Shader学习笔记 02 - 水(无光照)
反射、折射贴图
- 使用GrabPass
GrabPass { "_GrabTexture" }
vert {
float4 screenpos = ComputeGrabScreenPos(o.vertex);
}
frag {
tex2Dproj(_GrabTexture, screenpos);
}
- 使用相机的Render Texture
render texture的高宽比一般与相机viewport的高宽比相同。
扭曲 Distortion
扭曲的方法多种多样,一般原理都是使用时间错位(time offset)获取两次扭曲结果,然后将两者组合起来消除视觉上的不连续性。
1. 使用噪声
方法1
混合UV不同方向运动,两个uv扭曲的方向差不多相差90度,简单有效适合水下的扭曲。

示例源码:
Shader "Unlit/River02Sh" { Properties { _MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {} _Tint ("Texture", Color) = (0.3,1,0.8,1) _Speed("Speed", float) = 1 _NoiseSize("Noise Size", float) = 1 } SubShader { Tags {"Queue"="Transparent" "RenderType"="Transparent"} GrabPass { "_GrabTexture" }Pass { CGPROGRAM #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "Noise.cginc" struct appdata { float4 vertex : POSITION; float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; }; struct v2f { float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; float4 uvgrab : TEXCOORD1; float4 vertex : SV_POSITION; }; sampler2D _MainTex; sampler2D _GrabTexture; float4 _MainTex_ST; fixed4 _Tint; float _Speed,_NoiseSize; v2f vert (appdata v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex); o.uvgrab = ComputeGrabScreenPos(o.vertex); return o; } fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target { float time = _Time.y*_Speed; float offset = 0.4; float2 motion1 = float2(time*0.3, time*-0.4); float2 motion2 = float2(time*0.1, time*0.5); float2 uv1 = i.uv; float2 uv2 = i.uv + offset; float2 dis1 = float2(noise(uv1 + motion1), noise(uv2 + motion1)); float2 dis2 = float2(noise(uv1 + motion2), noise(uv2 + motion2)); float2 dis = (dis1 + dis2 - 1)*_NoiseSize; // sample the texture float4 grabPosUV = UNITY_PROJ_COORD(i.uvgrab); grabPosUV.xy += dis; fixed4 col = tex2Dproj(_GrabTexture, grabPosUV)*_Tint; return col; } ENDCG } }
}
方法2
修改噪声tiling,将噪声拉伸,然后生成两个对立方向移动的噪声,再相乘合并。
官方demo上shader graph预览:
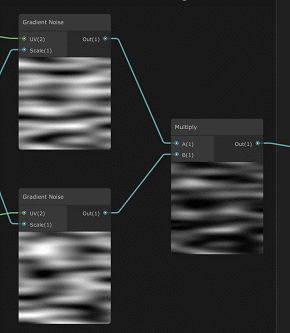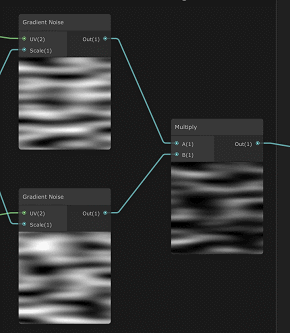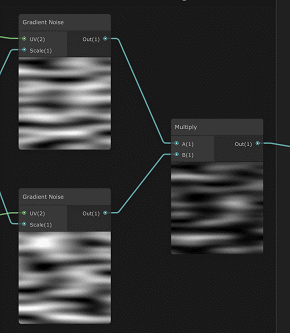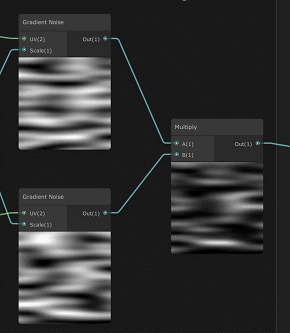
效果:

