网络编程笔记
01、什么是计算机网络
1.1、概述
地区村:对地球的一种比喻说法。现代科技的迅速发展,缩小了地球上的时空距离,国际交往日益频繁便利,因而整个地球就如同是茫茫宇宙中的一个小村落。
信件:
计算机网络:
计算机网络是指将地理位置不同的具有独立功能的多台计算机及其外部设备,通过通信线路连接起来,在网络操作系统,网络管理软件及网络通信协议的管理和协调下,实现资源共享和信息传递的计算机系统。
网络编程的目的:
无线电台...传播交流信息,数据交换。通信
想要达到这个效果需要干什么:
- 如何准确的定位网络上的一台主机 192.168.6.14 端口, 定位到计算机上的某个资源
- 找到了这个主机,如何传输数据
Javaweb:网页编程 B/S
网络编程:TCP/IP C/S
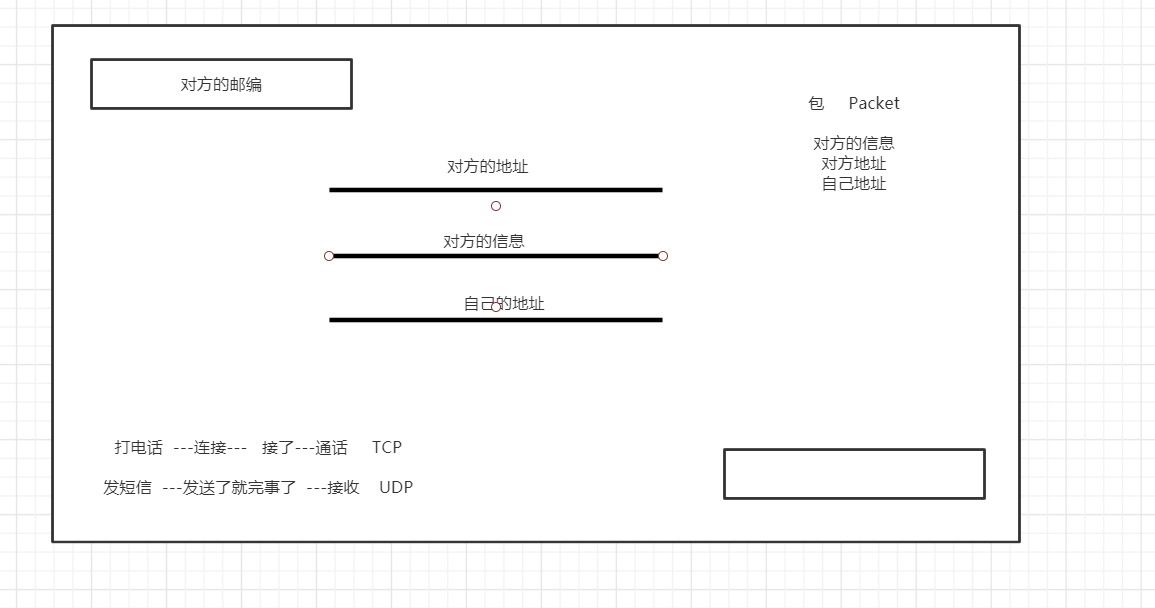
02、网络通信的两个要素
如何实现网络的通信?
通信双方的地址:
- ip
- 端口号
- 192.168.124:5900(就能定位到一台具体计算机上的某一个应用)
规则:网络通信协议


小结:
- 网络编程中有两个主要的问题
- 如何准确的定位到网络上的一台或者多台主机
- 找到主机后如何进行通信(ping www.baidu.com)
- 网络编程中的要素
- IP和端口号 IP
- 网络通信协议 udp ,tcp
- 万物皆对象
03、IP地址
IP地址:inetAddress
- 唯一定位一台网络计算机
- 127.0.0.1:本机 localhost(自己给自己呼叫没有网也可以ping成功)
- IP地址分类
- ipv4/ipv6
- ipv4 127.0.0.1 ,4个字节组成, 0~255 ,42亿 ;30亿都在北美,亚洲4亿,2011年就用尽
- ipv6 fe80::504:5568:36ca:aa54%6 , ipconfig(查看本机IP)128位,;8个无符号整数! abcde
- 公网(互联网)/私网(局域网)
- ABCD类地址
- 192.168.xxx,专门给组织内部使用的
- ipv4/ipv6
- 域名:记忆IP问题!
