leetcode142. 环形链表 II
142. 环形链表 II
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
示例 1:
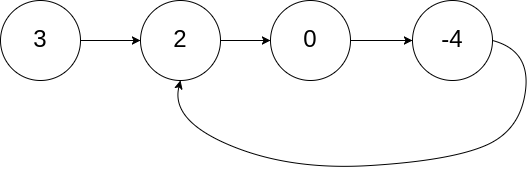
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:tail connects to node index 1
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:tail connects to node index 0
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。

示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:no cycle
解释:链表中没有环。

/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { } }
解法1:用set或map,边遍历链表中的节点边把他们加入set(或map)中,若该节点已存在则证明有环,且该节点为链表开始入环的第一个节点。
代码:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { Set<ListNode> map = new HashSet<>(); while(head !=null ) { if(map.contains(head)) { return head; } map.add(head); head = head.next; } return null; } }
解法2:先用快慢指针判断是否有环。快指针每次走两步,慢指每次针走一步,所以快指针走的长度是慢指针的两倍。
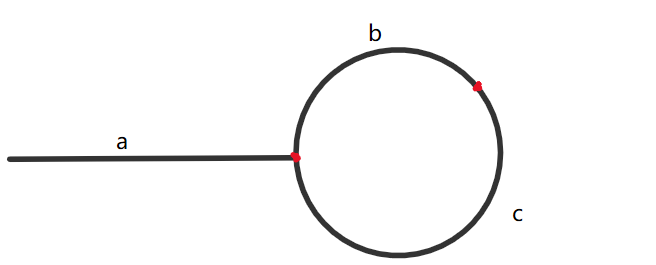
由图,a为头节点到入环第一个节点的长度,b为入环第一个节点到两指针相遇的节点的长度,c为环除了b剩下的长度。
我们知道快指针走的长度为:a+n(b+c)+b ,慢指针走的长度为:a+b,又因为快指针走的长度为慢指针的两倍,则:2(a+b) = a+n(b+c)+b
化简得:a = (n-1)(b+c)+c
意味着从头结点和相遇点出发一步步走,会在入环的第一个节点相遇。
代码:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode p1 = head; ListNode p2 = head; while(p1 != null && p2 != null) { p1 = p1.next; p2 = p2.next; if (p2 == null) break; p2 = p2.next; if (p1.equals(p2)) { p2 = head; while(p2 != p1) { p1 = p1.next; p2 = p2.next; } return p1; } } return null; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号