前段知识
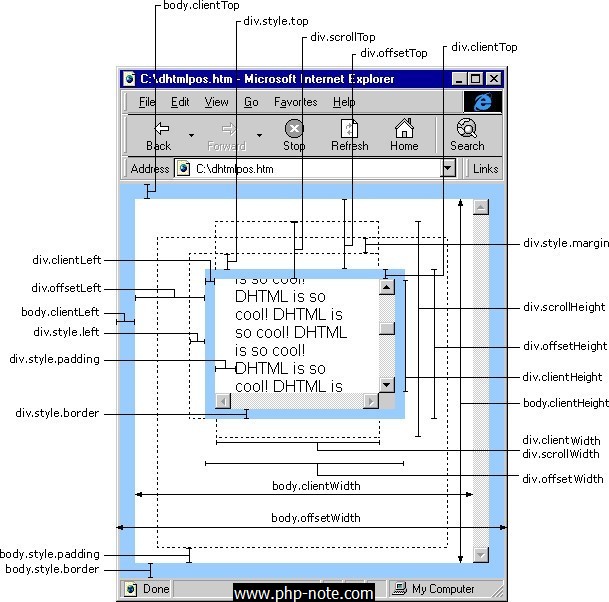
IE中:
document.body.clientWidth ==> BODY对象宽度
document.body.clientHeight ==> BODY对象高度
document.documentElement.clientWidth ==> 可见区域宽度
document.documentElement.clientHeight ==> 可见区域高度
FireFox中:
document.body.clientWidth ==> BODY对象宽度
document.body.clientHeight ==> BODY对象高度
document.documentElement.clientWidth ==> 可见区域宽度
document.documentElement.clientHeight ==> 可见区域高度
Opera中:
document.body.clientWidth ==> 可见区域宽度
document.body.clientHeight ==> 可见区域高度
document.documentElement.clientWidth ==> 页面对象宽度(即BODY对象宽度加上Margin宽)
document.documentElement.clientHeight ==> 页面对象高度(即BODY对象高度加上Margin高)
没有定义W3C的标准,则
IE为:
document.documentElement.clientWidth ==> 0
document.documentElement.clientHeight ==> 0
FireFox为:
document.documentElement.clientWidth ==> 页面对象宽度(即BODY对象宽度加上Margin宽)
document.documentElement.clientHeight ==> 页面对象高度(即BODY对象高度加上Margin高)
Opera为:
document.documentElement.clientWidth ==> 页面对象宽度(即BODY对象宽度加上Margin宽)
document.documentElement.clientHeight ==> 页面对象高度(即BODY对象高度加上Margin高)
网页可见区域宽: document.body.clientWidth
网页可见区域高: document.body.clientHeight
网页可见区域宽: document.body.offsetWidth (包括边线的宽)
网页可见区域高: document.body.offsetHeight (包括边线的高)
网页正文全文宽: document.body.scrollWidth
网页正文全文高: document.body.scrollHeight
网页被卷去的高: document.body.scrollTop
网页被卷去的左: document.body.scrollLeft
网页正文部分上: window.screenTop
网页正文部分左: window.screenLeft
屏幕分辨率的高: window.screen.height
屏幕分辨率的宽: window.screen.width
屏幕可用工作区高度: window.screen.availHeight
屏幕可用工作区宽度: window.screen.availWidth
(注意:CSS中的margin属性,与clientWidth、offsetWidth、clientHeight、offsetHeight均无关)
HTML精确定位:scrollLeft、scrollWidth、clientWidth、offsetWidth
scrollWidth ==> 获取对象的滚动宽度
scrollHeight ==> 获取对象的滚动高度
scrollLeft ==> 设置或获取位于对象左边界和窗口中目前可见内容的最左端之间的距离(被卷去的左)
scrollTop ==> 设置或获取位于对象最顶端和窗口中可见内容的最顶端之间的距离(被卷去的高)
offsetLeft ==> 获取对象相对于版面或由 offsetParent 属性指定的父坐标的计算左侧位置
offsetTop ==> 获取对象相对于版面或由 offsetTop 属性指定的父坐标的计算顶端位置
offsetHeight ==> 获取对象相对于版面或由父坐标 offsetParent 属性指定的父坐标的高度
event.clientX ==> 相对文档的水平座标
event.clientY ==> 相对文档的垂直座标
event.offsetX ==> 相对容器的水平坐标
event.offsetY ==> 相对容器的垂直坐标
document.documentElement.scrollTop ==> 垂直方向滚动的值
event.clientX+document.documentElement.scrollTop ==> 相对文档的水平座标+垂直方向滚动的量
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <title>请调整浏览器窗口</title> <meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312"> </meta></head> <body> <h2 align="center">请调整浏览器窗口大小</h2><hr /> <form action="#" method="get" name="form1" id="form1"> <!--显示浏览器窗口的实际尺寸--> 浏览器窗口 的 实际高度: <input type="text" name="availHeight" size="4"/><br /> 浏览器窗口 的 实际宽度: <input type="text" name="availWidth" size="4"/><br /> </form> <script type="text/javascript"> <!