【最短路径】Dijkstra算法
Dijkstra算法
给定一个源顶点 \(s\) 从一组顶点 \(V\) 在加权有向图中,其中所有边权重 \(w(u, v)\) 均是非负的,找到最短路径权重 \(d(s, v)\) 从源头 \(s\) 对于所有顶点 \(v\) 出现在\(Graph\)中。
\(Dijkstra\) 算法是一种求解非负权图上单源最短路径的算法。
算法分析
我们以下图为例,计算起点 \(A\) 到每个顶点的最短距离:
我们先定义一个 \(distances[5]\) 数组,用于记录起点到所有顶点的距离,这里我们假设数组中的元素序号 0 ~ 4 分别表示顶点 A ~ E ,将数组中的所有元素都初始化为无效值(或者无穷大),即:
初始条件
由于,我们从顶点 \(A\) 开始,所以顶点 \(A\) 的距离为 \(0\),即 \(distances[0] = 0\) 。

第一次查找
我们用\(S\)记录最短路径,从顶点A开始计算A的邻居节点B,E,由于B可以通过A直接到达,我们暂时记录 \(S_{AB} = 10\),,同理,顶点A到顶点E的距离 \(S_{AE} = 3\),即

第二次查找
我们考虑,从 \(\{S_{AB},\ S_{AE}\}\) 中选择权重最小的边 \(S_{AE}\)作为路径,继续查找:

第三次查找

第四次查找

第五次查找

第六次查找

代码模板
这里我们直接给出代码模板:
import heapq
from typing import List, Tuple
class NodeState(object):
def __init__(self, node_id: int, distance: int = 0):
# 节点id
self._id = node_id
# 从起点到当前节点的距离
self._distance = distance
def get_id(self):
return self._id
def get_distance(self):
return self._distance
def __lt__(self, other):
""" 小的节点在堆顶 """
return self.get_distance() - other.get_distance()
def dijkstra(start: int, graph: List[List[Tuple[int]]]):
""" 单源最短路径:计算从起点到每个节点的距离
:param start: 起点
:param graph: 邻接表
:return:
"""
distances = [float("INF")] * len(graph)
distances[start] = 0
# 使用优先级队列保存所有的节点,保证堆顶的元素最小
queue = list()
heapq.heappush(queue, NodeState(start, 0))
while len(queue) != 0:
current_stat = heapq.heappop(queue)
if current_stat.get_distance() > distances[current_stat.get_id()]:
continue
for neighbor in graph[current_stat.get_id()]:
# 当前节点的序号
_id = neighbor[0]
# 起点到当前节点的距离
distance = distances[current_stat.get_id()] + neighbor[1]
if distance < distances[_id]:
distances[_id] = distance
heapq.heappush(queue, NodeState(_id, distance))
return distances
应用
应用 1:Leetcode.743
题目
有 n 个网络节点,标记为 1 到 n。
给你一个列表 times,表示信号经过 有向 边的传递时间。 \(times[i] = (u_i, v_i, w_i)\),其中 \(u_i\) 是源节点,\(v_i\) 是目标节点, \(w_i\) 是一个信号从源节点传递到目标节点的时间。
现在,从某个节点 K 发出一个信号。需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?如果不能使所有节点收到信号,返回 -1 。
示例 1:

输入:times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], n = 4, k = 2
输出:2
题目分析
这是一道典型的求最短路径的算法:加权有向图,没有负权重边,求最短路径。
我们将传播时间看成边\(V\)的权重,我们用邻接表来表示有向加权图,最后直接利用\(Dijkstra\)算法,计算出从起点到终点的每一个节点的最短传播路径即可。
这里我们直接给出 \(Dijkstra\) 算法的模板,套用模板即可。
需要注意:题目中的节点序号是从 \(1\) 开始的,所以我们生成邻接矩阵的时候,将所有的节点序号都减一,保证节点序号从 \(0\) 开始。
代码实现
【JAVA实现】:
class Solution {
public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) {
List<List<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] time : times) {
graph.get(time[0] - 1).add(new Node(time[1] - 1, time[2]));
}
int[] distances = dijkstra(k - 1, graph);
int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int distance : distances) {
result = Math.max(result, distance);
}
return result == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : result;
}
private int[] dijkstra(int start, List<List<Node>> graph) {
int[] distances = new int[graph.size()];
Arrays.fill(distances, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
distances[start] = 0;
PriorityQueue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b.getDistance() - a.getDistance());
queue.add(new Node(start, 0));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node currentNode = queue.poll();
int u = currentNode.getId();
if (currentNode.getDistance() > distances[u]) {
continue;
}
for (Node neighbor : graph.get(u)) {
int v = neighbor.getId();
int distance = distances[u] + neighbor.getDistance();
if (distance < distances[v]) {
distances[v] = distance;
queue.offer(new Node(v, distance));
}
}
}
return distances;
}
private static class Node {
private final int id;
private final int distance;
public Node(int id, int distance) {
this.id = id;
this.distance = distance;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public int getDistance() {
return distance;
}
}
}
【Python实现】:
import heapq
from typing import List
class Solution:
def networkDelayTime(self, times: List[List[int]], n: int, k: int) -> int:
graph = [list() for _ in range(n)]
for _time in times:
graph[_time[0] - 1].append((_time[2], _time[1] - 1))
distances = self.dijkstra(graph, k - 1)
result = max(distances) if max(distances) < float("INF") else -1
return int(result)
def dijkstra(self, graph, start):
distances = [float("INF")] * len(graph)
distances[start] = 0
queue = list()
heapq.heappush(queue, (0, start))
while queue:
_node = heapq.heappop(queue)
if distances[_node[1]] < _node[0]:
continue
for neighbor in graph[_node[1]]:
distance = _node[0] + neighbor[0]
if distance < distances[neighbor[1]]:
distances[neighbor[1]] = distance
heapq.heappush(queue, (distance, neighbor[1]))
return distances
应用 2:Leetcode.1514
题目
给你一个由 n 个节点(下标从 0 开始)组成的无向加权图,该图由一个描述边的列表组成,其中 edges[i] = [a, b] 表示连接节点 a 和 b 的一条无向边,且该边遍历成功的概率为 succProb[i] 。
指定两个节点分别作为起点 start 和终点 end ,请你找出从起点到终点成功概率最大的路径,并返回其成功概率。如果不存在从 start 到 end 的路径,请 返回 0 。只要答案与标准答案的误差不超过 1e-5 ,就会被视作正确答案。
示例 1:
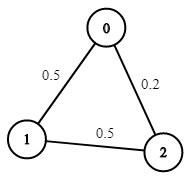
输入:n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.2], start = 0, end = 2
输出:0.25000
解释:从起点到终点有两条路径,其中一条的成功概率为 0.2 ,而另一条为 0.5 * 0.5 = 0.25
解题思路
这道题的特点:边有非负的权重,求单源最优路径。
可以转换为 \(Dijkstra\) 算法求解,\(Dijkstra\) 算法是为了求解单源最短路径,其实只要是图的路径具有非负权重,求单源最优路径,都可以通过 \(Dijsktra\) 算法求解,只是将路径累加换成概率相乘即可。
题目中的图是无向图,我们可以将无向图的边可以看成是双向的边即可。
首先,我们首先将图中的边转换为邻接表 \(graph\) ,主要保存每个顶点的邻近节点及其概率:
我们用一个优先级队列 \(queue\) 保存每个节点的概率及其节点序号:
然后,从起点开始更新邻近节点的概率,最后返回终点的概率即可。
代码实现
class Solution {
public double maxProbability(int n, int[][] edges, double[] successProb, int start_node, int end_node) {
List<List<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// 使用邻接矩阵构造无向图
for (int i = 0; i < successProb.length; i++) {
graph.get(edges[i][0]).add(new Node(edges[i][1], successProb[i]));
graph.get(edges[i][1]).add(new Node(edges[i][0], successProb[i]));