示例源码:
Shader "Unlit/DistortionSH" { Properties { _MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {} _DistortionST ("Distortion Tiling & Offset", vector) = (0.18,1,0,0) _DistortionSize ("Distortion Size", float) = 10 _DistortionStrength ("Distortion Strength", range(0,1)) = 1 _Speed ("Speed", float) = 1 } SubShader { Tags {"Queue"="Transparent" "RenderType"="Transparent"}GrabPass { "_GrabTexture" } Pass { CGPROGRAM #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag #pragma fragmentoption ARB_precision_hint_fastest #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "Noise.cginc" struct appdata { float4 vertex : POSITION; float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; }; struct v2f { float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; float4 uvgrab : TEXCOORD1; float4 vertex : SV_POSITION; }; sampler2D _MainTex; float4 _MainTex_ST; sampler2D _GrabTexture; float4 _DistortionST; float _DistortionStrength; float _DistortionSize; float _Speed; v2f vert (appdata v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); float4 screenpos = ComputeGrabScreenPos(o.vertex); //o.uvgrab = screenpos.xy / screenpos.w; o.uvgrab = screenpos; o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex); return o; } fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target { float disSpeed = _Time.y*_Speed; float2 disUV1 = i.uv*_DistortionST.xy + _DistortionST.zw + float2(0, disSpeed); float2 disUV2 = i.uv*_DistortionST.xy + _DistortionST.zw + float2(0, 1 - disSpeed); float dis1 = noise(disUV1*_DistortionSize); float dis2 = noise(disUV2*_DistortionSize); float disStr = lerp(0,0.1,_DistortionStrength); float dis = dis1*dis2*disStr; return tex2Dproj(_GrabTexture, i.uvgrab + float4(dis, 0, 0 ,0)); } ENDCG } }
}
2. 使用纹理贴图
来源 catlikecoding - texture distortion,去除了光照相关部分。
利用frac(time)让扭曲循环,使用时间错位frac(time + offset)获取另一个扭曲,两者相加去除视觉上的不连续性;两个扭曲明暗变化错位(呈锯齿状);uv跳跃等。
使用流动贴图 Flow Map 可以更加精细化的控制各个地方的扭曲方向,明暗,甚至是扭曲变化速度。
去光照简化版预览:

示例源码:
Shader "Unlit/DistortionSH" { Properties { _MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {} _Tint ("Texture", Color) = (0.3,1,0.8,1) _DistortionTexture ("Flow (RG, A noise)", 2D) = "bump" {} _DistortionSize ("Flow Strength", float) = 1 _Speed ("Speed", float) = 1 _WeihtNoise("Weight Noise", float) = 1 _UJump ("U jump per phase", Range(-0.25, 0.25)) = 0.25 _VJump ("V jump per phase", Range(-0.25, 0.25)) = 0.25 } SubShader { Tags {"Queue"="Transparent" "RenderType"="Transparent"}GrabPass { "_GrabTexture" } Pass { CGPROGRAM #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag #pragma fragmentoption ARB_precision_hint_fastest #include "UnityCG.cginc" struct appdata { float4 vertex : POSITION; float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; }; struct v2f { float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; float4 uvgrab : TEXCOORD1; float4 vertex : SV_POSITION; }; sampler2D _MainTex; sampler2D _GrabTexture; float4 _MainTex_ST; fixed4 _Tint; sampler2D _DistortionTexture; float4 _DistortionTexture_ST; float _DistortionSize,_Speed,_WeihtNoise; float _UJump, _VJump; v2f vert (appdata v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); float4 screenpos = ComputeGrabScreenPos(o.vertex); //o.uvgrab = screenpos.xy / screenpos.w; o.uvgrab = screenpos; o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex); return o; } float3 FlowUVW(float2 uv, float2 flowVector,float2 jump, float time, float offset) { float3 uvw; float progress = frac(time + offset); uvw.xy = uv - flowVector * (progress + offset); uvw.xy += offset; // 使用grab texture的uv不能超出01范围内。wrap mode 不知道怎么改成repeat uvw.xy += (time - progress) % 2 * jump * 0.01; //uvw.xy += (time - progress) * jump; // 一般贴图扭曲 uvw.z = 1 - abs(1 - 2 * progress); return uvw; } fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target { float4 grabPosUV = UNITY_PROJ_COORD(i.uvgrab); float4 dis = tex2D(_DistortionTexture, i.uv*_DistortionTexture_ST.xy + _DistortionTexture_ST.zw); float2 disUV = dis.rg * 2 - 1; disUV *= _DistortionSize; float time = _Time.y * _Speed + dis.a*_WeihtNoise; float2 jump = float2(_UJump, _VJump); float3 uvw1 = FlowUVW(grabPosUV.xy, disUV, jump, time, 0); float3 uvw2 = FlowUVW(grabPosUV.xy, disUV, jump, time, 0.5); fixed4 col = tex2Dproj(_GrabTexture, float4(uvw1.xy,grabPosUV.z, grabPosUV.w))*uvw1.z; fixed4 col2 = tex2Dproj(_GrabTexture, float4(uvw2.xy,grabPosUV.z, grabPosUV.w))*uvw2.z; return (col + col2) * _Tint; } ENDCG } }
}
深度
2d的深度使用uv坐标模拟,菲涅尔反射也可以通过这个方法模拟。
// 上
float topEdgeGradient = pow(i.uv.y, 13.1);
// 下
float bottomEdgeGradient = pow(-i.uv.y + 1, 13.1);
// 圆
float circleEdgeGradient = pow(distance(i.uv, float2(0.5,0.5)),13.1)

