使用线程池
简介
创建线程是昂贵的操作,为每一个短暂的异步操作创建线程会产生显著的开销。


在线程池中调用委托
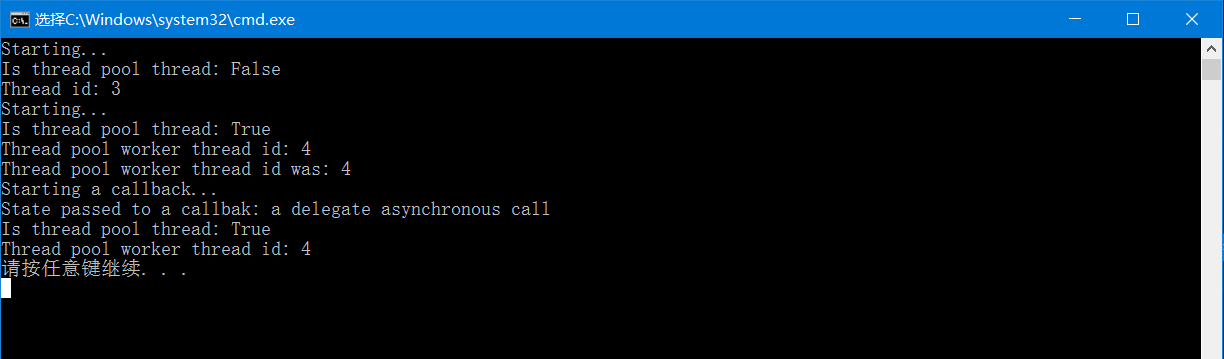
1 using System; 2 using System.Threading; 3 4 namespace Chapter3.Recipe1 5 { 6 class Program 7 { 8 static void Main(string[] args) 9 { 10 int threadId = 0; 11 12 RunOnThreadPool poolDelegate = Test; 13 14 var t = new Thread(() => Test(out threadId)); 15 t.Start(); 16 t.Join(); 17 18 Console.WriteLine("Thread id: {0}", threadId); 19 20 //调用BeginInvoke()运行委托,回调函数在异步操作完成后被调用 21 //BeginInvoke()调用后会立即返回,线程池中的工作线程在执行异步操作时,仍允许继续其他工作。 22 IAsyncResult r = poolDelegate.BeginInvoke(out threadId, Callback, "a delegate asynchronous call"); 23 r.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne(); //等待异步操作完成 24 //事实上EndInvoke()会等待异步操作的完成,所以r.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne();并不是必要的 25 string result = poolDelegate.EndInvoke(out threadId, r); 26 //异步操作完成后,回调函数会被放置到线程池中,确切的说是一个工作线程中。 27 Console.WriteLine("Thread pool worker thread id: {0}", threadId); 28 Console.WriteLine(result); 29 30 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 31 } 32 33 private delegate string RunOnThreadPool(out int threadId); 34 35 private static void Callback(IAsyncResult ar)//回调函数 36 { 37 Console.WriteLine("Starting a callback..."); 38 Console.WriteLine("State passed to a callbak: {0}", ar.AsyncState); 39 Console.WriteLine("Is thread pool thread: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); 40 Console.WriteLine("Thread pool worker thread id: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); 41 } 42 43 44 private static string Test(out int threadId) 45 { 46 Console.WriteLine("Starting..."); 47 Console.WriteLine("Is thread pool thread: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread); 48 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 49 threadId = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId; 50 return string.Format("Thread pool worker thread id was: {0}", threadId); 51 } 52 } 53 }
使用BeginOperationName/EndOperation方法和.NET中的IAsyncResult对象等方式被称为异步编程模型,这样的方法对被称为异步方法。
向线程池放入异步操作
1 using System; 2 using System.Threading; 3 4 namespace Chapter3.Recipe2 5 { 6 class Program 7 { 8 static void Main(string[] args) 9 { 10 const int x = 1; 11 const int y = 2; 12 const string lambdaState = "lambda state 2"; 13 14 //使用ThreadPool的静态方法QueueUserWorkItem()将方法放到线程池中 15 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(AsyncOperation); 16 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); 17 //Thread.Sleep()让线程池拥有为新操作重用线程的可能性 18 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(AsyncOperation, "async state"); 19 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); 20 //使用lambda表达式方式 21 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(state => { 22 Console.WriteLine("Operation state: {0}", state); 23 Console.WriteLine("Worker thread id: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); 24 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 25 }, "lambda state"); 26 //使用闭包机制 27 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => 28 { 29 Console.WriteLine("Operation state: {0}, {1}", x + y, lambdaState); 30 Console.WriteLine("Worker thread id: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); 31 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 32 }, "lambda state"); 33 34 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 35 } 36 37 private static void AsyncOperation(object state) 38 { 39 Console.WriteLine("Operation state: {0}", state ?? "(null)"); 40 Console.WriteLine("Worker thread id: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); 41 Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 42 } 43 } 44 }