}
double[] distances = dijkstra(start_node, graph, n);
return distances[end_node] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : distances[end_node];
}
private double[] dijkstra(int start, List<List<Node>> graph, int n) {
// 初始每个节点的概率为零
double[] distances = new double[n];
// 大顶堆
PriorityQueue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> Double.compare(b.getDistance(), a.getDistance()));
// 起点的概率设置为 1
distances[start] = 1;
q.offer(new Node(start, 1));
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node candidate = q.poll();
int u = candidate.getId();
// 如果堆顶的元素的权重更小,就跳过
if (candidate.getDistance() < distances[u]) {
continue;
}
// 遍历邻近节点
for (Node neighbor : graph.get(u)) {
int v = neighbor.getId();
// 起点到当前节点的权重
double distance = distances[u] * neighbor.getDistance();
if (distances[v] < distance) {
distances[v] = distance;
q.offer(new Node(v, distance));
}
}
}
return distances;
}
private static class Node {
private final int id;
private final double distance;
public Node(int id, double distance) {
this.id = id;
this.distance = distance;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public double getDistance() {
return distance;
}
}
}
注意:
- Python:这道题直接使用模板,会有用例超时,这里将顶点及其概率,直接通过元祖保存到优先级队列里面,避免创建对象引用的开销,避免用例超时。
- Java:使用邻接矩阵会超时,需要使用邻接表才能通过。
应用 3:Leetcode.1631
题目
你准备参加一场远足活动。给你一个二维 rows x columns 的地图 heights ,其中 heights[row][col] 表示格子 (row, col) 的高度。一开始你在最左上角的格子 (0, 0) ,且你希望去最右下角的格子 (rows-1, columns-1) (注意下标从 0 开始编号)。你每次可以往 上,下,左,右 四个方向之一移动,你想要找到耗费 体力 最小的一条路径。
一条路径耗费的 体力值 是路径上相邻格子之间 高度差绝对值 的 最大值 决定的。
请你返回从左上角走到右下角的最小 体力消耗值 。
示例 1:
输入:heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]]
输出:2
解释:路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 连续格子的差值绝对值最大为 2 。
这条路径比路径 [1,2,2,2,5] 更优,因为另一条路径差值最大值为 3 。
解题思路
这里的矩阵,我们可以类似的看成一个有向无环图,因为矩阵中的每一个点,都可以向四周邻近的点延伸。同时,需要注意,矩阵中已经搜索过的节点,不能再次重复搜索,每次搜索的时候,我们更新到达每个点所需要的权重(即题目中的体力值)。
显然,这是一个在有向加权图中,并且权重都是非负值,求源顶点 \(S\) 到目的顶点 \(V\) 的最小权重的路径的过程,因此,我们可以考虑使用 \(Dijkstra\) 算法求解。
通常,我们使用 \(Dijkstra\) 算法时,都会给定一个使用邻接表或者邻接矩阵表示的有向图。
这里,我们可以直接使用给定的矩阵 \(heights\),和一个辅助的二维矩阵 \(visit\),来遍历题目中的有向图,即对于矩阵中的每一个点,都可以向四周扩散,同时不能重复访问已经经过的节点。对于每一个节点,如果它的权重更小,就更新它的权重,并且将其重新加入优先级队列。
更新完所有节点的权重之后,就可以得到源顶点 \(S\) 到目的顶点 \(V\) 的最小权重的路径了。
代码实现
class Solution {
private static int[][] DIRECTIONS = new int[][]{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length;
int[][] distances = dijkstra(heights);
return distances[m - 1][n - 1];
}
private int[][] dijkstra(int[][] heights) {
int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length;
// 记录起点到每一个位置的距离
int[][] distances = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
Arrays.fill(distances[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
// 维护一个小根堆
PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[2] - b[2]);
// 初始化起点
distances[0][0] = 0;
q.offer(new int[]{0, 0, 0});
// 维护一个visit数组,避免走回头路
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[m][n];
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] candidate = q.poll();
int u1 = candidate[0], u2 = candidate[1];
// 已经访问过,就跳过
if (visit[u1][u2]) {
continue;
}
// 到达终点,则退出
if (u1 == m - 1 && u2 == n - 1) {
break;
}
visit[u1][u2] = true;
// 遍历邻近的节点
for (int[] direction : DIRECTIONS) {
int v1 = u1 + direction[0];
int v2 = u2 + direction[1];
if (v1 < 0 || v1 >= m || v2 < 0 || v2 >= n) {
continue;
}
// 如果到达位置(v1,v2) 需要消耗的能量更小,就更新到达这个位置的路径,并将其入队
int distance = Math.max(candidate[2], Math.abs(heights[v1][v2] - heights[u1][u2]));
if (distance < distances[v1][v2]) {
distances[v1][v2] = Math.max(candidate[2], distance);
q.offer(new int[]{v1, v2, distance});
}
}
}
return distances;
}
}
总结
\(Dijkstra\) 算法:可以求解 非负权重图 上的 单源 最优路径的问题。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号