大多数javaer都知道HashMap是线程不安全的,多线程环境下数据可能会发生错乱,一定要谨慎使用。这个结论是没错,
可是HashMap的线程不安全远远不是数据脏读这么简单,它还有可能会发生死锁,造成内存飙升100%的问题
参见:https://www.cnblogs.com/wyq178/p/8676655.html
案例一
@Test public void HashMapTest1() throws InterruptedException { Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); //线程T-1 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for(int i=1;i<500;i++) { map.put("a"+i,i); try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-1").start(); //线程T-2 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for(int i=500;i<=1000;i++) { map.put("a"+i,i); try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-2").start(); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("大小:"+map.size()); }
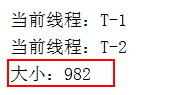
案例二(线程安全)
@Test public void HashMapTest1() throws InterruptedException { // Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); Map<String, Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); //线程T-1 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for(int i=1;i<500;i++) { map.put("a"+i,i); try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-1").start(); //线程T-2 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for(int i=500;i<=1000;i++) { map.put("a"+i,i); try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-2").start(); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("大小:"+map.size()); }

案例三(线程安全)
@Test public void HashMapTest1() throws InterruptedException { // Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); Map<String, Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); //线程T-1 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for (int i = 1; i < 500; i++) { map.put("a" + i, i); try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-1").start(); //线程T-2 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for (int i = 500; i <= 1000; i++) { map.put("a" + i, i); try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-2").start(); //线程T-3 new Thread(() -> { System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); for (int i = 500; i <= 1000; i++) { if (map.containsKey("a120")) { map.put("a120", 888); } try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "T-3").start(); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("a120= "+map.get("a120")); System.out.println("a130= "+map.get("a130")); System.out.println("大小:" + map.size()); }

补充:如何选择合适的Map
- HashMap可实现快速存储和检索,但其缺点是其包含的元素是无序的,这导致它在存在大量迭代的情况下表现不佳。
- LinkedHashMap保留了HashMap的优势,且其包含的元素是有序的。它在有大量迭代的情况下表现更好。
- TreeMap能便捷的实现对其内部元素的各种排序,但其一般性能比前两种map差。
LinkedHashMap映射减少了HashMap排序中的混乱,且不会导致TreeMap的性能损失。
扩展:如果将对象作为key 存贮,就是他们的内容一样,但是对象不一样,
map.containsKey()这个方法将永远返回false ,这个时候需要重写hashCode和 equal这两个方法
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/panxuejun/p/5958875.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号