- IP:www.jd.com
- IP:www.vip.com
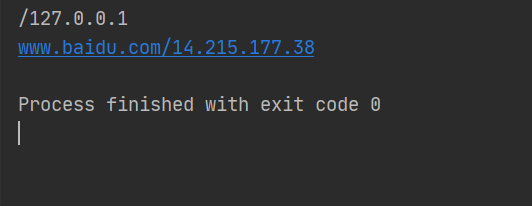
//测试IP
public class TestInetAddress {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
InetAddress inetAddress1 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
System.out.println(inetAddress1);
InetAddress inetAddress2 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
System.out.println(inetAddress2);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
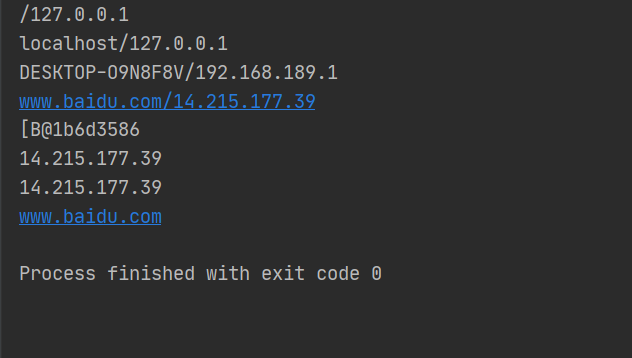
//测试IP
public class TestInetAddress {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//查询本机地址
InetAddress inetAddress1 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
System.out.println(inetAddress1);
InetAddress inetAddress3 = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
System.out.println(inetAddress3);
InetAddress inetAddress4 = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println(inetAddress4);
//查询网站IP地址
InetAddress inetAddress2 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
System.out.println(inetAddress2);
//常用方法
//System.out.println(inetAddress2.getAddress());
System.out.println(inetAddress2.getCanonicalHostName());//规范的名字
System.out.println(inetAddress2.getHostAddress());//ip
System.out.println(inetAddress2.getHostName());//域名或者是自己电脑的名字
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
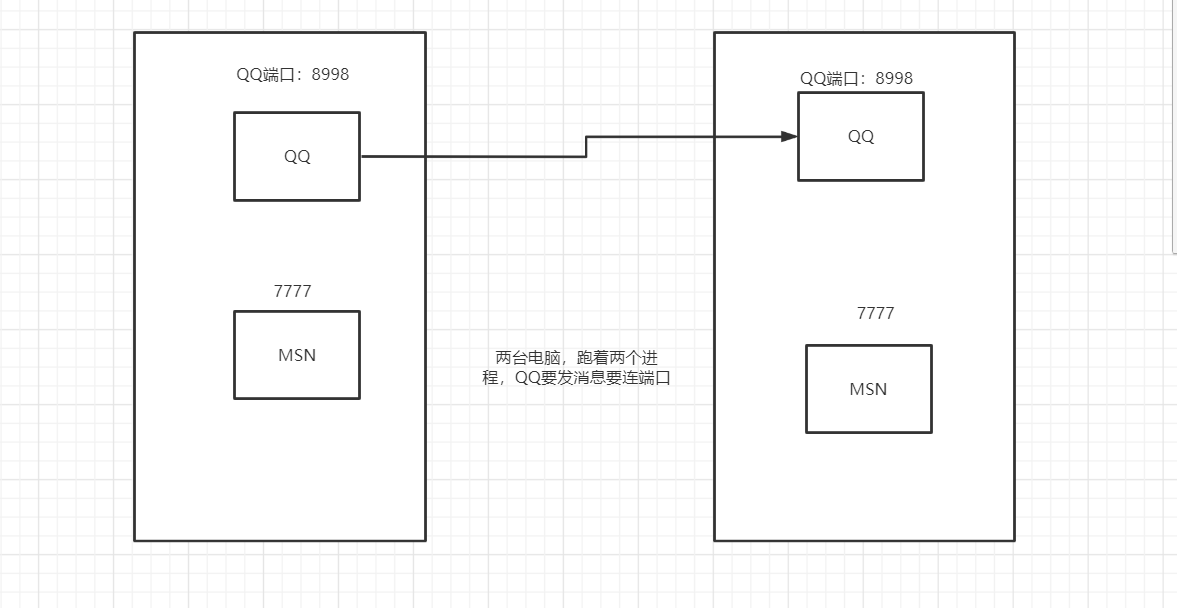
04、端口Port
端口表示计算机上的一个程序进程
-
不同的进程有不同的端口号!用来区分软件!
