位置,在离开每一个节点时,记录当前节点及其子树的状态,这里我们可以考虑使用字符串序列化每一个子树的状态。
同时,为了去重,我们可以使用一个哈希表来记录已有的结果,如果遇到重复的子树,只添加一次即可。
注意,序列化一棵子树的顺序一定要和访问这棵子树的顺序相同。
例如,如下代码实现是按照后序遍历,即访问顺序为:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根节点,那么,序列化的时候,也要按照相同的方式记录后序遍历的路径。
2.4.3. 代码实现
class Solution { public List<TreeNode> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode root) { List<TreeNode> result = new ArrayList<>(); Map<String, Integer> cache = new HashMap<>(); dfs(root, result, cache); return result; } private String dfs(TreeNode root, List<TreeNode> result, Map<String, Integer> cache) { if (root == null) { return "#"; } String left = dfs(root.left, result, cache); String right = dfs(root.right, result, cache); String subTree = left + "." + right + "." + root.val; int count = cache.getOrDefault(subTree, 0); if (count == 1) { result.add(root); } cache.put(subTree, count + 1); return subTree; } }
参考:
本文作者:LARRY1024
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/larry1024/p/17991436
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步