Caustic
生成 Voronoi, 使用pow加强明暗变化。
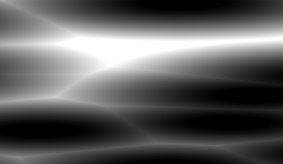
生成的噪声可以用hdr的材质参数颜色着色下直接与扭曲后的贴图相加,效果并不算很好,caustic的效果与扭曲并不协调。
float causticShuffleSpeed = _Time.y*0.58;
float causticScale = float2(0.3,3);
float causticBrightness = 1.3;
float voronoiNoise = voronoi(i.uv*causticScale, causticShuffleSpeed);
voronoiNoise = clamp(0, 1, pow(voronoiNoise*causticBrightness, 4));
float4 causticColor = voronoiNoise * _CausticColorTint;
causticColor.a = voronoiNoise;

生成的噪声还应该作为uv扭曲的参数,协调扭曲与caustic视觉效果。

官方案例 Lost Crypt 中 ShaderGraph_Water_Unlit 改为一般shader的代码:
Shader "Unlit/CausticSh" { Properties { [NoScaleOffset]_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {} _WaterColor("Water Color", color) = (0.2877358,1,0.9352488,1) [HDR]_CausticColor("Caustic Color", color) = (0.2237989,0.2833061,0.272957,1) [NoScaleOffset]_RenderTex ("Render Texture", 2D) = "white" {} _RenderTextureBrightness("Render Texture Brightness", float) = 2 _RippleScale("Ripple Scale", float) = 10.4 _RefractionStrength("Refraction Strength", range(0,1)) = 1 _CausticScale("Caustic Scale", Vector) = (1, 1, 0, 0) _CausticBrightness("Caustic Brightness", float) = 1 _WaveStrength("Wave Strength", range(0,1)) = 1 _EdgeStrength("Edge Strength", float) = 5 } SubShader { Tags {"Queue"="Transparent" "IgnoreProjector"="true" "RenderType"="Transparent"} ZWrite Off Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha Cull OffPass { CGPROGRAM #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "Noise.cginc" struct appdata { float4 vertex : POSITION; float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; }; struct v2f { float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; float3 worldPos: TEXCOORD1; float4 vertex : SV_POSITION; }; sampler2D _MainTex; float4 _MainTex_ST; fixed4 _WaterColor,_CausticColor; float _RenderTextureBrightness; float _RippleScale; float _RefractionStrength; float4 _CausticScale; float _CausticBrightness, _WaveStrength; sampler2D _RenderTex; float4 _RenderTex_ST; float _EdgeStrength; float Remap(float x, float2 inMinMax, float2 outMinMax) { // (x - inMinMax.x)/(inMinMax.y - inMinMax.x) = (out - outMinMax.x)/(outMinMax.y - outMinMax.x) return (x - inMinMax.x)* (outMinMax.y - outMinMax.x)/(inMinMax.y - inMinMax.x) + outMinMax.x; } v2f vert (appdata v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); o.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz; o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex); return o; } fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target { // UV Auto Scroll Speed float uvSpeed = _Time.y*0.05; // Auto-Scroll UV Downwards float2 tiling = float2(0.18,1); float2 offset = float2(0, uvSpeed); float2 uv = i.uv*tiling + offset; // Auto-Scroll UV Upwards float2 tiling2 = float2(0.18,1); float2 offset2 = float2(0, 1 - uvSpeed); float2 uv2 = i.uv*tiling2 + offset2; // Generate Auto-Scroll Noise and Blend Together float noise1 = noise(uv*_RippleScale); float noise2 = noise(uv2*_RippleScale); float noisesum = noise1 * noise2; // Calculate Top Edge Gradient float topEdgeGradient = pow(abs(i.uv.y), 13.1); // Blend Water Ripples with Refraction Strength float refractionStrength = Remap(_RefractionStrength, float2(0, 1), float2(0, 0.1)); float waterRipples = lerp(refractionStrength*noisesum, 0, topEdgeGradient); // Caustic Shuffle Speed float causticShuffleSpeed = _Time.y*0.58; // Calculate Voronoi Noise for Caustics float voronoiNoise = voronoi(i.worldPos*_CausticScale, causticShuffleSpeed); // Adjustments to Caustic Visuals voronoiNoise = clamp(0, 1, pow(abs(voronoiNoise*_CausticBrightness), 4)); // Adjust Water Ripples & Caustics into UV for Reflection Texture float2 adjUV = i.uv*float2(1,-1) + float2(waterRipples, voronoiNoise*_WaveStrength + 1); float4 renderTexColor = tex2D(_RenderTex, adjUV); renderTexColor = clamp(0,1,renderTexColor * _WaterColor * _RenderTextureBrightness); // Calculate Edge Gradient (Top and Bottom) float topEdge = clamp(0, 1, pow(i.uv.y, 13.16)); float bottomEdge = clamp(0, 1, pow(-i.uv.y + 1, 13.16)); float topBottomEdge = (topEdge + bottomEdge) * _EdgeStrength; float4 voronoiColor = (topBottomEdge + voronoiNoise)*_CausticColor; voronoiColor.a = voronoiNoise; return renderTexColor + voronoiColor; } ENDCG } }
}
河流
波纹
2d河流最主要的便是波纹的流动,波纹的外表取决于噪声的选择。
- Caustic:生成voronoi噪声的参数随时间递增。

