《UnixLinux系统编程》10章学习笔记
sh脚本
一个包含sh语句的文本文件,命令解释程序sh要执行该语句。
#! /bin/bash
# comment line
echo hello
- 使用
chmod +x mysh使其可执行 - 以#!组合开始
sh脚本与C程序
- sh:解释程序,逐行读取sh脚本文件并直接执行这些行.
如果行是可执行命令且为内置命令,那么sh可直接执行。否则,它会复刻一个子进程来执行命令。
示例:
mysh a b c d
$0 $1 $2 $3 $4
C语言:必须先编译链接到一个二进制可执行文件,然后通过主sh的子进程运行二进制可执行文件
a.out a b c d
main (int argc, char *argv[])
-
sh:变量都是字符串
C :变量必须有一个类型
-
sh:不需要
main函数C :需要
main函数
命令行参数
可使用与运行sh命令完全相同的参数调用sh脚本
mysh one two three
S#= 命令行参数$1到$n的数量S*= 所有命令行参数,包括$0$S= 执行sh的进程PID$?= 最后一个命令执行的退出状态(如果成功,则为0,否则为非0)
# 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
1. #! /bin/bash
2. echo \$# = $# # $# = 12
3. echo \$* = $* # $* = abc D E F G H I J K L M N
4. echo $1 $9 $10# abc K abc0 (note: $10becomes abc0)
5. echo $1 $9 ${10}# abc K L (note: ${10}is L)
6. shift # replace $1, $2 .. with $2, $3,...
7. echo $1 $9 ${10} # D L M
sh变量
- 内置变量PATH、HOME TERM等,sh变量。
- 所有变量都是字符串。
- 未赋值的sh变量是NULL字符串。
- 赋值方法:
variable=string # NOTE:no white spaces allowed between tokens
示例
echo A ==> A
echo $A ==> (null if variable A is not set)
A="this is fun" # set A value
echo $A ==> this is fun
B=A # assign “A” to B
echo $B ==> A (B was assigned the string "A")
