asp.net权限认证:OWIN实现OAuth 2.0 之客户端模式(Client Credential)
客户端模式定义
客户端使用自己的名义,而不是用户的名义,向“服务提供商” 进行认证。
如何理解这句话? 乍一看,定义有点拗口,刚接触的童鞋可能完全不知所云。
没关系,我们先把他的工作流程图画出来,如下:
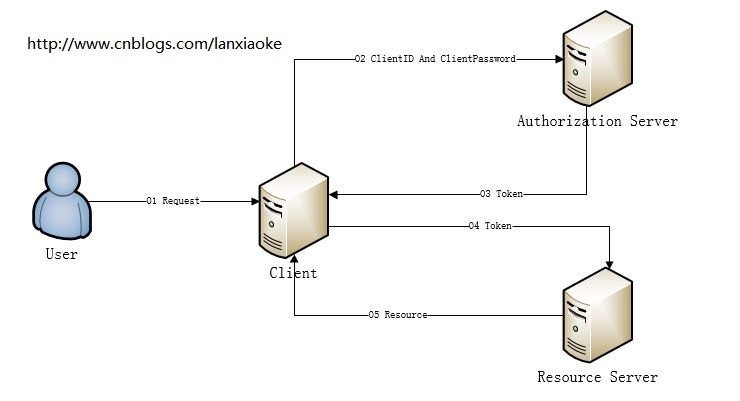
据上图,可以得出一个大概的结论
1、用户(User)通过客户端(Client)访问受限资源(Resource)
2、因为资源受限,所以需要授权;而这个授权是Client与Authentication之间完成的,可以说跟User没有什么关系
3、根据2得出,Resource与User没有关联关系,即User不是这个Resource的Owner(所有者)
既然是这样,那大概可以推出这种认证的适用范围。
第一,肯定不能用作登录认证!因为登录认证后需要得到用户的一些基本信息,如昵称,头像之类,这些信息是属于User的;
第二,适用于一些对于权限要求不强的资源认证,比如:仅用于区分用户是否登录,排除匿名用户获取资源
新建一个资源项目:ResourceServer
引用owin:install-package Microsoft.Owin -Version 2.1.0
新增Startup.cs
[assembly: OwinStartup(typeof(ResourceServer.Startup))]
namespace ResourceServer
{
public partial class Startup
{
public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app)
{
ConfigureAuth(app);
}
}
}
新增Startup.Auth.cs
namespace ResourceServer
{
public partial class Startup
{
public void ConfigureAuth(IAppBuilder app)
{
// 这句是资源服务器认证token的关键,认证逻辑在里边封装好了,我们看不到
app.UseOAuthBearerAuthentication(new Microsoft.Owin.Security.OAuth.OAuthBearerAuthenticationOptions());
}
}
}
新增ValuesController.cs
namespace ResourceServer.Controllers
{
[Authorize]
public class ValuesController : ApiController
{
public string Get()
{
return "lanxiaoke";
}
}
}
新建认证服务项目
修改Startup.Auth.cs
public partial class Startup
{
public void ConfigureAuth(IAppBuilder app)
{
// Setup Authorization Server
app.UseOAuthAuthorizationServer(new OAuthAuthorizationServerOptions
{
TokenEndpointPath = new PathString("/OAuth/Token"),
ApplicationCanDisplayErrors = true,
#if DEBUG
AllowInsecureHttp = true,
#endif
// Authorization server provider which controls the lifecycle of Authorization Server
Provider = new OAuthAuthorizationServerProvider
{
OnValidateClientAuthentication = ValidateClientAuthentication,
OnGrantClientCredentials = GrantClientCredetails
},
// Authorization code provider which creates and receives authorization code
AuthorizationCodeProvider = new AuthenticationTokenProvider
{
OnCreate = CreateAuthenticationCode,
OnReceive = ReceiveAuthenticationCode,
},
// Refresh token provider which creates and receives referesh token
RefreshTokenProvider = new AuthenticationTokenProvider
{
OnCreate = CreateRefreshToken,
OnReceive = ReceiveRefreshToken,
}
});
}
private Task ValidateClientAuthentication(OAuthValidateClientAuthenticationContext context)
{
string clientId;
string clientSecret;
if (context.TryGetBasicCredentials(out clientId, out clientSecret) ||
context.TryGetFormCredentials(out clientId, out clientSecret))
{
if (clientId == "123456" && clientSecret == "abcdef")
{
context.Validated();
}
}
return Task.FromResult(0);
}
private Task GrantClientCredetails(OAuthGrantClientCredentialsContext context)
{
var identity = new ClaimsIdentity(new GenericIdentity(context.ClientId, OAuthDefaults.AuthenticationType), context.Scope.Select(x => new Claim("urn:oauth:scope", x)));
context.Validated(identity);
return Task.FromResult(0);
}
private readonly ConcurrentDictionary<string, string> _authenticationCodes =
new ConcurrentDictionary<string, string>(StringComparer.Ordinal);
private void CreateAuthenticationCode(AuthenticationTokenCreateContext context)
{
context.SetToken(Guid.NewGuid().ToString("n") + Guid.NewGuid().ToString("n"));
_authenticationCodes[context.Token] = context.SerializeTicket();
}
private void ReceiveAuthenticationCode(AuthenticationTokenReceiveContext context)
{
string value;
if (_authenticationCodes.TryRemove(context.Token, out value))
{
context.DeserializeTicket(value);
}
}
private void CreateRefreshToken(AuthenticationTokenCreateContext context)
{
context.SetToken(context.SerializeTicket());
}
private void ReceiveRefreshToken(AuthenticationTokenReceiveContext context)
{
context.DeserializeTicket(context.Token);
}
}
自此,认证服务项目算是建好了,因为对于客户端模式,认证服务器只需要返回token
新增Client项目
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var authorizationServerUri = new Uri("http://localhost:8270/");
var authorizationServerDescription = new AuthorizationServerDescription
{
TokenEndpoint = new Uri(authorizationServerUri, "OAuth/Token")
};
var client = new WebServerClient(authorizationServerDescription, "123456", "abcdef");
var state = client.GetClientAccessToken(new[] { "scopes1", "scopes2" });
var token = state.AccessToken;
Console.WriteLine("Token: {0}", token);
var resourceServerUri = new Uri("http://localhost:8001/");
var httpClient = new HttpClient(client.CreateAuthorizingHandler(token));
var values = httpClient.GetStringAsync(new Uri(resourceServerUri, "api/Values")).Result;
Console.WriteLine("Result: {0}", values);
Console.ReadKey();
}
OK,Client环境搭好了,我们来运行下试试
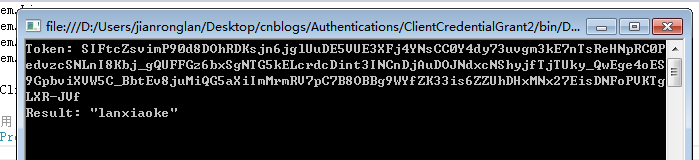
认证成功!
asp.net权限认证系列
- asp.net权限认证:Forms认证
- asp.net权限认证:HTTP基本认证(http basic)
- asp.net权限认证:Windows认证
- asp.net权限认证:摘要认证(digest authentication)
- asp.net权限认证:OWIN实现OAuth 2.0 之客户端模式(Client Credential)
- asp.net权限认证:OWIN实现OAuth 2.0 之密码模式(Resource Owner Password Credential)
- asp.net权限认证:OWIN实现OAuth 2.0 之授权码模式(Authorization Code)
- asp.net权限认证:OWIN实现OAuth 2.0 之简化模式(Implicit)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号