使用计时器
using System; using System.Threading; namespace Chapter3.Recipe6 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Press 'Enter' to stop the timer..."); DateTime start = DateTime.Now; //传入回调函数,用户状态对象,调用回调函数之前的时间延迟量,时间间隔 _timer = new Timer(_ => TimerOperation(start), null, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1), TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(6)); _timer.Change(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1), TimeSpan.FromSeconds(4)); Console.ReadLine(); _timer.Dispose(); } static Timer _timer; static void TimerOperation(DateTime start)//回调函数,在线程池中被执行 { TimeSpan elapsed = DateTime.Now - start; Console.WriteLine("{0} seconds from {1}. Timer thread pool thread id: {2}", elapsed.Seconds, start, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } } }
使用BackgroundWorker组件
除了将异步API组织为Begin/End方法对外,还可以启动一个异步操作然后订阅给不同的事件,这种方式被称为基于事件的异步模式(Event-based Asynchronous Pattern,EAP)。
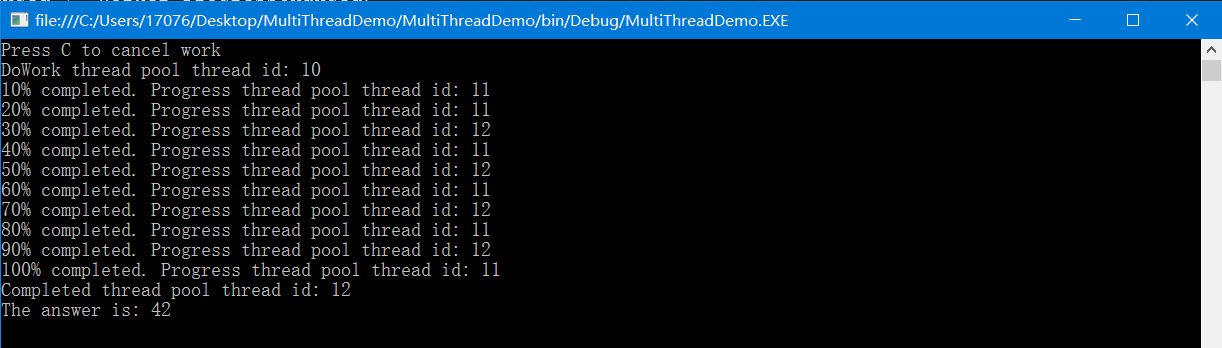
using System; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Threading; namespace Chapter3.Recipe7 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var bw = new BackgroundWorker(); bw.WorkerReportsProgress = true; //指示该后台工作线程支持操作进度的通知 bw.WorkerSupportsCancellation = true; //指示该后台工作线程支持取消操作 bw.DoWork += Worker_DoWork; //调用RunWorkerAsync()时发生 bw.ProgressChanged += Worker_ProgressChanged; bw.RunWorkerCompleted += Worker_Completed; //后台操作完成、被取消或者异常时发生 bw.RunWorkerAsync();//后台工作对象bw通过RunWorkerAsync()方法启动异步操作 Console.WriteLine("Press C to cancel work"); do { if (Console.ReadKey(true).KeyChar == 'C') { bw.CancelAsync(); } } while (bw.IsBusy);//指示是否正在运行异步操作 } static void Worker_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("DoWork thread pool thread id: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); var bw = (BackgroundWorker)sender; for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { if (bw.CancellationPending)//指示应用程序是否已取消程序后台操作 { e.Cancel = true; return; } if (i % 10 == 0) { bw.ReportProgress(i); } Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.1)); } e.Result = 42; //异步操作的结果 } static void Worker_ProgressChanged(object sender, ProgressChangedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("{0}% completed. Progress thread pool thread id: {1}", e.ProgressPercentage, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } static void Worker_Completed(object sender, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("Completed thread pool thread id: {0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); if (e.Error != null)//异步操作发生错误 { Console.WriteLine("Exception {0} has occured.", e.Error.Message); } else if (e.Cancelled)//异步操作被取消 { Console.WriteLine("Operation has been canceled."); } else//异步操作成功完成 { Console.WriteLine("The answer is: {0}", e.Result); } } } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号