B=$A (B takes the VALUE of A)
echo $B ==> this is fun

sh中的引号
特殊字符:¥、/、*、>、<
若想用作普通字符,可使用\或单引号使用
示例:
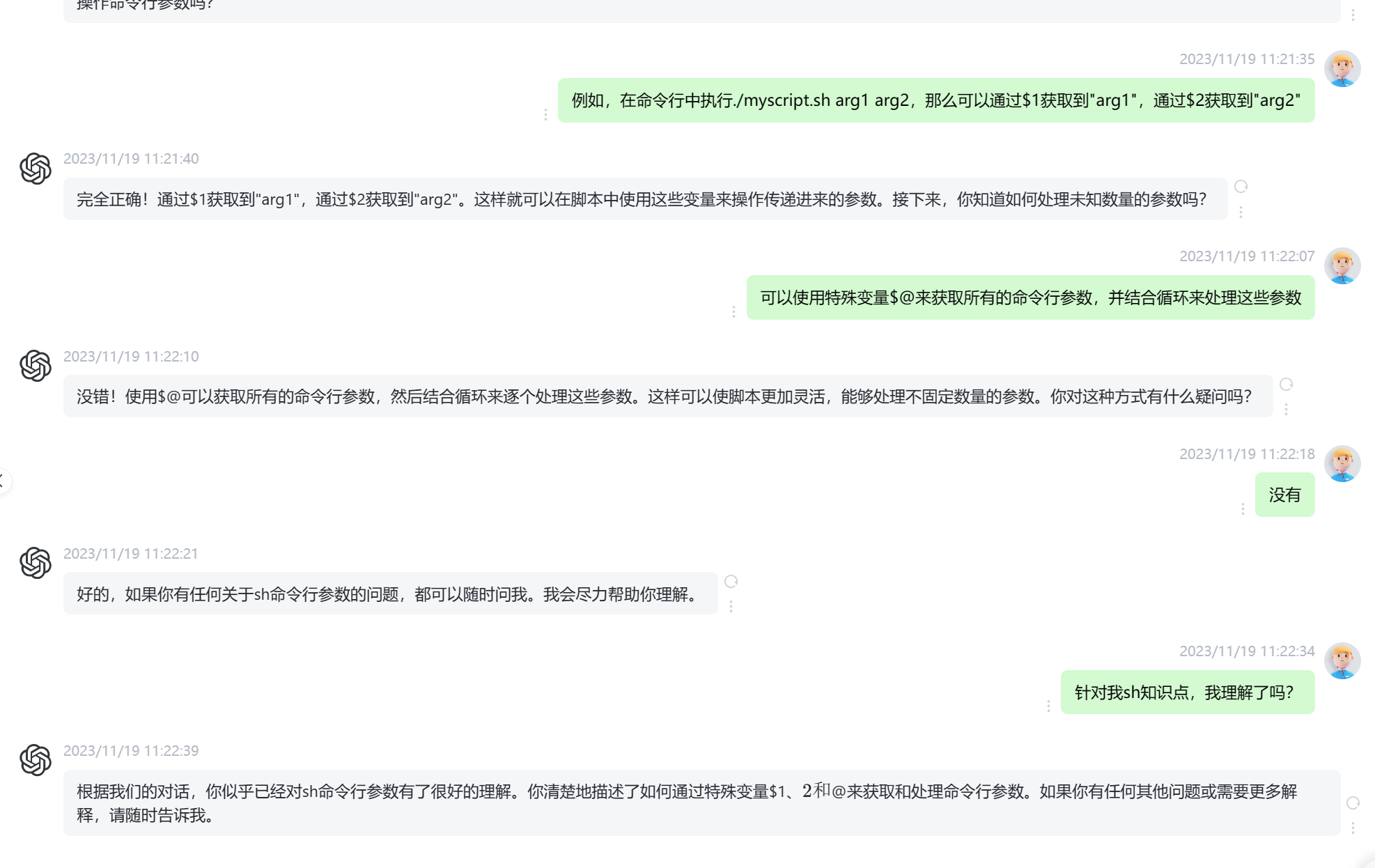
A=xyz
echo \$A ==> $A # back quote $ as is
echo '$A' ==> $A # NO substitution within SINGLE quotes
echo "see $A" ==> see xyz# substitute $Ain DOUBLE quotes
\:用于引用单个字符':用于引用长字符
sh语句
示例:
ls
ls > outfile
date
cp f1 f2
mkdir newdir
cat < filename
- Unix/Linux命令
- I/O重定向
- 控制sh程序执行的测试条件、循环、case等
sh命令
- 内置命令
.file:读取并执行文件break [n]:从最近的第n个嵌套循环中退出cd [dirname]:更换目录continue [n]:重启最近的第n个嵌套循环eval [arg...]:计算一次参数并让sh执行生成的命令exit [n]:通过这个sh执行命令,sh将会退出export [var...]:使sh退出,退出状态为nread [var...]:将变量到处到随后执行的命令set [arg...]:从stdin中读取一行并为变量赋值shift:将未知参数$2 $3...重命名为$1 $2trap [arg] [n]:接收到信号n后执行参数umask [ddd]:将掩码设置为八进制数ddd的wait [pid]:等待进程pid,如果没有给出pid,则等待所有活动子进程
read命令:当sh执行read时,将等待来自stdin的输入行。
- Linux命令
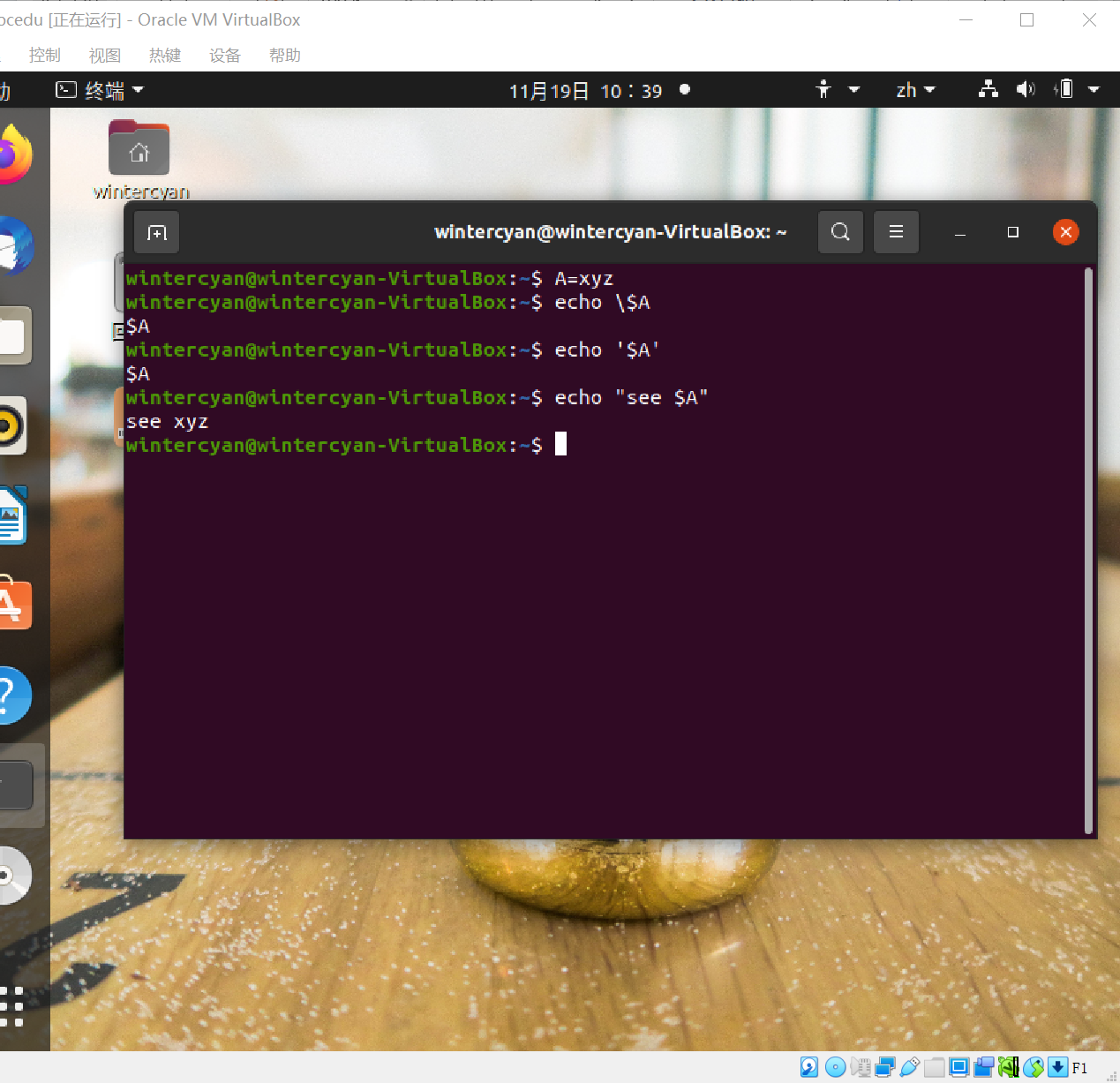
echo命令:将参数字符串作为行回显到stdout
示例:
echo This is a line # display This is a line
echo "This is a line" # display This is a line
echo -n hi # display hi without NEWLINE
echo there # display hithere

expr命令:间接更改sh变量的值- 管道命令:在sh脚本中经常使用管道作为过滤器
命令替换
在sh中,$A会被替换为A值
sh遇到'cmd'或$(cmd)时,会先执行cmd,再替换$(cmd)