-- var winWidth = 0; var winHeight = 0; //函数:获取尺寸 function findDimensions() { //获取窗口宽度 if (window.innerWidth) { winWidth = window.innerWidth; } else if ((document.body) && (document.body.clientWidth)) { winWidth = document.body.clientWidth; } //获取窗口高度 if (window.innerHeight) { winHeight = window.innerHeight; } else if ((document.body) && (document.body.clientHeight)) { winHeight = document.body.clientHeight; } //通过深入Document内部对body进行检测,获取窗口大小 if (document.documentElement && document.documentElement.clientHeight && document.documentElement.clientWidth) { winHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight; winWidth = document.documentElement.clientWidth; } //结果输出至两个文本框 document.form1.availHeight.value = winHeight; document.form1.availWidth.value = winWidth; } findDimensions(); //调用函数,获取数值 window.onresize = findDimensions; //--> </script> </body> </html>
汇总
////////浏览器视口的高度
function windowHeight() {
var myHeight = 0;
if (typeof(window.innerHeight) == 'number') {
//Non-IE
myHeight = window.innerHeight;
} else if (document.documentElement && (document.documentElement.clientHeight)) {
//IE 6+ in 'standards compliant mode'
myHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight;
} else if (document.body && (document.body.clientHeight)) {
//IE 4 compatible
myHeight = document.body.clientHeight;
}
return myHeight;
}
/////////浏览器视口的宽度
function windowWidth() {
var myWidth = 0;
if (typeof(window.innerWidth) == 'number') {
//Non-IE
myWidth = window.innerWidth;
} else if (document.documentElement && (document.documentElement.clientWidth)) {
//IE 6+ in 'standards compliant mode'
myWidth = document.documentElement.clientWidth;
} else if (document.body && (document.body.clientWidth)) {
//IE 4 compatible
myWidth = document.body.clientWidth;
}
return myWidth;
}
/**** 浏览器垂直滚动位置 ****/
function scrollY() {
var de = document.documentElement;
return window.pageYOffset || (de && de.scrollTop) || document.body.scrollTop;
}
/**** 浏览器水平滚动位置 ****/
function scrollX() {
var de = document.documentElement;
return window.pageXOffset || (de && de.scrollLeft) || document.body.scrollLeft;
}
/**** 当前页面高度 ****/
function pageHeight() {
return document.body.scrollHeight;
}
/**** 当前页面宽度 ****/
function pageWidth() {
return document.body.scrollWidth;
}
扩展jQuery插件和方法的作用是非常强大的,它可以节省大量开发时间。这篇文章将概述jQuery插件开发的基本知识,最佳做法和常见的陷阱。
一、入门
编写一个jQuery插件开始于给jQuery.fn加入新的功能属性,此处添加的对象属性的名称就是你插件的名称:
jQuery.fn.myPlugin = function() {//你自己的插件代码 };
用户非常喜欢的$符号哪里去了? 它仍然存在,但是,为了避免和其他JavaScript库冲突,我们最好将jQuery传递给一个自我执行的封闭程序,jQuery在此程序中映射为$符号,这样可以避免$号被其他库覆写。
(function($) { $.fn.myPlugin = function() { //你自己的插件代码 }; })(jQuery);
在这个封闭程序中,我们可以无限制的使用$符号来表示jQuery函数。
二、环境
现在,我们可以开始编写实际的插件代码。 但是,在这之前,我们必须得对插件所处的环境有个概念。 在插件的范围里, this关键字代表了这个插件将要执行的jQuery对象, 这里容易产生一个普遍的误区,因为在其他包含callback的jQuery函数中,this关键字代表了原生的DOM元素。这常常会导致开发者误将this关键字无谓的包在jQuery中,如下所示。
