Windows 消息机制
Windows 和消息
消息和消息队列
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 消息和消息队列 | 本部分介绍消息和消息队列,以及如何在应用程序中使用它们。 |
| 关于消息和消息队列 | 本部分讨论 Windows 消息和消息队列。 |
| 使用消息和消息队列 | 以下代码示例演示如何执行与 Windows 消息和消息队列关联的以下任务。 |
| 消息引用 | 包含 API 引用。 |
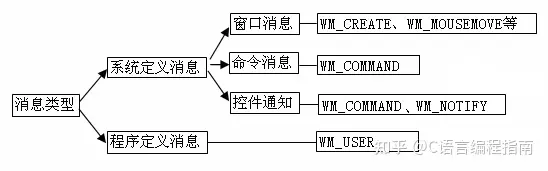
Windows消息类型
根据消息的来源进行分类,可以分为:
根据消息的路由方式分类,可以分为:
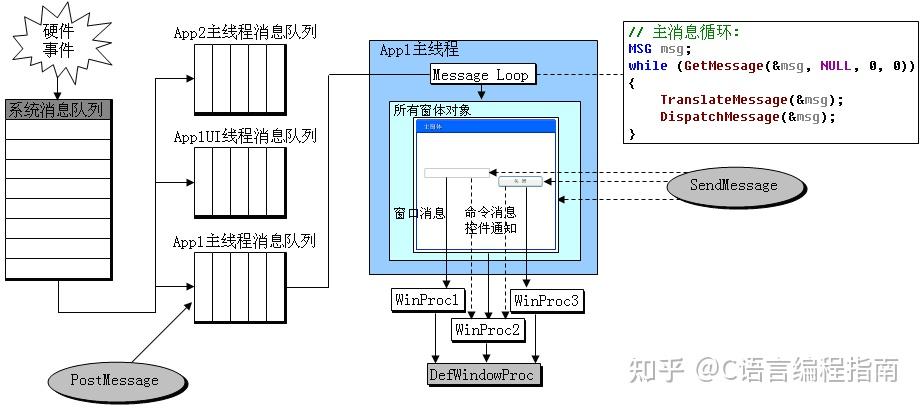
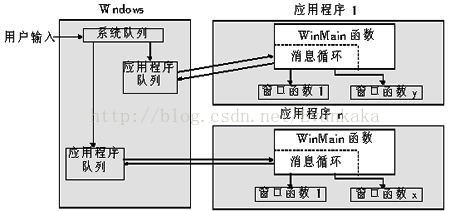
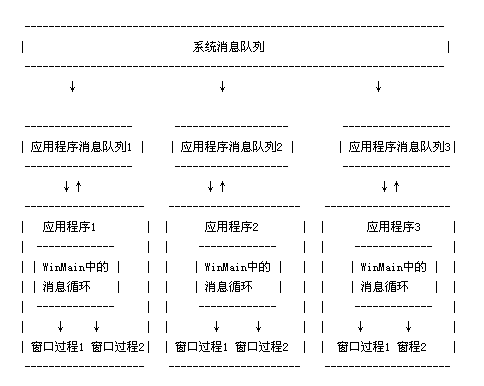
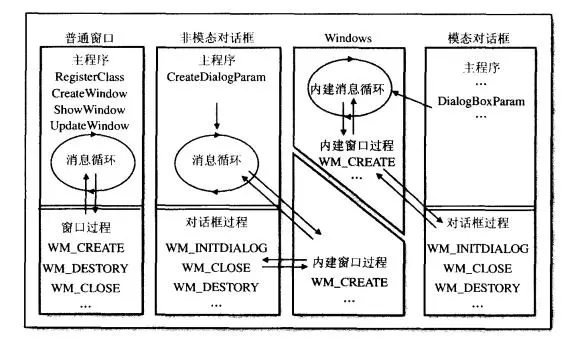
Windows系统的整个消息系统分为3个层级
-
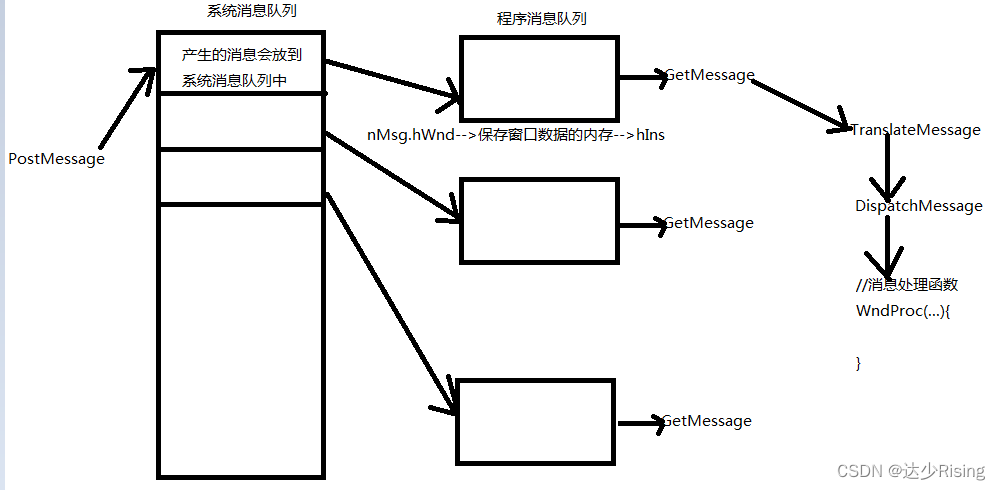
Windows内核的系统消息队列
Windows内核维护着一个全局的系统消息队列;按照线程的不同,系统消息队列中的消息会分发到应用程序的UI线程的消息队列中;
-
应用程序UI线程消息队列
应用程序的每一个UI线程都有自己的消息循环,会不停地从自己的消息队列取出消息,并发送给Windows窗体对象(WinForm控件);
-
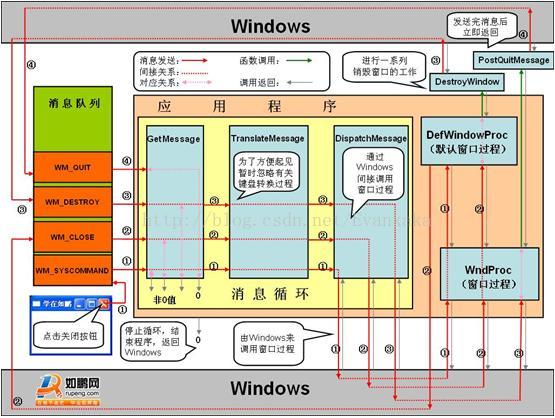
每个控件自己的消息处理函数
WinForm 中的
void WndProc(ref Message m)消息处理函数
Q&A
- 进程消息队列(应用程序消息队列)和主线程的消息队列是一回事吗?
在 WinForm 程序中,进程消息队列指的是主线程的消息队列。WinForm 应用程序是单线程的,所有的 UI 操作都必须在主线程中执行。当用户与应用程序的界面交互时,操作系统会将相关的消息发送到应用程序的消息队列中,然后主线程从消息队列中逐个获取并处理这些消息,以更新界面状态和响应用户操作。因此,进程消息队列实际上就是主线程的消息队列。
- 线程中消息队列消息的结构是怎样的?