echo $(date)# display the result string of date command
echo $(ls dir)# display the result string of ls dircommand
sh控制语句
- if-else-fi语句
if [condition]
then
statements
else
statements
fi
- for语句
for VARIABLE in string1 string2 ... stringn
do
commands
done
示例:
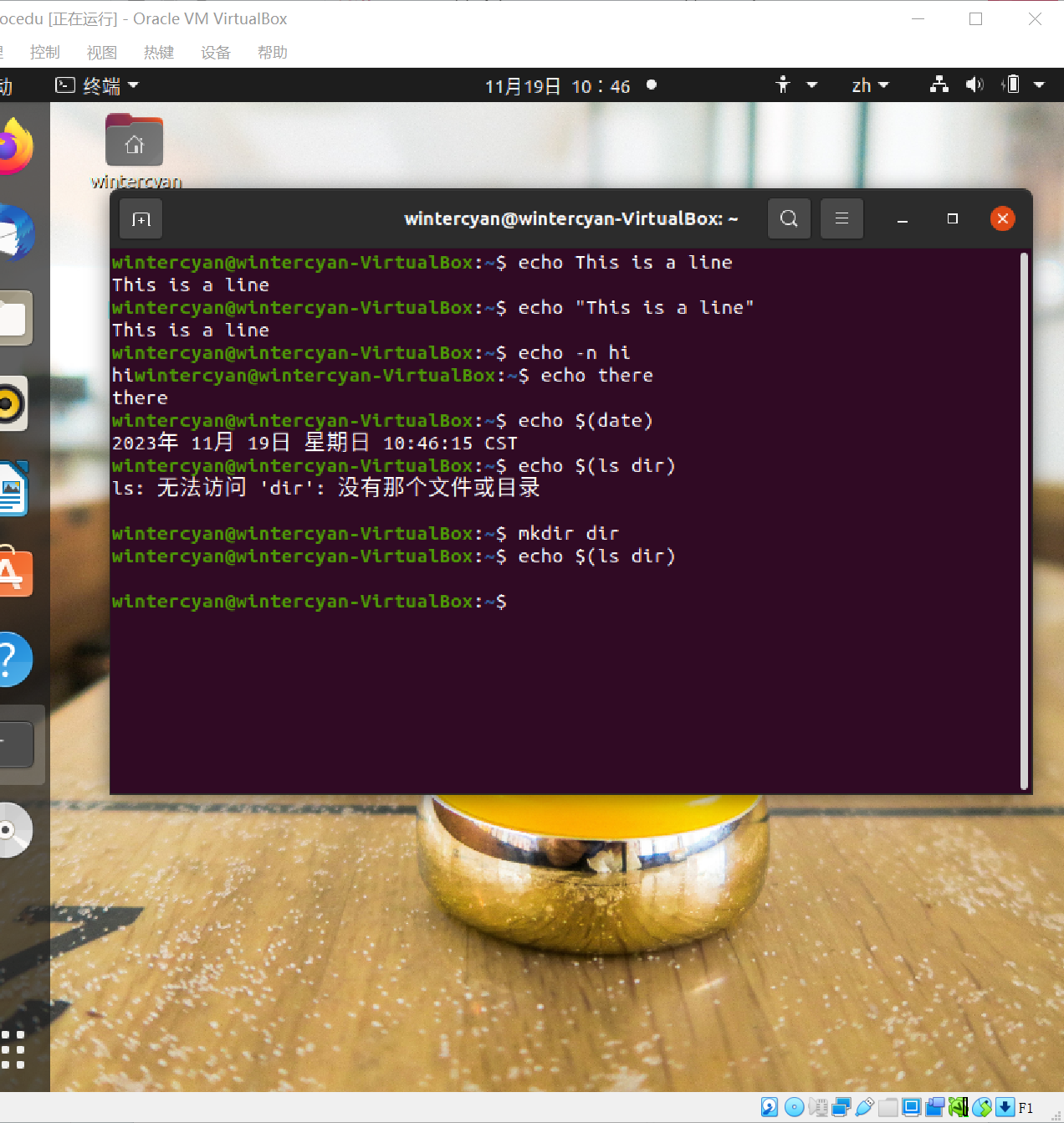
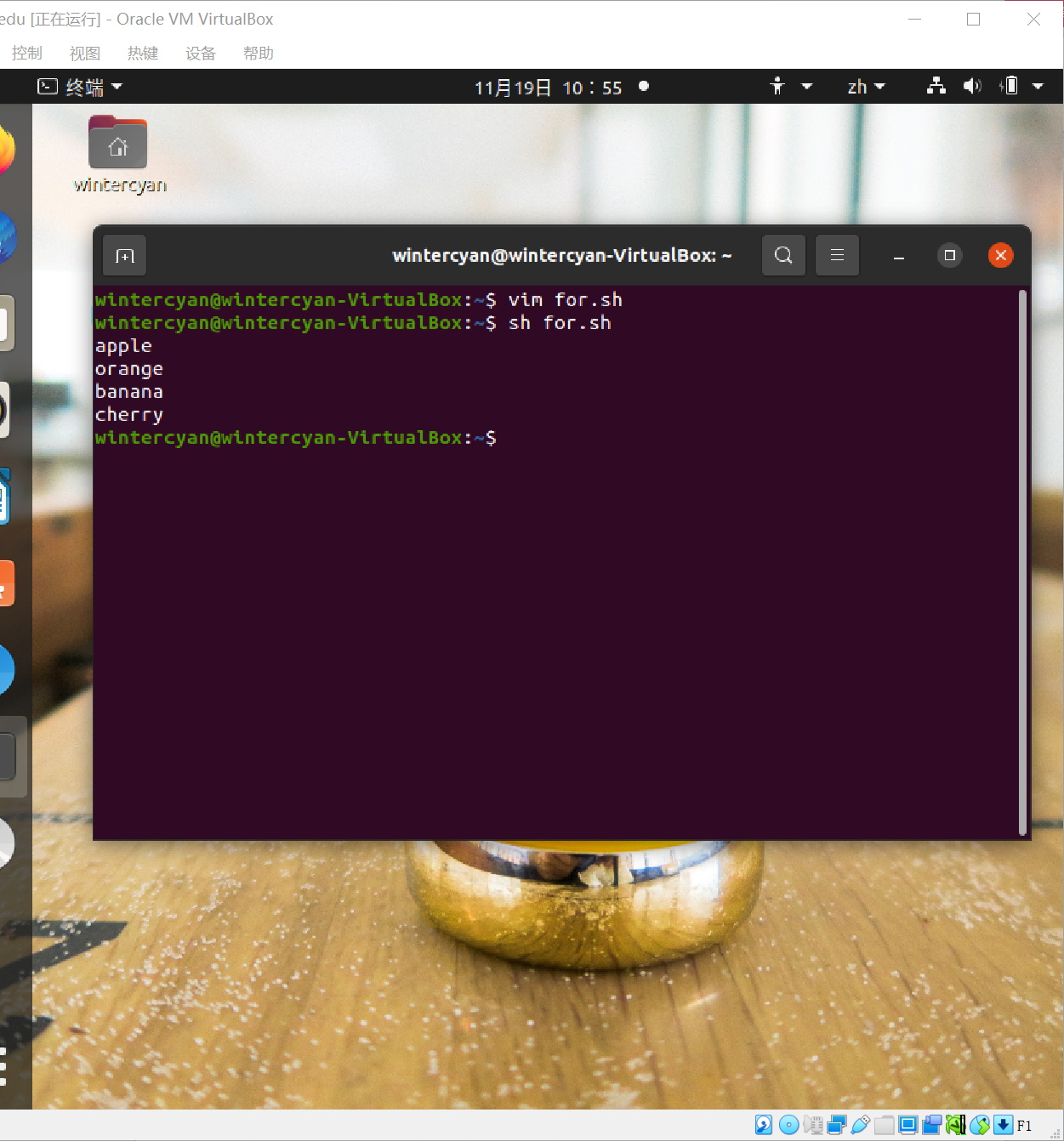
for FRUIT in apple orange banana cherry
do
echo $FRUIT # print lines of apple orange banana cherry
done
for NAME in $*
do
echo $NAME # list all command-line parameter strings
if [ -f $NAME ]; then
echo $NAME is a file
