链表和数组区别,链表不是顺序存储。每一个节点里面存着下一个节点的指针。
优点:无需实现申明大小,插入方便。
缺点:查询速度比不上数组。
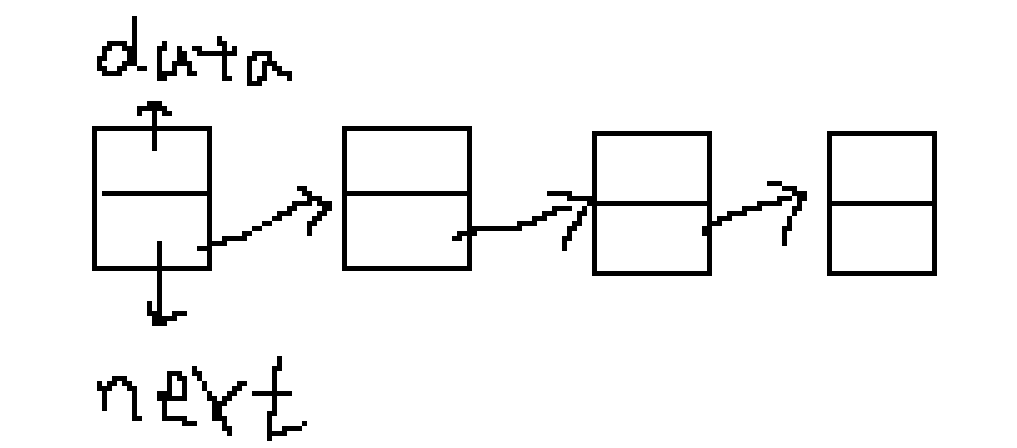
单链表插入节点
1、找到该链表的最后一个节点
2、最后一个节点的指针指向新节点。
3、返回自身。
代码
public class Node { int data; Node next; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; } public Node add(Node node) { Node curNode = this; // 找到该链表最后一个节点 while (true) { Node nextNode = curNode.next; // 如果节点为空 意味着curNode为最后一个节点 if (nextNode == null) { break; } curNode = nextNode; } // 最后一个节点下一个节点指向 node curNode.next = node; return this; } }
删除节点。
1、取出该节点的下下节点。
2、把下下节点赋值给当前节点的下个节点。
3、返回删除数据。
代码实现
public class Node { int data; Node next; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; } // 删除节点 public int remove() { // 先取出下下个节点 int result = next.data; Node nextNode = next.next; this.next = nextNode; return result; } }
查找元素
1、当前节点的值和目标元素的值进行比较,相等返回该节点,不相同进行下一步。
2、节点向后移动一位,继续进行比较。
代码实现
public class Node { int data; Node next; public Node find(int data) { Node current = this; while (current != null) { if (data == current.data) { return current; } current = current.next; } return null; } }
所有代码
public class Node { int data; Node next; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; } public Node add(Node node) { Node curNode = this; // 找到该链表最后一个节点 while (true) { Node nextNode = curNode.next; // 如果节点为空 意味着curNode为最后一个节点 if (nextNode == null) { break; } curNode = nextNode; } // 最后一个节点下一个节点指向 node curNode.next = node; return this; } // 删除节点 public int remove() { // 先取出下下个节点 int result = next.data; Node nextNode = next.next; this.next = nextNode; return result; } public Node find(int data) { Node current = this; while (current != null) { if (data == current.data) { return current; } current = current.next; } return null; } // 打印节点 public void show() { Node curNode = this; while (true) { System.out.print(curNode.data + " "); Node nextNode = curNode.next; // 如果节点为空 if (nextNode == null) { break; } curNode = nextNode; } System.out.println(); } public Node next() { return this.next; } public int getData() { return data; } }
测试代码
public class NodeTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Node node = new Node(1); Node node2 = new Node(2); Node node3 = new Node(3); Node node4 = new Node(4); node.add(node2).add(node3).add(node4); node.show(); System.out.println(node3.remove()); node.show(); System.out.println(node.find(3).data); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号