【C++标准库】STL算法
使用C++标准库的算法,需包含头文件<algorithm>
STL算法用于处理一个或多个iterator区间,第一个区间通常以起点和终点表示,其他区间则多数情况下只需提供起点足矣,其终点可以根据第一区间的元素数量推导出来。调用者需保证区间的有效性。STL算法命名时,引入了两种特殊的后缀:

STL算法分类
- 非更易型算法(nomodifying algorithm)
- 更易型算法(modifying algorithm)
- 移除型算法(removing algorithm)
- 变序型算法(mutating algorithm)
- 排序算法(sorting algorithm)
- 已排序区间算法(sorted-range algorithm)
- 数值算法(numeric algorithm)
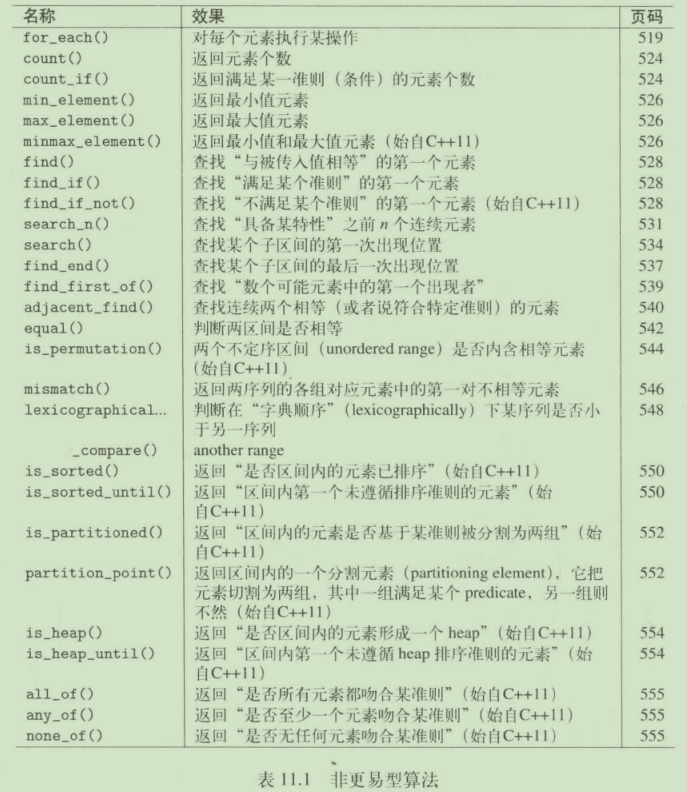
非更易型算法
更易型算法


/* The following code example is taken from the book * "The C++ Standard Library - A Tutorial and Reference, 2nd Edition" * by Nicolai M. Josuttis, Addison-Wesley, 2012 * * (C) Copyright Nicolai M. Josuttis 2012. * Permission to copy, use, modify, sell and distribute this software * is granted provided this copyright notice appears in all copies. * This software is provided "as is" without express or implied * warranty, and with no claim as to its suitability for any purpose. */ #include "algostuff.hpp" using namespace std; int main() { vector<string> coll1 = { "Hello", "this", "is", "an", "example" }; list<string> coll2; // copy elements of coll1 into coll2 // - use back inserter to insert instead of overwrite // - use copy() because the elements in coll1 are used again copy(coll1.cbegin(), coll1.cend(), // source range back_inserter(coll2)); // destination range // print elements of coll2 // - copy elements to cout using an ostream iterator // - use move() because these elements in coll2 are not used again move(coll2.cbegin(), coll2.cend(), // source range ostream_iterator<string>(cout, " ")); // destination range cout << endl; // copy elements of coll1 into coll2 in reverse order // - now overwriting (coll2.size() still fits) // - use move() because the elements in coll1 are not used again move(coll1.crbegin(), coll1.crend(), // source range coll2.begin()); // destination range // print elements of coll2 again // - use move() because the elements in coll2 are not used again move(coll2.cbegin(), coll2.cend(), // source range ostream_iterator<string>(cout, " ")); // destination range cout << endl; }

#include "algostuff.hpp" using namespace std; int main() { array<int, 10> coll; iota(coll.begin(), coll.end(), 42); PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll,"coll:"); //42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 return 0; }

#include "algostuff.hpp" using namespace std; using namespace std::placeholders; int main() { list<int> coll; INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll, 2, 6); INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll, 4, 9); PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll); //print all elements with 5 replaced with 55 replace_copy(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "), 5, 55); cout << endl; //print all elements with a value less than 5 replaced with 42 replace_copy_if(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "), bind(less<int>(), _1, 5), 42); cout << endl; //print all elements while each odd value replaced with 0 replace_copy_if(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "), [](int elem) {return elem % 2 == 1;}, 0); cout << endl; return 0; }

