快捷键:
Ctrl + Shift + ESC : 任务管理器
卸载JDK
1.删除java的安装目录
2.删除JAVA_HOME
3.删除path下关于java的目录
4.java -version
安装JDK
1.baidu搜索JDK8,找到下载地址
2.同意协议
3.下载电脑对应的版本
4.双击安装
5.记住安装的路径
6.配置环境变量
1.添加JAVA_HOME环境变量
2.配置path变量
%JAVA_HOME%\bin
%JAVA_HOME%\jre\bin
7.测试JDK是否安装成功
1.打开cmd
2.执行java -version
HelloWorld
1.随便新建一个文件夹,存放代码
2.新建一个java文件
- 文件后缀名为.java
- Hello.java
- 【注意点】系统没显示文件后缀名,需要手动打开
3.编写代码
Hello.java
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("Hello,World");
}
}
4.编译javac java文件,会生成一个class文件
5.运行class文件,java 文件名
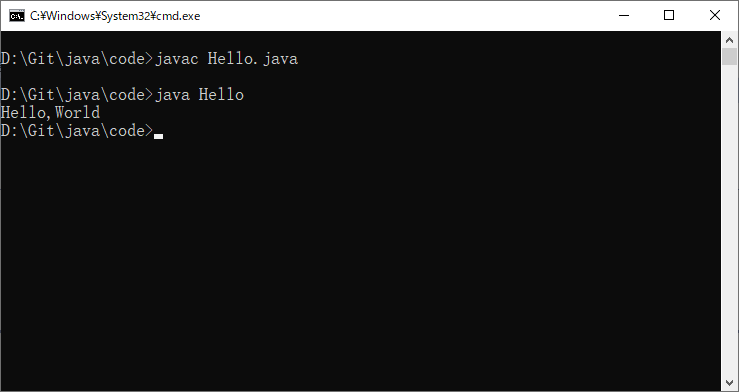
注意
1.每个单词的大小写不能出现问题,java大小写敏感。
2.尽量使用英文。
3.文件名和类名必须保持一致,并且首字母大写。
4.符号也不能使用中文的。
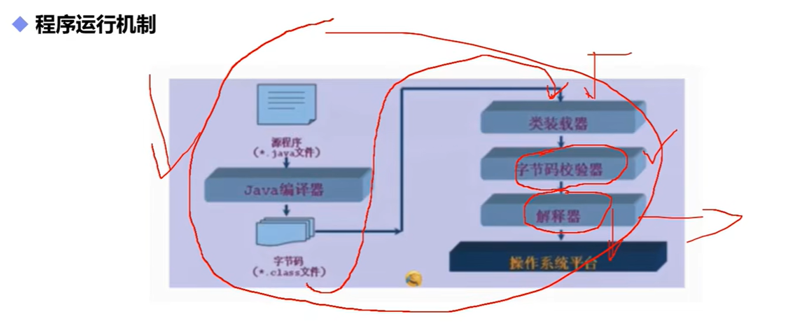
java程序运行机制
-
编译型
-
解释型
-
程序运行机制
![]()
IDEA安装
集成开发环境
https://www.jetbrains.com/ja-jp/
JetBrains 是捷克的一个公司。
快捷键:
psvm:public static void main(String[] args) {
sout:System.out.println();
IDEA优化
搜索:IDEA优化
可以找到很多文章。
工欲善其事必先利其器。
注释
java中注释有三种:
- 单行注释 //
- 多行注释 /* 多行注释 */
- 文档注释 /** 文档注释 */
有趣的代码注释
网上去搜索就能找到!