(function($) { $.fn.myPlugin = function() { //此处没有必要将this包在$号中如$(this),因为this已经是一个jQuery对象。 //$(this)等同于 $($('#element')); this.fadeIn('normal', function() { //此处callback函数中this关键字代表一个DOM元素 }); }; })(jQuery); $('#element').myPlugin();
三、基础知识
现在,我们理解了jQuery插件的基础知识,让我们写一个插件,做一些事情。
(function($) { $.fn.maxHeight = function() { var max = 0; this.each(function() { max = Math.max(max, $(this).height()); }); return max; }; })(jQuery); var tallest = $('div').maxHeight(); //返回高度最大的div元素的高度
这是一个简单的插件,利用.height()返回页面中高度最大的div元素的高度
四、维护Chainability
很多时候,一个插件的意图仅仅是以某种方式修改收集的元素,并把它们传递给链中的下一个方法。 这是jQuery的设计之美,是jQuery如此受欢迎的原因之一。 因此,要保持一个插件的chainability,你必须确保你的插件返回this关键字。
(function($) { $.fn.lockDimensions = function(type) { return this.each(function() { var $this = $(this); if (!type || type == 'width') { $this.width($this.width()); } if (!type || type == 'height') { $this.height($this.height()); } }); }; })(jQuery); $('div').lockDimensions('width').CSS('color', 'red');
由于插件返回this关键字,它保持了chainability,这样jQuery收集的元素可以继续被jQuery方法如.css控制。 因此,如果你的插件不返回固有的价值,你应该总是在其作用范围内返回this关键字。 此外,你可能会推断出,传递给插件的参数将会在插件的作用范围内被传递。 因此,在前面的例子,字符串'width'变成了插件的类型参数。
五、默认值和选项
对于比较复杂的和提供了许多选项可定制的的插件,最好有一个当插件被调用的时候可以被拓展的默认设置(通过使用$.extend)。 因此,相对于调用一个有大量参数的插件,你可以调用一个对象参数,包含你了你想覆写的设置。
(function($) { $.fn.tooltip = function(options) { //创建一些默认值,拓展任何被提供的选项 var settings = $.extend({ 'location': 'top', 'background-color': 'blue' }, options); return this.each(function() { // Tooltip插件代码 }); }; })(jQuery); $('div').tooltip({ 'location': 'left' });
在这个例子中,调用tooltip插件时覆写了默认设置中的location选项,background-color选项保持默认值,所以最终被调用的设定值为:
{ 'location': 'left', 'background-color': 'blue' }
这是一个很灵活的方式,提供一个高度可配置的插件,而无需开发人员定义所有可用的选项。
六、命名空间
正确命名空间你的插件是插件开发的一个非常重要的一部分。 正确的命名空间,可以保证你的插件将有一个非常低的机会被其他插件或同一页上的其他代码覆盖。 命名空间也使得你的生活作为一个插件开发人员更容易,因为它可以帮助你更好地跟踪你的方法,事件和数据。
七、插件方法
在任何情况下,一个单独的插件不应该在jQuery.fnjQuery.fn对象里有多个命名空间。
(function($) { $.fn.tooltip = function(options) { // this }; $.fn.tooltipShow = function() { // is }; $.fn.tooltipHide = function() { // bad }; $.fn.tooltipUpdate = function(content) { // !!! }; })(jQuery);
这是不被鼓励的,因为它$.fn使$.fn命名空间混乱。 为了解决这个问题,你应该收集对象文本中的所有插件的方法,通过传递该方法的字符串名称给插件以调用它们。
(function($) { var methods = { init: function(options) { // this }, show: function() { // is }, hide: function() { // good }, update: function(content) { // !!! } }; $.fn.tooltip = function(method) { // 方法调用 if (methods[method]) { return methods[method].apply(this, Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1)); } else if (typeof method === 'object' || !method) { return methods.init.apply(this, arguments); } else { $.error('Method' + method + 'does not exist on jQuery.tooltip'); } }; })(jQuery); //调用init方法 $('div').tooltip(); //调用init方法 $('div').tooltip({ foo: 'bar' }); // 调用hide方法 $('div').tooltip('hide'); //调用Update方法 $('div').tooltip('update', 'This is the new tooltip content!');