-
一般端口被规定:0~65535
-
TCP/UDP:65535*2 个端口 tcp用了80 , udp可以用80, 单个协议下端口号不能冲突
-
端口分类
-
共有端口0~1023
- HTTP:80
- HTTPS:443
- FTP:21
- SSH:22(远程连接)
- TELENT:23(远程监听)
-
程序注册端口:1014~49151,分配用户或者程序
- Tomcat:8080
- MySQL:3306
- Oracle:1521
-
动态/私有:49152~65535
netstat -ano//查看所有端口 netstat -ano|findstr "5900"//查看所有端口 tasklist|findstr "8696"//查看指定端口的进程 CTRL+shift+ESC//打开任务管理器 -
public class TestInetSocketAddress { public static void main(String[] args) { InetSocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8080); System.out.println(socketAddress); InetSocketAddress socketAddress2 = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080); System.out.println(socketAddress2); System.out.println(socketAddress.getAddress()); System.out.println(socketAddress.getHostName());//host地址 System.out.println(socketAddress.getPort());//端口 } } -
-
-
05、通信协议
协议:约定,就好比我们现在说的是普通话
网络通信协议:速率,传输码率,代码结构,传输控制....
问题:非常的复杂?
大事化小:分层!
TCP/IP协议簇:实际上是一组协议
重要:
- TCP:用户传输协议
- UDP:用户数据报协议
出名的协议:
- TCP:用户传输协议
- IP:网络互联协议
TCP udp对比
TCP:打电话
-
连接,稳定
-
三次握手,四次挥手
A:你愁啥? B:瞅你咋地! A:干一场! A:我要离开了 B:你真的要离开了? B:你真的真的要离开了? A:我真的要离开了三次握手
四次挥手

-
客户端、服务端
-
传输完成,释放连接,效率低
UDP:发短信
- 不连接,不稳定
- 客户端、服务端:没有明确的界限
- 不管你有没有准备好,都可以发给你
- 导弹
- DDOS:洪水攻击(饱和攻击)
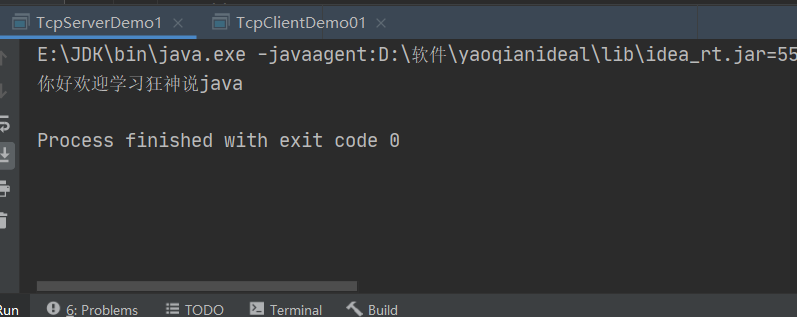
06、TCP实现聊天
客户端
- 连接服务器Socket
- 发送消息
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
//客户端
public class TcpClientDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//提升作用域
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
//1.要知道服务器的地址
InetAddress serverIP = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
//端口号
int port = 9999;
//2.创建一个socket连接
socket = new Socket(serverIP,port);
//3.发送消息 IO流
os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你好欢迎学习狂神说java".getBytes());//.getBytes()
} catch (Exception e) {//提升作用域
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭资源
if (socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (os!=null){
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
服务器
- 建立服务的端口
- 等待用户的连接accept
- 接收用户的消息
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
//服务端
public class TcpServerDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//提升作用域
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
try {
//我得有一个地址