数据类型
java是一种强类型语言。
所有变量必须先定义再使用。
//整数
int num1=10;
byte num2=20;
short num3 = 30;
long num4=40L; //Long类型要在数字后面加个L
//小数:浮点数
float num5 = 50.1F; //float类型要在数字后面加个F
double num6=3.1415966;
//字符
char name = 'A';
//字符串,String不是关键字,类
String name2 = "阿凡提";
数据类型扩展
整数扩展:
进制 二进制0b 十进制 八进制0 十六进制0x
//整数扩展
//进制 二进制0b 十进制 八进制0 十六进制0x
int i1=10;
int i2=010; //八进制0
int i3=0x10;//十六进制0x
System.out.println(i1);
System.out.println(i2);
System.out.println(i3);
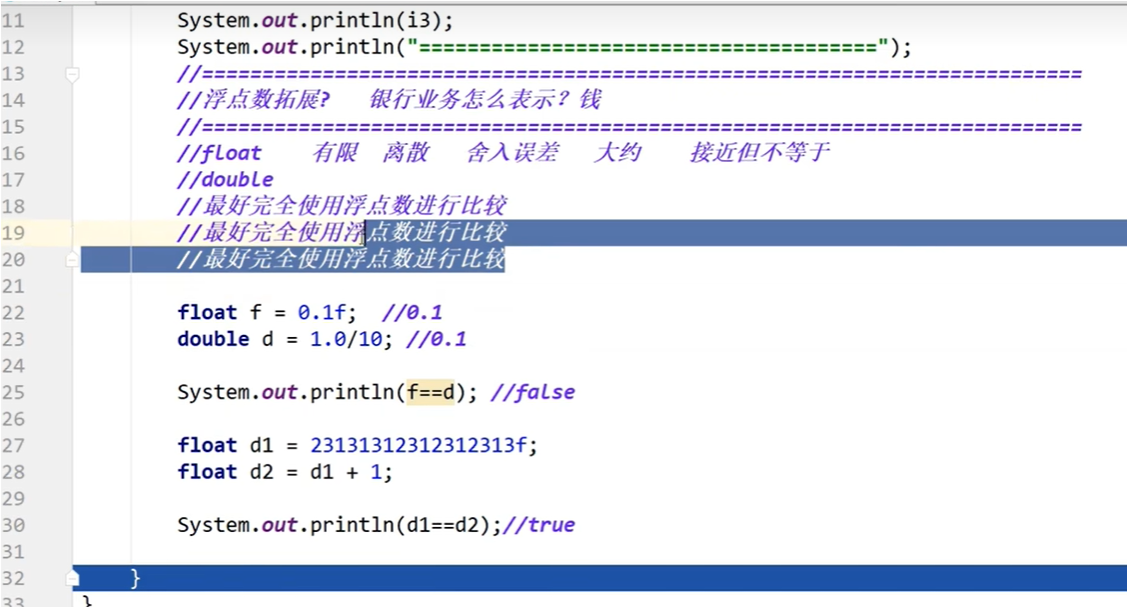
浮点数拓展
float 有限 舍入误差 接近但不等于
//最后完全使用浮点数进行比较
//________________________________
//浮点数拓展? 银行业务怎么表示?钱
//BigDecimal 数学工具类
//________________________________
//float
//double
float f = 0.1f; //0.1
double d = 1.0 / 10; //0.1
System.out.println(f == d); //false
System.out.println(f);
System.out.println(d);
float d1=23213131111111111111111111f;
float d2=d1+1;
System.out.println("d1=d1?" + (d1 == d2)); //true
字符拓展
所有的字符本质还是数字。
//________________________________
//字符拓展?
//________________________________
System.out.println("============");
char c1 = 'a';
char c2 = '中';
System.out.println(c1); //a
System.out.println((int)c1);//强制转换 97
System.out.println(c2); //中
System.out.println((int)c2);//强制转换 20013
//所有的字符本质还是数字。
//编码 Unicode表:(97=a 65=A)2字节 0~65536 Excle 2^16= 65536
// U0000 UFFFF
char c3 = '\u0061';
System.out.println(c3); //a
转义字符
// \t 制表符
// \n 换行
// ......
System.out.println("Hello\tWorld");
System.out.println("Hello\nWorld");
对象 从内存分析
System.out.println("==================");
String sa = new String("hellow world");
String sb = new String("hellow world");
System.out.println(sa==sb); //false
String sc = "hello world";
String sd = "hello world";
System.out.println(sc==sd); //true
//对象 从内存分析
布尔值扩展
//布尔值扩展
boolean flag =true;
if (flag==true) { } //新手
if (flag) { } //老手
// Less is more! 代码要精简易读
类型转换
//强制转换 (类型)变量名 高 → 低
//自动转换 低 → 高
注意:转化的时候可能存在内存溢出,或者精度问题!