- Perlin noise:生成噪声的参数随时间递增,噪声值高于或低于某个阈值便为波纹。
// 形状
float2 foamTiling = float2(2, 19);
// 阈值,控制数量、大小
float foamCutoff = 0.9;
// 波纹颜色
float4 foamColor = float4(1,1,1,1);
float speed = _Time.y*0.4;
float f = noise(i.uv*foamTiling + float2(speed, 0));
// 边缘平滑
f = smoothstep(foamCutoff - 0.01, foamCutoff + 0.01, f);
foamColor.a *= f;
float3 color = (foamColor.rgb * foamColor.a) + (col.rgb * (1 - foamColor.a));
float alpha = foamColor.a + col.a * (1 - foamColor.a);
float4 finalColor = float4(color, alpha);
这时候的波纹除了移动没有任何变化,在生成波纹噪声的地方加上扭曲变量,波纹在移动的过程便有了变化。扭曲变量可以来自重新生成的噪声变量、复用前面用于扭曲贴图的噪声值、自定义贴图中获取。

这种方法生成波纹的噪声并不参与最终图像的扭曲(折射)。
另一种方法是生成两个噪声,一个代表波纹参数、另一个代表水扭曲参数,两者混合作为最终的扭曲参数和波纹生成参数。
噪声生成可以同一来源通过tiling区分,但最好通过两种不同的贴图获取,尤其是扭曲贴图值扭曲uv的值应该是不同的(即扰动方向),扭曲贴图类似于法线贴图除了只有rg通道,类似于这种(来自catlikecoding-texture distortion)

// 方向
float dir = float4(1,0);
// 速度
float speed = _Time.y*0.3;
// 时间错位,让两个噪声生成错位,否则波纹没有变化
float2 timeOffset = float2(0.8, 0.4);
float motion = normalize(dir)*speed;
float4 dis = tex2D(_DistortionTexture, i.uv + motion*timeOffset.x);
float4 dis2 = tex2D(_DistortionTexture2,i.uv + motion*timeOffset.y);
float2 f = (normal.xy-0.5)*_DistortionSize + (dis2.xy-0.5)*_DistortionSize2;
fixed4 col = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv + f);
// 使用f生成波纹,同上
...

