【C++标准库】数值组件
随机数
使用随机数程序库,需包含头文件<random>。常用的属于随机数生成器指的是一个引擎和一个分布的组合。
引擎作为随机数的源头,它们是function object,能够产生随机的无符号值,并均匀分布于一个预定义的最大值和最小值之间。每次以operator()调用它,其内部状态会发生改变,使得此后可产生出一个新的随机值。
分布表示以何种方法将这些随机值转换为随机数。后者分布于由使用者指定的参数所指定的区间内。
int main(int argc, char** argv) { default_random_engine dre; //使用默认引擎 uniform_int_distribution<int> di(10, 20); //闭区间[10,20] for (int i = 0;i < 20;++i) { cout << di(dre) << " "; } cout << endl; uniform_real_distribution<double> dr(10.0, 20.0); //半开区间[10.0,20.0) for (int i = 0;i < 8;++i) { cout << dr(dre) << " "; } cout << endl; vector<int> v = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 }; shuffle(v.begin(), v.end(), dre); for (auto e : v) { cout << e << " "; } cout << endl; }
任何引擎的初始状态都有明确定义,并非随机的。如果需要产生一个不可预期的随机数,需要传递一个种子seed给引擎构造函数。
复数
定义于头文件<complex>中

/* The following code example is taken from the book * "The C++ Standard Library - A Tutorial and Reference, 2nd Edition" * by Nicolai M. Josuttis, Addison-Wesley, 2012 * * (C) Copyright Nicolai M. Josuttis 2012. * Permission to copy, use, modify, sell and distribute this software * is granted provided this copyright notice appears in all copies. * This software is provided "as is" without express or implied * warranty, and with no claim as to its suitability for any purpose. */ #include <iostream> #include <complex> using namespace std; int main() { // complex number with real and imaginary parts // - real part: 4.0 // - imaginary part: 3.0 complex<double> c1(4.0, 3.0); // create complex number from polar coordinates // - magnitude: 5.0 // - phase angle: 0.75 complex<float> c2(polar(5.0, 0.75)); // print complex numbers with real and imaginary parts cout << "c1: " << c1 << endl; cout << "c2: " << c2 << endl; // print complex numbers as polar coordinates cout << "c1: magnitude: " << abs(c1) << " (squared magnitude: " << norm(c1) << ") " << " phase angle: " << arg(c1) << endl; cout << "c2: magnitude: " << abs(c2) << " (squared magnitude: " << norm(c2) << ") " << " phase angle: " << arg(c2) << endl; // print complex conjugates cout << "c1 conjugated: " << conj(c1) << endl; cout << "c2 conjugated: " << conj(c2) << endl; // print result of a computation cout << "4.4 + c1 * 1.8: " << 4.4 + c1 * 1.8 << endl; // print sum of c1 and c2: // - note: different types cout << "c1 + c2: " << c1 + complex<double>(c2.real(), c2.imag()) << endl; // add square root of c1 to c1 and print the result cout << "c1 += sqrt(c1): " << (c1 += sqrt(c1)) << endl; }
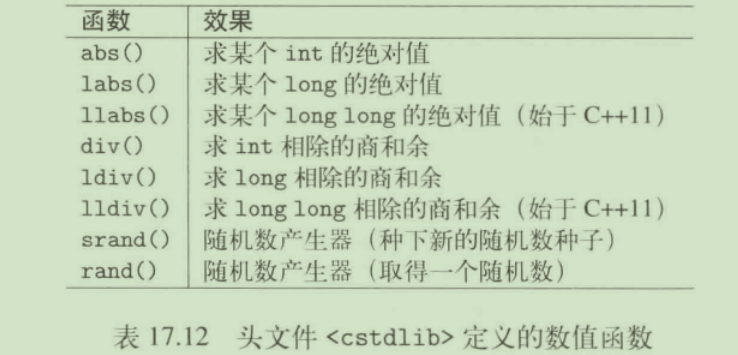
全局数值函数
头文件<cmath>和<cstdlib>提供自C继承而来的全局数值函数。