这种类型的插件架构允许您封装所有的方法在父包中,通过传递该方法的字符串名称和额外的此方法需要的参数来调用它们。 这种方法的封装和架构类型是jQuery插件社区的标准,它被无数的插件在使用,包括jQueryUI中的插件和widgets。
八、事件
一个鲜为人知bind方法的功能即允许绑定事件命名空间。 如果你的插件绑定一个事件,一个很好的做法是赋予此事件命名空间。 通过这种方式,当你在解除绑定的时候不会干扰其他可能已经绑定的同一类型事件。 你可以通过追加命名空间到你需要绑定的的事件通过 ‘.<namespace>'。
(function($) { var methods = { init: function(options) { return this.each(function() { $(window).bind('resize.tooltip', methods.reposition); }); }, destroy: function() { return this.each(function() { $(window).unbind('.tooltip'); }) }, reposition: function() { //... }, show: function() { //... }, hide: function() { //... }, update: function(content) { //... } }; $.fn.tooltip = function(method) { if (methods[method]) { return methods[method].apply(this, Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1)); } else if (typeof method === 'object' || !method) { return methods.init.apply(this, arguments); } else { $.error('Method ' + method + ' does not exist on jQuery.tooltip'); } }; })(jQuery); $('#fun').tooltip(); //一段时间之后... ... $('#fun').tooltip('destroy');
在这个例子中,当tooltip通过init方法初始化时,它将reposition方法绑定到resize事件并给reposition非那方法赋予命名空间通过追加.tooltip。 稍后, 当开发人员需要销毁tooltip的时候,我们可以同时解除其中reposition方法和resize事件的绑定,通过传递reposition的命名空间给插件。 这使我们能够安全地解除事件的绑定并不会影响到此插件之外的绑定。
九、数据
通常在插件开发的时候,你可能需要记录或者检查你的插件是否已经被初始化给了一个元素。 使用jQuery的data方法是一个很好的基于元素的记录变量的途径。尽管如此,相对于记录大量的不同名字的分离的data, 使用一个单独的对象保存所有变量,并通过一个单独的命名空间读取这个对象不失为一个更好的方法。
(function($) { var methods = { init: function(options) { return this.each(function() { var $this = $(this), data = $this.data('tooltip'), tooltip = $('<div />', { text: $this.attr('title') }); // If the plugin hasn't been initialized yet if (!data) { /* Do more setup stuff here */ $(this).data('tooltip', { target: $this, tooltip: tooltip }); } }); }, destroy: function() { return this.each(function() { var $this = $(this), data = $this.data('tooltip'); // Namespacing FTW $(window).unbind('.tooltip'); data.tooltip.remove(); $this.removeData('tooltip'); }) }, reposition: function() { // ... }, show: function() { // ... }, hide: function() { // ... }, update: function(content) { // ... } }; $.fn.tooltip = function(method) { if (methods[method]) { return methods[method].apply(this, Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1)); } else if (typeof method === 'object' || !method) { return methods.init.apply(this, arguments); } else { $.error('Method ' + method + ' does not exist on jQuery.tooltip'); } }; })(jQuery);
将数据通过命名空间封装在一个对象中,可以更容易的从一个集中的位置读取所有插件的属性。
十、总结和最佳做法
编写jQuery插件允许你做出库,将最有用的功能集成到可重用的代码,可以节省开发者的时间,使开发更高效。 开发jQuery插件时,要牢记:
1、始终包裹在一个封闭的插件:
(function($) { /* plugin goes here */ })(jQuery);
2、不要冗余包裹this关键字在插件的功能范围内;
3、除非插件返回特定值,否则总是返回this关键字来维持chainability;
4、传递一个可拓展的默认对象参数而不是大量的参数给插件;
5、不要在一个插件中多次命名不同方法;
6、始终命名空间的方法,事件和数据;


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号