平面河流
如果平面河流存在分支的话就需要制作一个流动贴图(flow map),来指定不同分支河路的流向,还需要一个mask贴图(或者流动贴图上的特定颜色表示 eg:(127,127,127);或者放在flow map的a通道)来指定非河流区域。河流交叉处的混合原理是将生成的波纹分成网格,将每个网格单元于四周的网格单元插值混合。
这个是用画图制作出来的:

使用之前的caustic distortion water,网格单元的大小不是参考上的固定为1,而是根据像素大小划分。最终效果:
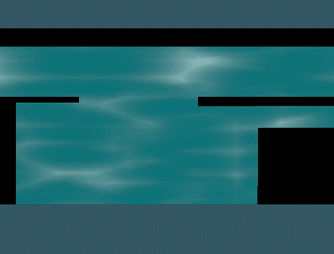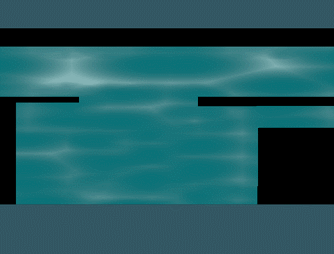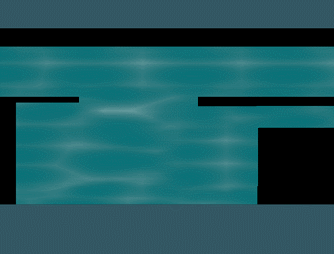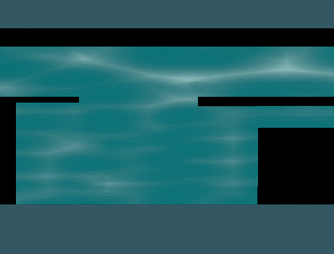
示例源码:
Shader "Unlit/PlaneRiver2D" { Properties { [NoScaleOffset]_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {} _WaterColor("Water Color", color) = (0.2877358,1,0.9352488,1) [HDR]_CausticColor("Caustic Color", color) = (0.2237989,0.2833061,0.272957,1) [NoScaleOffset]_RenderTex ("Render Texture", 2D) = "white" {} _RenderTextureBrightness("Render Texture Brightness", float) = 2 _RippleScale("Ripple Scale", float) = 10.4 _RefractionStrength("Refraction Strength", range(0,1)) = 1 _CausticScale("Caustic Scale", Vector) = (1, 1, 0, 0) _CausticBrightness("Caustic Brightness", float) = 1 _WaveStrength("Wave Strength", range(0,1)) = 1 _EdgeStrength("Edge Strength", float) = 5 [Header(Flow Properties)] _FlowSpeed("Flow Speed", float) = 0.1 _FlowMap("FlowMap",2D) = "bump" {} _CellSize("PixelSize Per Cell", float) = 10 _MaskTex("Mask", 2D) = "white" {} } SubShader { Tags {"Queue"="Transparent" "IgnoreProjector"="true" "RenderType"="Transparent"}GrabPass { "_GrabTexture" } Pass { CGPROGRAM #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "Noise.cginc" struct appdata { float4 vertex : POSITION; float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; }; struct v2f { float2 uv : TEXCOORD0; float3 worldPos: TEXCOORD1; float4 uvgrab: TEXCOORD2; float4 vertex : SV_POSITION; }; sampler2D _MainTex; float4 _MainTex_ST; fixed4 _WaterColor,_CausticColor; float _RenderTextureBrightness; float _RippleScale; float _RefractionStrength; float4 _CausticScale; float _CausticBrightness, _WaveStrength; sampler2D _RenderTex; float4 _RenderTex_ST; float4 _RenderTex_TexelSize; float _EdgeStrength; sampler2D _GrabTexture; sampler2D _FlowMap,_MaskTex; float4 _FlowMap_TexelSize; float _FlowSpeed; float _CellSize; float Remap(float x, float2 inMinMax, float2 outMinMax) { // (x - inMinMax.x)/(inMinMax.y - inMinMax.x) = (out - outMinMax.x)/(outMinMax.y - outMinMax.x) return (x - inMinMax.x)* (outMinMax.y - outMinMax.x)/(inMinMax.y - inMinMax.x) + outMinMax.x; } v2f vert (appdata v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); o.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz; o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex); return o; } float2 flowCell(float2 uv, float2 flowUV, float2 offset, float time) { flowUV += offset; // 使用tex2Dgrad防止mipmapping或filtering float2 flowVector = tex2Dgrad(_FlowMap, flowUV*_FlowMap_TexelSize,0,0).rg*2.0 - 1.0; flowVector = normalize(flowVector); uv += flowVector*time; return uv; } float flowGrid(float2 uv) { float flowSpeed = _FlowSpeed*_Time.y; float causticShuffleSpeed = _Time.y*0.58; // 网格单元坐下角的值作为整个单元的值 float2 