一、使用常识
HashMap是一中比较常用的,也比较好用的集合,但是HashMap有一个顺序的问题,就是在对HashMap进行迭代访问时,
添加的顺序和访问的顺序可能就不一样的,这个时候我们可以选择LinkedHashMap,
LinkedHashMap继承了HashMap,所以拥有和HashMap一样的功能;而且在此基础上有增加了一个双向链表来实现元素迭代的顺序,但是肯定会增加时间和空间的消耗,
LinkedHashMap和HashMap一样,也是非线程安全的
我们还是先来看一个LinkedHashMap的实例,操作数据的方法和HasMap是一样的,代码如下:
案例一 基本使用
@Test public void LinkHashMapTest1() { Map<String, Object> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); map.put("name","洛少"); map.put("age",18); map.put("adress","斗破大陆"); map.put(null,null); map.put(null,1); map.put("test",null); System.out.println("map= "+map); }
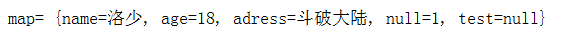
结论:
LinkedHashMap的输入顺序和输出顺序是一致的。
LinkedHashMap允许Key和Value都可以null
LinkedHashMap中添加元素时,如果Key重复,则后添加的会覆盖前面已经存在的值
分析源码得出:从以上可以判断LinkedHashMap的实现就是 HashMap+LinkedList 的实现方式,
用HashMap维护数据结构,用LinkList的方式维护数据插入顺序。
二、多线程分析:
案例一、线程不安全
@Test public void LinkHashMapTest2() throws InterruptedException { Map<String, Object> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); //线程T-1 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for (int i = 1; i < 500; i++) { map.put("a" + i, i); try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-1").start(); //线程T-2 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for (int i = 500; i <= 1000; i++) { map.put("a" + i, i); try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-2").start(); //线程T-3 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for (int i = 500; i <= 1000; i++) { if (map.containsKey("a120")) { map.put("a120", 888); } try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-3").start(); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("a120= "+map.get("a120")); System.out.println("大小:" + map.size()); }

案例二: 线程安全
如果必须使用 LinkedHashMap 且要线程安全
@Test public void LinkHashMapTest2() throws InterruptedException { //Map<String, Object> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); Map<String, Object> map = Collections.synchronizedMap(new LinkedHashMap<>()); //线程T-1 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for (int i = 1; i < 500; i++) { map.put("a" + i, i); try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-1").start(); //线程T-2 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for (int i = 500; i <= 1000; i++) { map.put("a" + i, i); try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-2").start(); //线程T-3 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for (int i = 500; i <= 1000; i++) { if (map.containsKey("a120")) { map.put("a120", 888); } try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-3").start(); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("a120= "+map.get("a120")); System.out.println("大小:" + map.size()); }

补充:
图解LinkedHashMap原理


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号