elif [ -d $NAME ]; then
echo $NAME is a DIR
fi
done
- while语句
while [condition]
do
commands
done
示例:
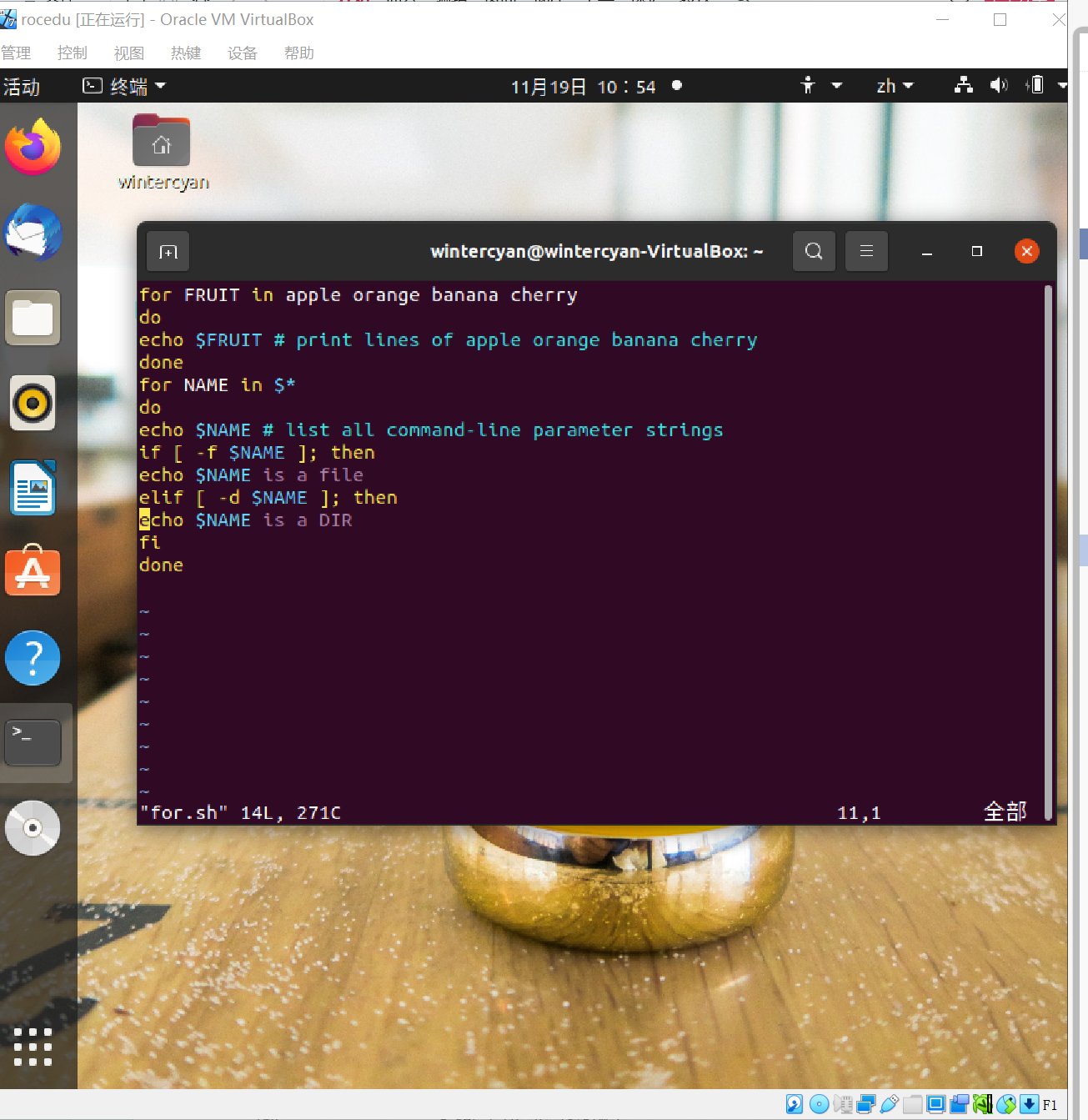
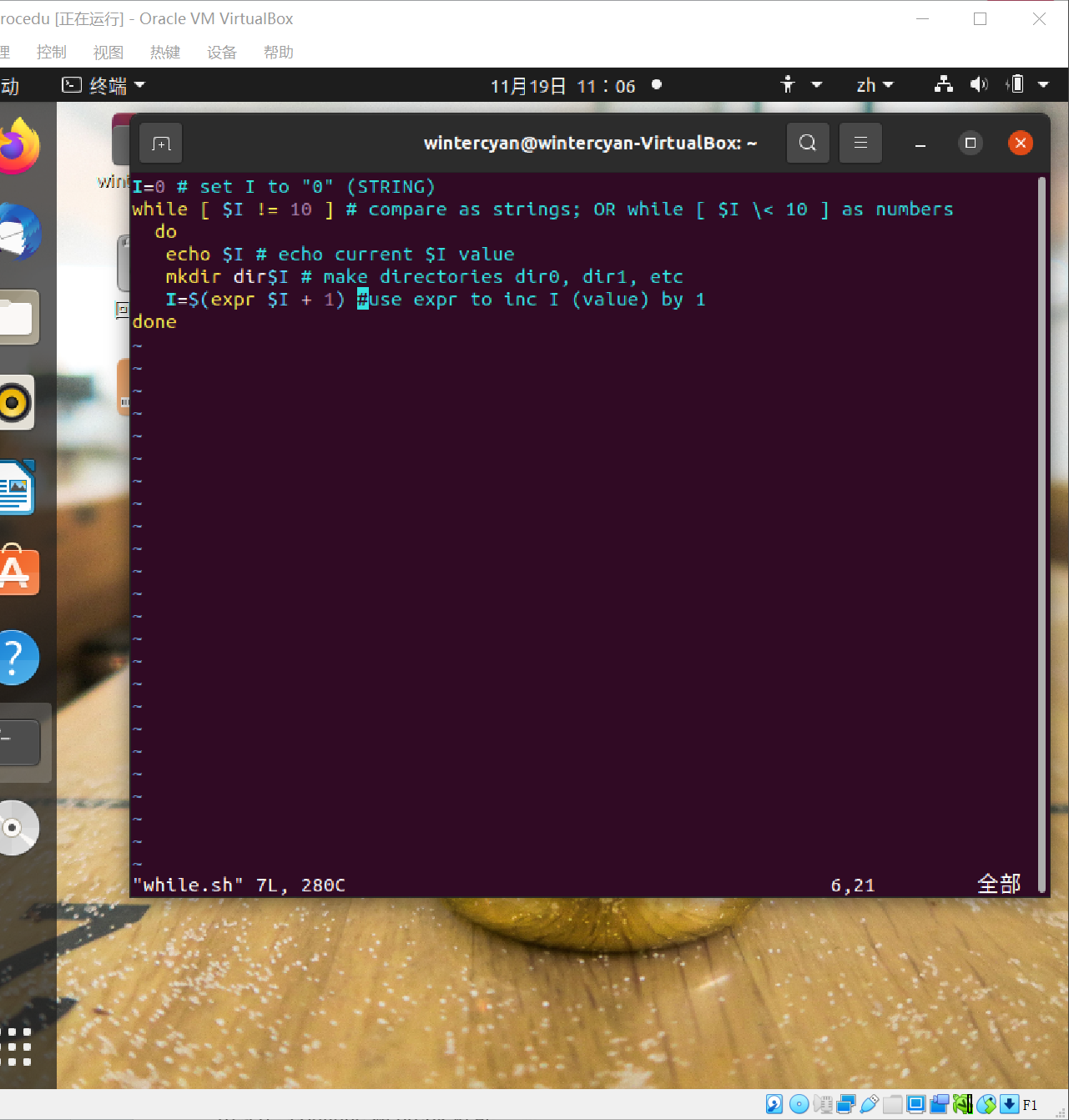
I=0 # set I to "0" (STRING)
while [ $I != 10 ] # compare as strings; OR while [ $I \< 10 ] as numbers
do
echo $I # echo current $I value
mkdir dir$I # make directories dir0, dir1, etc
I=$(expr $I + 1)# use expr to inc I (value) by 1
done
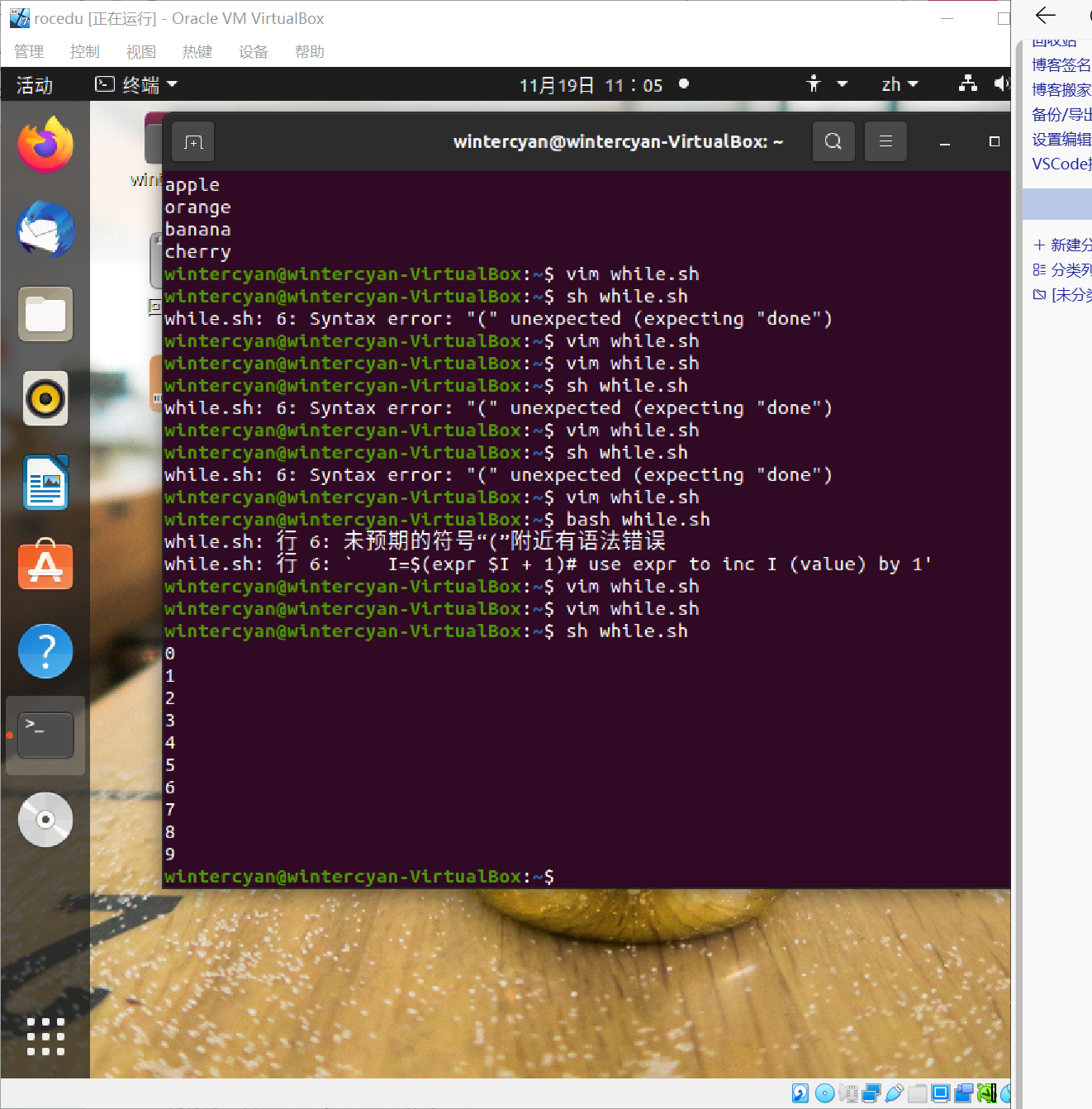
一开始运行报错,经检查后发现第六行注释用的‘#’与代码相连,增加空格随后成功。
- until-do语句
until [ $ANS = "give up"]
do
echo -n "enter your answer : "
read ANS
done