flowUV = floor(uv*_FlowMap_TexelSize.zw/_CellSize)*_CellSize; // 当前网格单元及其右、上、右上的晶格 float2 cellFlowUV1 = flowCell(uv, flowUV , float2(0,0), flowSpeed); float2 cellFlowUV2 = flowCell(uv, flowUV , float2(_CellSize, 0), flowSpeed); float2 cellFlowUV3 = flowCell(uv, flowUV , float2(_CellSize, _CellSize), flowSpeed); float2 cellFlowUV4 = flowCell(uv, flowUV , float2(0, _CellSize), flowSpeed); float voronoiNoise1 = voronoi(cellFlowUV1*_CausticScale, causticShuffleSpeed); float voronoiNoise2 = voronoi(cellFlowUV2*_CausticScale, causticShuffleSpeed); float voronoiNoise3 = voronoi(cellFlowUV3*_CausticScale, causticShuffleSpeed); float voronoiNoise4 = voronoi(cellFlowUV4*_CausticScale, causticShuffleSpeed); // 计算当前点至各个网格单元的权重 float2 offset1 = (uv*_FlowMap_TexelSize.zw - flowUV)/_CellSize; float fade1 = 1 - saturate(dot(offset1, offset1)); float2 offset2 = (uv*_FlowMap_TexelSize.zw - flowUV - float2(_CellSize, 0))/_CellSize; float fade2 = 1 - saturate(dot(offset2, offset2)); float2 offset3 = (uv*_FlowMap_TexelSize.zw - flowUV - float2(_CellSize, _CellSize))/_CellSize; float fade3 = 1 - saturate(dot(offset3, offset3)); float2 offset4 = (uv*_FlowMap_TexelSize.zw - flowUV - float2(0, _CellSize))/_CellSize; float fade4 = 1 - saturate(dot(offset4, offset4)); // 透明度混合 float voronoiNoise = (voronoiNoise1*fade1 + voronoiNoise2*fade2 + voronoiNoise3*fade3 + voronoiNoise4*fade4)/(fade1+fade2+fade3+fade4); return voronoiNoise; } fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target { float uvSpeed = _Time.y*0.05; float2 uv = i.uv; // Auto-Scroll UV Downwards float2 tiling = float2(0.18,1); float2 offset = float2(0, uvSpeed); float2 uv1 = uv*tiling + offset; // Auto-Scroll UV Upwards float2 tiling2 = float2(0.18,1); float2 offset2 = float2(0, 1 - uvSpeed); float2 uv2 = uv*tiling2 + offset2; // Generate Auto-Scroll Noise and Blend Together float noise1 = noise(uv1*_RippleScale); float noise2 = noise(uv2*_RippleScale); float noisesum = noise1 * noise2; // Calculate Top Edge Gradient float topEdgeGradient = pow(abs(uv.y), 13.1); // Blend Water Ripples with Refraction Strength float refractionStrength = Remap(_RefractionStrength, float2(0, 1), float2(0, 0.1)); float waterRipples = lerp(refractionStrength*noisesum, 0, topEdgeGradient); //float causticShuffleSpeed = _Time.y*0.58; //float voronoiNoise = voronoi(i.worldPos*_CausticScale, causticShuffleSpeed, 10); // flow float voronoiNoise = flowGrid(i.uv); float mask = tex2Dgrad(_MaskTex, i.uv,0,0).r; //float voronoiNoise = voronoi(t, causticShuffleSpeed, 10); voronoiNoise = clamp(0, 1, pow(voronoiNoise*_CausticBrightness, 4)); float2 adjUV = uv*float2(1,-1) + float2(waterRipples, voronoiNoise*_WaveStrength + 1); float4 renderTexColor = tex2D(_RenderTex, adjUV); renderTexColor = clamp(0,1,renderTexColor * _WaterColor * _RenderTextureBrightness); float4 color = (voronoiNoise)*_CausticColor; color.a = voronoiNoise; return (renderTexColor + color)*mask; } ENDCG } }
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号