使用任务并行库
任务并行库(Task Parallel Library,TPL)可以被认为是线程池上的又一个抽象层,其对程序员隐藏了与线程池交互的底层代码,并提供了更方便的细粒度的API。
创建任务
using System; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Chapter4.Recipe1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var t1 = new Task(() => TaskMethod("Task 1")); var t2 = new Task(() => TaskMethod("Task 2")); t2.Start(); t1.Start(); Task.Run(() => TaskMethod("Task 3")); Task.Factory.StartNew(() => TaskMethod("Task 4")); Task.Factory.StartNew(() => TaskMethod("Task 5"), TaskCreationOptions.LongRunning); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); } static void TaskMethod(string name) { Console.WriteLine("Task {0} is running on a thread id {1}. Is thread pool thread: {2}", name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); } } }
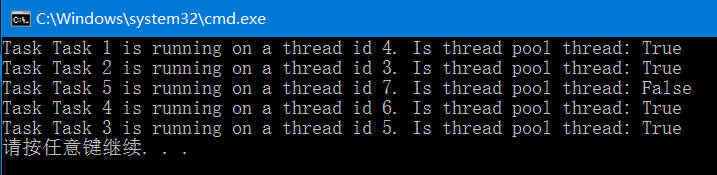
1. 使用构造函数创建任务,传入一个lambda表达式作为Action委托,调用Start()启动任务。
2. 使用Task.Run()运行任务,与使用构造函数创建任务不同,Task.Run()创建的任务会立刻开始执行,无需调用Start()
3.使用Task.Factory.StartNew()运行任务,与使用构造函数创建任务不同,Task.Factory.StartNew()创建的任务会立刻开始执行,无需调用Start()
4.标记任务为长时间操作,结果该任务将不会使用线程池,而在单独的线程中运行。
使用任务执行基本的操作
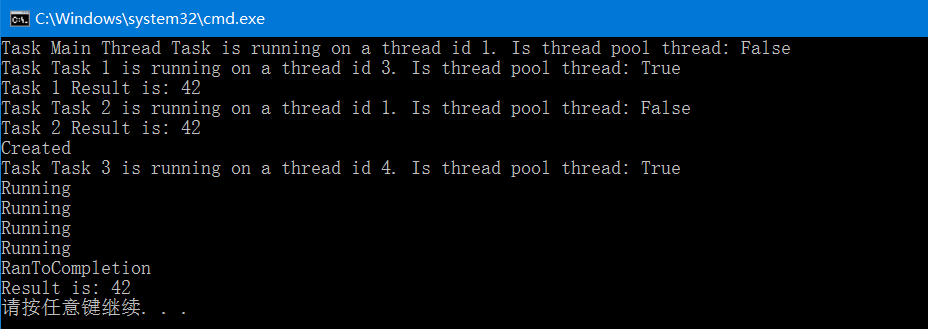
using System; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Chapter4.Recipe2 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { TaskMethod("Main Thread Task"); Task<int> task = CreateTask("Task 1"); task.Start(); int result = task.Result; //主线程等待任务返回 Console.WriteLine("Task 1 Result is: {0}", result); task = CreateTask("Task 2"); task.RunSynchronously(); //同步运行Task,运行在主线程中 result = task.Result; Console.WriteLine("Task 2 Result is: {0}", result); task = CreateTask("Task 3"); Console.WriteLine(task.Status); task.Start(); while (!task.IsCompleted) //循环打印任务状态,不阻塞主线程 { Console.WriteLine(task.Status); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5)); } Console.WriteLine(task.Status); result = task.Result; Console.WriteLine("Result is: {0}", result); } static Task<int> CreateTask(string name) { return new Task<int>(() => TaskMethod(name)); } static int TaskMethod(string name) { Console.WriteLine("Task {0} is running on a thread id {1}. Is thread pool thread: {2}", name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); return 42; } } }
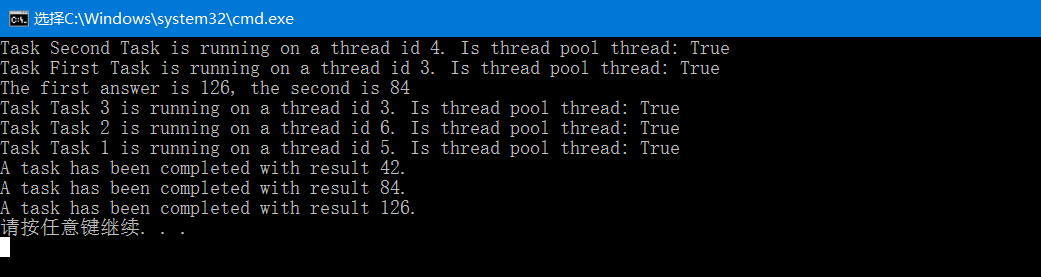
并行运行任务

1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Threading; 4 using System.Threading.Tasks; 5 6 namespace Chapter4.Recipe8 7 { 8 class Program 9 { 10 static void Main(string[] args) 11 { 12 var firstTask = new Task<int>(() => TaskMethod("First Task", 3)); 13 var secondTask = new Task<int>(() => TaskMethod("Second Task", 2)); 14 //借助于Task.WhenAll方法创建第三个任务,该任务将会在所有任务完成后运行 15 var whenAllTask = Task.WhenAll(firstTask, secondTask); 16 //该任务的结果提供了一个结果数组,第一个元素是第一个任务的结果,第二个元素是第二个任务的结果 17 whenAllTask.ContinueWith(t => 18 Console.WriteLine("The first answer is {0}, the second is {1}", t.Result[0], t.Result[1]), 19 TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnRanToCompletion 20 ); 21 22 firstTask.Start(); 23 secondTask.Start(); 24 25 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(4)); 26 27 var tasks = new List<Task<int>>(); 28 for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) 29 { 30 int counter = i; 31 var task = new Task<int>(() => TaskMethod(string.Format("Task {0}", counter), counter)); 32 tasks.Add(task); 33 task.Start(); 34 } 35 36 while (tasks.Count > 0) 37 { 38 //使用Task.WhenAny方法等待任务tasks中的任何一个任务完成... 39 var completedTask = Task.WhenAny(tasks).Result; 40 tasks.Remove(completedTask); 41 Console.WriteLine("A task has been completed with result {0}.", completedTask.Result); 42 } 43 44 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); 45 } 46 47 static int TaskMethod(string name, int seconds) 48 { 49 Console.WriteLine("Task {0} is running on a thread id {1}. Is thread pool thread: {2}", 50 name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); 51 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(seconds)); 52 return 42 * seconds; 53 } 54 } 55 }