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 128;
byte b=(byte)i; // 内存溢出
double b2 = i;
//强制转换 (类型)变量名 高 → 低
//自动转换 低 → 高
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(b); //-128
System.out.println(b2);
/*
注意点:
1.不能对布尔值进行转换
2.不能把对象类型转化为不相干的类型
3.把高容量转化为低容量的时候,强制转换
4.转化的时候可能存在内存溢出,或者精度问题!
*/
System.out.println("======================");
System.out.println((int)23.7); //23
System.out.println((int)-45.89f); //-45
System.out.println("======================");
char c = 'a';
int d = c + 1;
System.out.println(d); //98
System.out.println((char) d); //b
System.out.println("======================");
//常见的问题
//操作表达的数的时候,注意溢出问题
//JDK7新特性,数字之间可以用下划线分割
//int money= 1000000000;
int money= 10_0000_0000;
int years = 20;
int total = money * years;//-1474836480 计算的时候溢出了
long total2 = money * years;//-1474836480 默认是int,转换之前已经存在问题了
long total3 = money * ((long) years); //先把一个数转换为long
long total4 = ((long) money) * years;
System.out.println(total); //-1474836480
System.out.println(total2); //-1474836480
System.out.println(total3); //20000000000
System.out.println(total4); //20000000000
}
}
变量,常量(final), 作用域
变量类型有:局部变量,实例变量,类变量(static)。
修饰符,不存在先后顺序
注意:
1.所有变量,方法,类名:见名知意
2.变量(类成员变量,局部变量):首字母小写和驼峰原则
eg:monthSalary
3.常量:大写字母和下划线:MAX_VALUE
4.类名:首字母大写和驼峰原则
5.方法名:首字母小写和驼峰原则
public class Demo04 {
//属性:变量 static
static double salary = 2500;
//修饰符,不存在先后顺序
static final double PI = 3.14;
//实例变量:从属于对象;如果不自行初始化,这个类型的默认值 0 0.0
//布尔型:默认是false
//除了基本类型,其余的默认值都是null
String name;
int age;
//main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//局部变量:必须声明和初始化值
int i=10;
System.out.println(i);
//变量类型 变量名字= new Demo04();
Demo04 demo04=new Demo04();
System.out.println(demo04.name);
System.out.println(demo04.age);
//类变量 static
System.out.println(salary);
System.out.println(PI);
}
//其他方法
public void add() {
}
}
运算符
算数运算符
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//二元运算符
//ctrl + D:复制当前行到下一行
int a=10;
int b=20;
int c=25;
int d=25;
System.out.println(a+b);
System.out.println(a-b);
System.out.println(a*b);
//System.out.println(a/b); //0
System.out.println(a/(double)b); //0.5
}
}
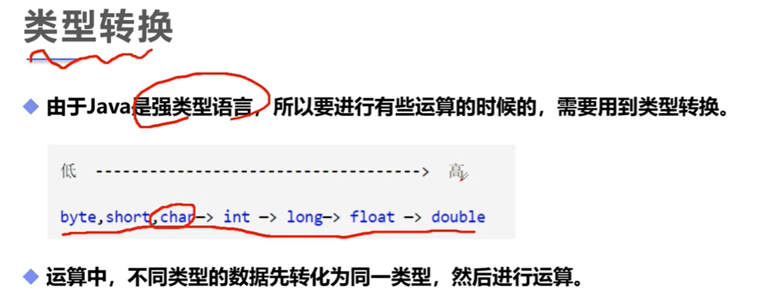
运算时,运算结果的类型,以最长的为准
没有Long或float,double,统一按照Int做计算。
应该就是下面这个图表述的类型转换顺序。
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long a = 123123123123123L;
int b = 123;
short c = 10;
byte d = 8;
System.out.println(a + b + c + d); //Long
System.out.println(b + c + d); //Int
System.out.println(c + d); //Int
// System.out.println((String) (c + d)); //Int 用这个写法会发生语法错误,提示里就能知道 c+d的运算结果类型。
System.out.println(String.valueOf(c + d)); //如果一定要写String类型,可以这样写。
}
}
取余数,(也叫模运算)
int a1 = 10;
int c1 = 21;
//取余数 (模运算)
System.out.println(c1 % a1); // c / a 21 / 10 = 2 ... 1
//++ -- 自加, 自减 一元运算符
//幂运算 2^3 222 = 8
//很多运算,我们使用工具类来操作
//幂运算 2^3 2*2*2 = 8
double pow = Math.pow(2, 3);
System.out.println(pow); //8.0
逻辑运算符
与and 或or 非(取反)
package operator;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//与and 或or 非(取反)
boolean a = true;
boolean b = false;
System.out.println("b && a :" + (b && a));
System.out.println("a || b :" + (a || b));
System.out.println("!(a && b) :" + !(a && b));
//短路运算
int c = 5;
boolean d = (c < 4) && (c++ < 4);//因为短路,后面的处理(c++ < 4)未执行,所以c还是原来的值5,而不是6。
System.out.println(d);//false
System.out.println(c);//5
}
}
位运算
效率极高!!!