移除型算法

移除型算法只是从“逻辑上”移除元素,其手段是将不应移除的元素往前覆盖应被移除的元素,因此其并未改变操作区间内元素的个数,而是返回逻辑上新终点的位置。
变序型算法



#include "algostuff.hpp" using namespace std; using namespace std::placeholders; int main() { vector<int> coll = { 1,6,33,7,22,4,11,33,2,7,0,42,5 }; PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll, "coll:"); vector<int> evenColl; vector<int> oddColl; //copy all elements accordingly into even and odd elements partition_copy(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),back_inserter(evenColl),back_inserter(oddColl),[](int elem) {return elem % 2 == 0;}); PRINT_ELEMENTS(evenColl, "evenColl:"); PRINT_ELEMENTS(oddColl, "oddColl:"); return 0; }
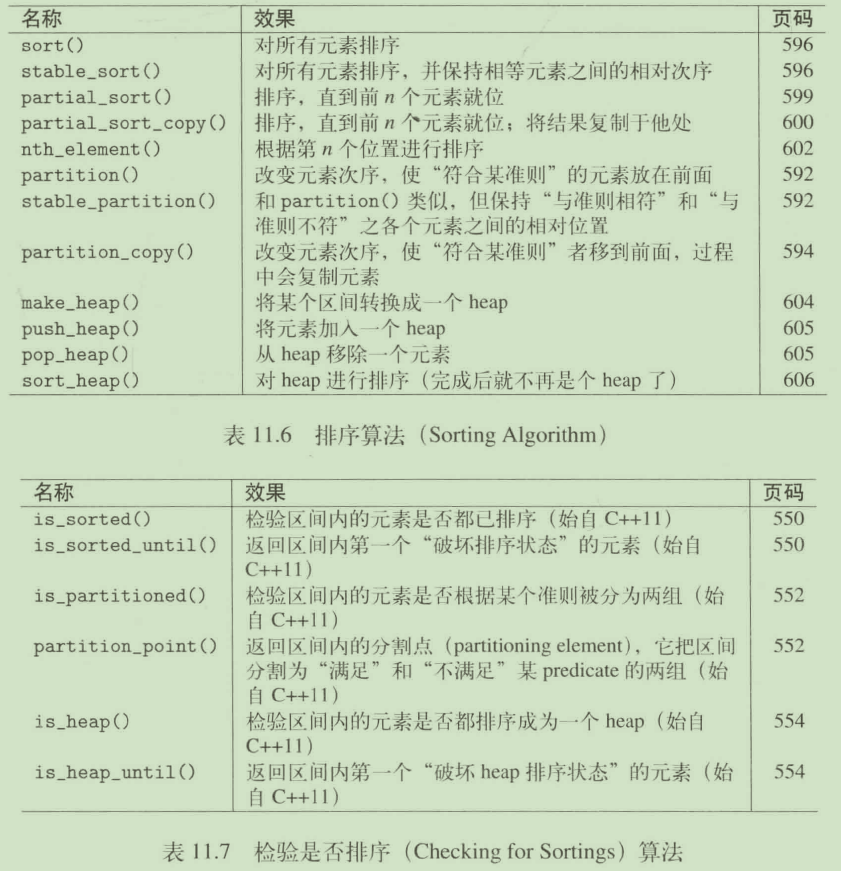
排序算法
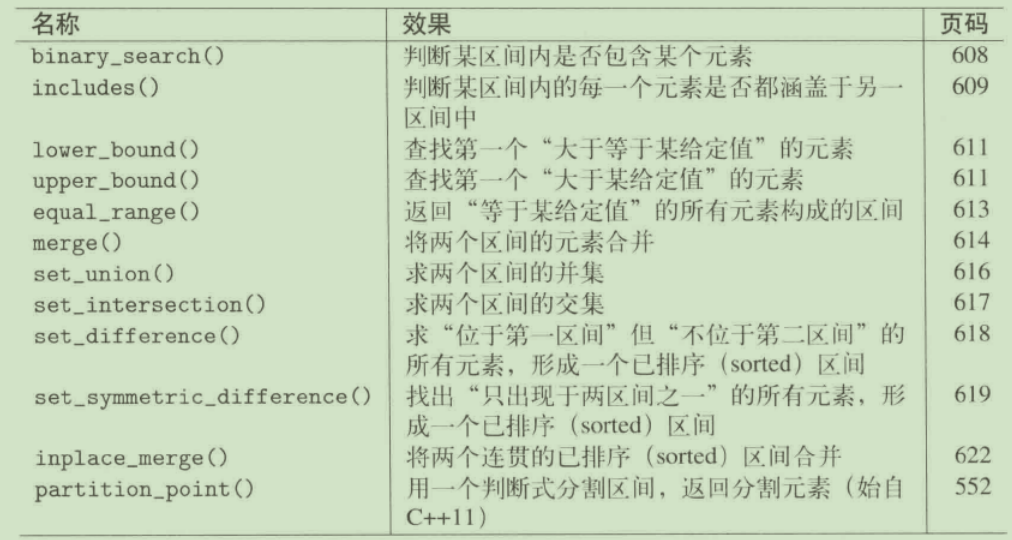
已排序区间算法
数值算法

使用数值算法时,需包含头文件<numeric>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号