typedef struct tagMSG { // 接收消息的窗口的句柄。 当消息是线程消息时,此成员为 NULL 。 HWND hwnd; // 消息的标识符。 应用程序只能使用低字;高字由系统保留。 UINT message; // 消息的附加信息。 确切含义取决于 消息 成员的值。 WPARAM wParam; // 消息的附加信息。 确切含义取决于 消息 成员的值。 LPARAM lParam; // 消息的发布时间。 DWORD time; // 发布消息时的光标位置(以屏幕坐标表示)。 POINT pt; // DWORD lPrivate; } MSG, *PMSG, *NPMSG, *LPMSG;
- 在WinForm程序中线程Id和托管线程Id是一回事吗?
线程Id和托管线程Id是不一样的!
可以通过以下方法获取线程的Id
/// <summary> /// 获取操作系统线程ID,Windows 10下的偏移量为0x022C(x64-bit-Application)和0x0160(x32-bit-Application): /// https://www.ibckf.com/questions/1679243 /// </summary> /// <param name="thread"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static int GetNativeThreadId(Thread thread) { var f = typeof(Thread).GetField("DONT_USE_InternalThread", BindingFlags.GetField | BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance); var pInternalThread = (IntPtr)f.GetValue(thread); var nativeId = Marshal.ReadInt32(pInternalThread, (IntPtr.Size == 8) ? 0x022C : 0x0160); // found by analyzing the memory return nativeId; }
获取当前线程的托管线程Id
public static string CurrentThreadId { get { var thread = Thread.CurrentThread; var threadId = GetNativeThreadId(thread); return $"{thread.ManagedThreadId} - ({threadId}, 0x{threadId.ToString("x2")})"; } }
- 知道控件的句柄如何获取该控件所在的进程和线程信息?