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);//Socket:插座
//2.等待客户端连接过来
socket = serverSocket.accept();
//3.读取客户端的消息
is = socket.getInputStream();
/*
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
String msg new String(buffer,0,len);
System.out.println(msg);
}
*/
//管道流
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭资源
if (baos!=null){
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (is!=null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (serverSocket!=null){
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
07、TCP文件上传实现
08、初识Tomcat
服务端
- 自定义S
- Tomca服务器S
客户端
- 自定义C
- 浏览器B
09、UDP消息发送
10、UDP聊天实现
循环发送消息
public class UdpSenderDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(8888);
//准备数据:控制台读取数据 system.in
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (true){
String date = reader.readLine();//读取这一行的数据
byte[] datas = date.getBytes();//转换成byte[]数据
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas,0,datas.length,new InetSocketAddress("localhost",6666));
socket.send(packet);
if (date.equals("bye")){
break;
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
接收消息
public class UdpreceideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(6666);
while (true){
//准备接收包裹
byte[] container = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(container,0,container.length);
socket.receive(packet);//阻塞式包裹
//断开连接 bye
byte[] data = packet.getData();
String receiveData = new String(data, 0, data.length);
//读取数据
System.out.println(receiveData);
if (data.equals("bye")){
break;
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
11.UDP多线程在线咨询
同一资源定位符:定位资源的,定位互联网上的某一资源
DNS 域名解析 www.bai.du
协议://IP地址:端口号/项目名/资源 (URL由五部分组成:能少不能多)
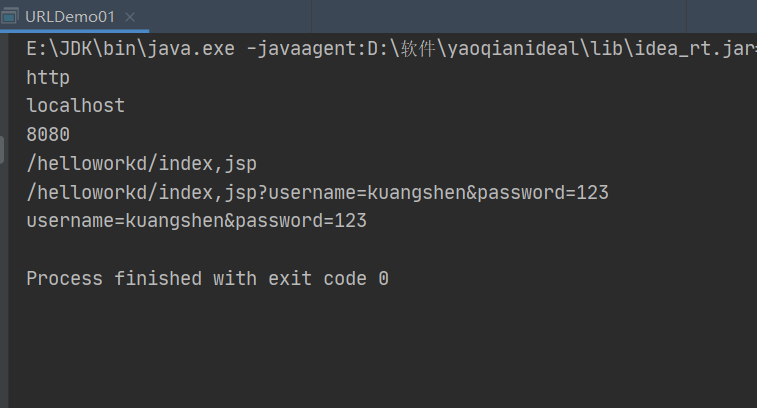
12.URL下载网络资源
public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException {
//此地址是随意编写的
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8080/helloworkd/index,jsp?username=kuangshen&password=123");
//协议名
System.out.println(url.getProtocol());
//得到主机ip
System.out.println(url.getHost());
//端口号
System.out.println(url.getPort());
//文件的地址
System.out.println(url.getPath());
//文件全路径
System.out.println(url.getFile());
//得到URL的查询名字(参数)
System.out.println(url.getQuery());
}
(学习笔记仅供参考!)