<< *2
>> /2
/*
A = 0011 1100
B = 0000 1101
A&B=0000 1100
A|B=0011 1101
A^B=0011 0001
~B =1111 0010
*/
byte A = 0b00111100;
byte B = 0b00001101;
System.out.println(A&B); //12
System.out.println(A|B); //61 32+16+8+4+1=61
System.out.println(A^B); //49 32+16+1=49
System.out.println(~B); //242 128+64+32+16+2=242 1101 8+4+1=13
/*
2*8 = 16 2* 2*2*2
效率极高!!!
<< *2
>> /2
0000 0000 0
0000 0001 1
0000 0010 2
0000 0011 3
0000 0100 4
0000 0101 5
0000 0110 6
0000 0111 7
0000 1000 8
0001 0000 16
*/
System.out.println(7 << 3); //56 7 * 2^
//字符串连接符 + String
//字符串连接符 + String
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println(a+b); //30
System.out.println(""+a+b); //1020 运算时遇到字符串就按都按照字符串进行处理了。
System.out.println(a+b+""); //30
三元运算符
//三元运算符
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// x ? y : z
//如果x==true,则结果为y,否则结果为z
int score = 80;
String type = score < 60 ? "不及格" : "及格";
System.out.println(type);//及格
}
}
运算符优先级
可以加括号,更能明确优先级 ( )
包机制
一般利用公司域名倒置作为包名:
www.baidu.com com.baidu.www

java Doc
javadoc是用来自己生成API文档的
参考信息:@author, @version, @since 等等
在IEDA中输入/**之后一回车,就自动能生成一些要写的doc内容。
之后,可以在cmd窗口执行javadoc命令生成doc文档。
D:\workspace\Java\J2SE\basicSyntax\src\com\mysoft\base>javadoc Doc.java
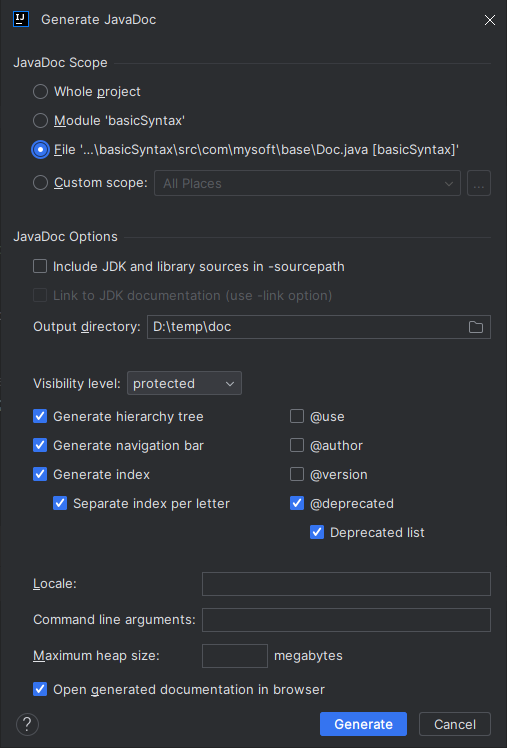
或者 从IDEA的TOOL找到生成javadoc的菜单【Generate JavaDoc】。这样更方便。
可以指定生成哪些对象,javadoc的生成场所等等。
package com.mysoft.base;
/**
* @author panda
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.8
*/
public class Doc {
String name;
/**
* @author panda
* @param name
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public String test(String name) throws Exception {
return name;
}
}
生成效果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号