public static class Extensions { // 导入 Windows API 函数 /// <summary> /// 检索创建指定窗口的线程的标识符,以及创建该窗口的进程(可选)的标识符。 /// GetWindowThreadProcessId 函数 : https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/windows/win32/api/winuser/nf-winuser-getwindowthreadprocessid /// </summary> /// <param name="hWnd">控件句柄</param> /// <param name="processId">控件所属进程Id</param> /// <returns>控件所属线程Id</returns> [DllImport("user32.dll")] private static extern int GetWindowThreadProcessId(IntPtr hWnd, out int processId); public static void ConsoleHandleInfo(this Control ctrl, string name) { var handle = ctrl.Handle; var threadId = GetWindowThreadProcessId(handle, out int processId); Console.WriteLine($"{ThreadInfo.CurrentThreadId} -> 创建 {name} 的进程Id = {processId},线程Id = {threadId}"); } }
WinForm程序中消息处理的相关方法
按调用顺序依次介绍,可以对消息进行拦截与处理
-
IMessageFilter的消息处理
一般处理逻辑,在构造函数中调用Application.AddMessageFilter(this);添加消息筛选器,在析构函数中调用Application.RemoveMessageFilter(this);移除消息筛选器,然后重写PreProcessMessage消息处理函数。
返回值:如果消息已处理,则为
true;否则为false。影响级别:应用程序级
-
Control.PreProcessMessage
在调度键盘或输入消息之前,在消息循环内对它们进行预处理(键盘消息预处理函数)。
返回值:如果消息已由控件处理,则为
true;否则为false。影响级别:应用程序级
重写 PreProcessMessage时,控件返回
true以指示它已处理消息。 对于控件未处理的消息,应返回base.PreProcessMessage的结果 。 控件通常会替代更专用的方法之一,例如 IsInputChar、 IsInputKey、 ProcessCmdKey、 ProcessDialogChar或 ProcessDialogKey ,而不是重写 PreProcessMessage。 -
键盘消息的其他处理函数,如 protected override bool IsInputKey(Keys keyData)
-
控件的消息处理函数
protected override void WndProc(ref Message m) { // 控件内消息处理函数 //Console.WriteLine($"WndProc-> {m}"); base.WndProc(ref m); }
其他代码片段
bool PreProcessMessage(ref Message msg)实现
/// <summary> /// This method is called by the application's message loop to pre-process input messages before they /// are dispatched. If this method processes the message it must return true, in which case the message /// loop will not dispatch the message. /// </summary> /// <remarks> /// <para> /// The messages that this method handles are WM_KEYDOWN, WM_SYSKEYDOWN, WM_CHAR, and WM_SYSCHAR. /// </para> /// <para> /// For WM_KEYDOWN and WM_SYSKEYDOWN messages, this first calls <see cref="ProcessCmdKey(ref Message, Keys)"/> /// to check for command keys such as accelerators and menu shortcuts. If it doesn't process the message, then /// <see cref="IsInputKey(Keys)"/> is called to check whether the key message represents an input key for the /// control. Finally, if <see cref="IsInputKey(Keys)"/> indicates that the control isn't interested in the key /// message, then <see cref="ProcessDialogKey(Keys)"/> is called to check for dialog keys such as TAB, arrow /// keys, and mnemonics. /// </para> /// <para> /// For WM_CHAR messages, <see cref="IsInputChar(char)"/> is first called to check whether the character /// message represents an input character for the control. If <see cref="IsInputChar(char)"/> indicates that /// the control isn't interested in the character message, then <see cref="ProcessDialogChar(char)"/> is /// called to check for dialog characters such as mnemonics. /// </para> /// <para> /// For WM_SYSCHAR messages, this calls <see cref="ProcessDialogChar(char)"/> to check for dialog characters /// such as mnemonics. /// </para> /// <para> /// When overriding this method, a control should return true to indicate that it has processed the message. /// For messages that aren't processed by the control, the result of "base.PreProcessMessage()" should be /// returned. /// </para> /// <para> /// Controls will typically override one of the more specialized methods (<see cref="IsInputChar(char)"/>, /// <see cref="IsInputKey(Keys)"/>, <see cref="ProcessCmdKey(ref Message, Keys)"/>, <see cref="ProcessDialogChar(char)"/>, /// or <see cref="ProcessDialogKey(Keys)"/>) instead of overriding this method. /// </para> /// </remarks> public virtual bool PreProcessMessage(ref Message msg) { bool result; if (msg.MsgInternal == PInvoke.WM_KEYDOWN || msg.MsgInternal == PInvoke.WM_SYSKEYDOWN) { if (!GetExtendedState(ExtendedStates.UiCues)) { ProcessUICues(ref msg); } Keys keyData = (Keys)(nint)msg.WParamInternal | ModifierKeys; if (ProcessCmdKey(ref msg, keyData)) { result = true; } else if (IsInputKey(keyData)) { SetExtendedState(ExtendedStates.InputKey, true); result = false; } else { result = ProcessDialogKey(keyData); } } else if (msg.MsgInternal == PInvoke.WM_CHAR || msg.MsgInternal == PInvoke.WM_SYSCHAR) { if (msg.MsgInternal == PInvoke.WM_CHAR && IsInputChar((char)(nint)msg.WParamInternal)) { SetExtendedState(ExtendedStates.InputChar, true); result = false; } else { result = ProcessDialogChar((char)(nint)msg.WParamInternal); } } else { result = false; } return result; }
相关参考
- msg 结构 (winuser.h)
- Message 结构
- 关于消息和消息队列
- 使用消息和消息队列
- Windows消息机制(MFC深度详解)
- windows消息机制深入详解
- WINDOWS消息,消息的解析可以参考此篇
- 线程与消息队列,介绍线程间相互通信相关的函数




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)