- case语句
case $variable in
pattern1) commands;;
pattern2) commands;;
pattern3) commands;;
esac
-
continue和break语句
与C语言中相同
I/O重定向
- >file:stdout转向文件,如果文件不存在,将会创建文件
- >>file:stdout追加到文件
- <file:将文件用作stdin,文件必须存在并具有r权限
- <<word:从“here”文件中获取输入,直到只包含“word”的行
嵌入文档
echo << END
END
cat << DONE
DONE
sh函数
func()
{
#function code
}
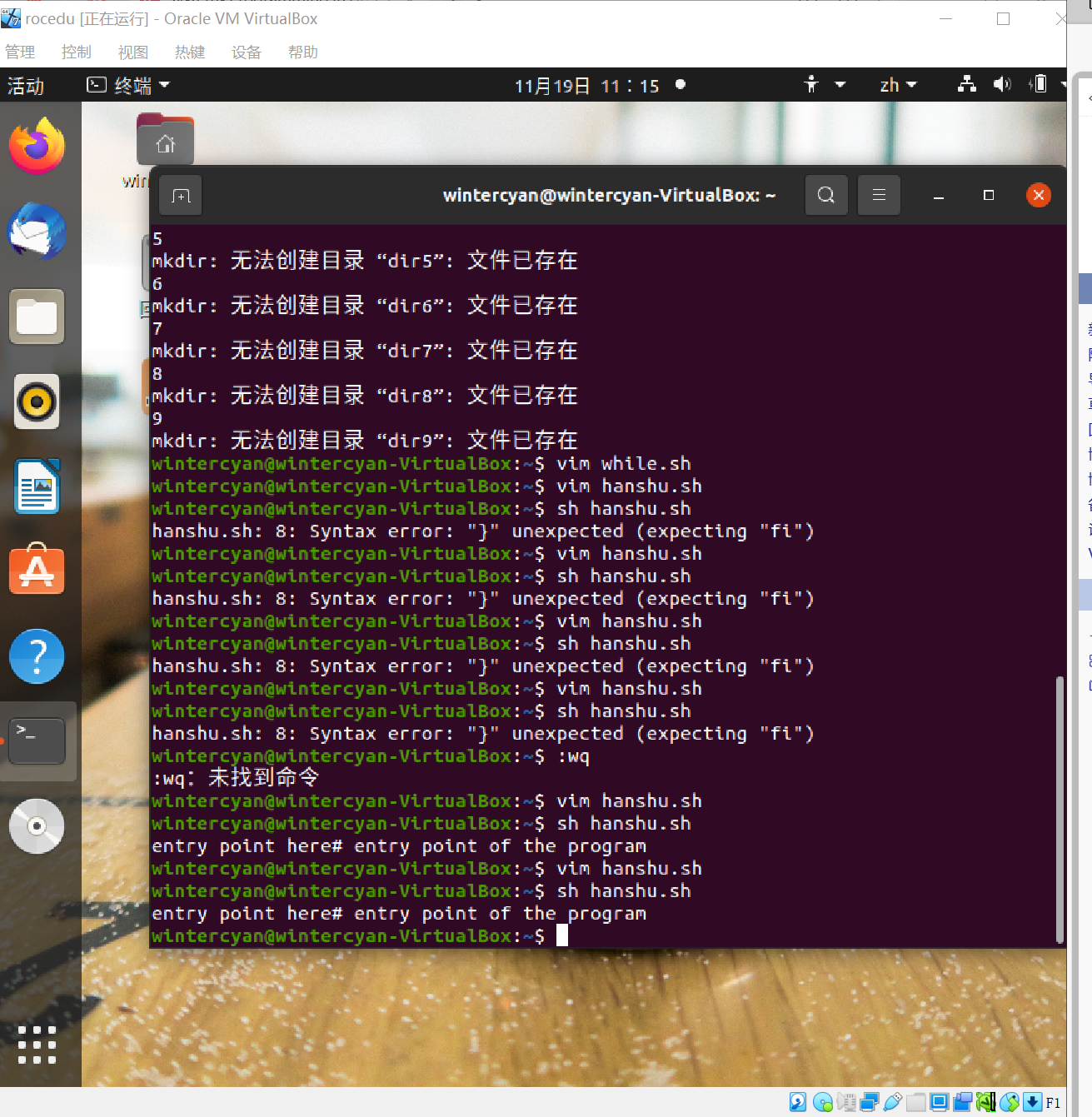
示例:sh函数
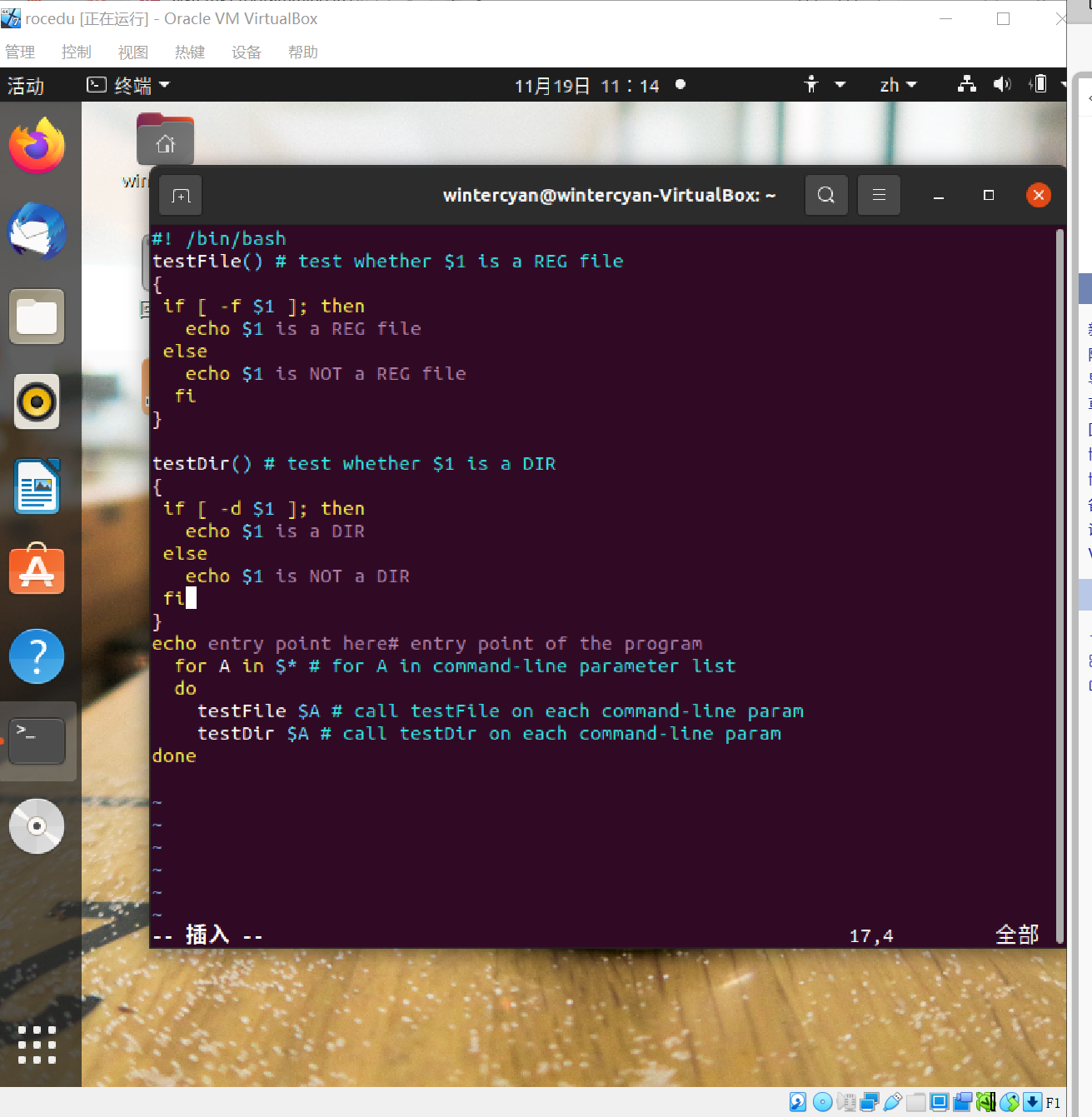
#! /bin/bash
testFile() # test whether $1 is a REG file
{
if [ -f $1 ]; then
echo $1 is a REG file
else
echo $1 is NOT a REG file
}
testDir() # test whether $1 is a DIR
{
if [ -d $1 ]; then
echo $1 is a DIR
else
echo $1 is NOT a DIR
}
echo entry point here# entry point of the program
for A in $* # for A in command-line parameter list
do
testFile $A # call testFile on each command-line param
testDir $A # call testDir on each command-line param
done
提示缺少else结束后缺少fi

添加后正常运行
~
sh中的通配符
- 星号通配符
file *列出当前目录中所有文件信息
ls *.c - ?通配符
file ???
ls *.?? - [ ]通配符
file [ab]
ls [xyz]
ls [a-m]
命令分组
在sh脚本中,可以用"{}""[]"对命令进行分组
eval语句
eval [arg1 arg2 ... argn]
将输入参数字符串连接到一个字符串中,计算一次,即执行变量和命令替换,然后给出结果字符串供sh执行。
- 参数替换
- 命令替换
- 通配符扩展
调试sh脚本
bash -x mysh
苏格拉底挑战