Oracle-函数-多表查询
1.1 函数
函数一般是在数据上执行的,它给数据的转换和处理提供了方便。只是将取出的数据进行处理,不会改变数据库中的值。
函数根据处理的数据分为单行函数和聚合函数(组函数)
组函数又被称作聚合函数,用于对多行数据进行操作,并返回一个单一的结果,组函数仅可用于选择列表或查询的having子句
单行函数对单个数值进行操作,并返回一个值。
1.2 字符相关
-- dual用于测试,dual是一个系统表。注意用于测试。 select * from dual; -- 1.字符串连接 select concat('aa','12') from dual; select 'aa'||'12' from dual; -- 2.首字母大写 select initcap('abc') from dual; --- 把大写转化小写 select lower('ABc') from dual; select upper('abc') from dual; -- 把所有员工的姓名小写输出 select lower(e.ename),e.empno from emp e -- 3.填充字符lpad/rpad select lpad('sxt',5,'*') from dual; select rpad('sxt',5,'*') from dual; -- 4.去掉空白字符 select ' kallen' from dual; select ltrim(' kallen',' ') from dual; select rtrim(' kallen ',' ') from dual; -- trim 删除左右两边的字符 select trim('a' from 'abc') from dual; -- 5.求子串 substr(str,loc,len)-->loc从1开始 select substr('abcd',2,2) from dual; -- 6.查找字符串 /* 如果找到返回>=1的索引;如果没找到返回0 */ select instr('abcd','b') from dual; -- 7.求长度 select length('abcd') from dual;
例题:格式化电话号码
select substr('18612341234',1,3)||'-'||substr('18612341234',4,4)||'-'||substr('18612341234',8,4)
from dual;
1.3 数值型函数
-- 数值型函数 -- 四舍五入round(x,y)对x保留y为小数 select round(23.652) from dual; select round(23.652,1) from dual; select round(25.652,-1) from dual; -- 返回x按精度y截取后的值 select trunc(23.652) from dual; select trunc(23.652,2) from dual; select trunc(23.652,-1) from dual; -- mod(x,y)求余数 select mod(9,2) from dual; -- ceil 向上取整 select ceil(1.9) from dual; -- floor 向下取整 select floor(1.9) from dual;
1.4 日期时间函数
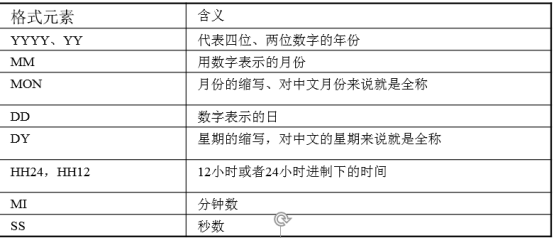
1.4.1 日期函数
-- 返回系统当前时间 select sysdate from dual; -- 返回当前会话时区中的当前日期 select current_date from dual; -- 添加月数 select add_months(sysdate,1) from dual; -- 返回两个时间相差的月数 select months_between(sysdate,add_months(sysdate,2)) from dual; -- 需求:查询工作年限在30年以上 select e.ename,e.hiredate from emp e where months_between(sysdate,e.hiredate)/12 > 30 -- 返回date所在月份最后的一天 select last_day(add_months(sysdate,1)) from dual; -- next_day(date1,week) 返回date1下周星期几的日期 select sysdate "当时日期",next_day(sysdate,'Monday') "下周星期一" from dual; -- 查询会话的环境参数 select * from nls_session_parameters;
1.4.2 日期计算相关
select sysdate+2 from dual;
select sysdate-2 from dual;
两个时间进行四则运算的单位是天。
1.5 转换函数
转换函数就是把字符、日期、数值型数据进行相互转换。类型转换分两种:隐式类型转换和显式类型转换
1.5.1 隐式类型转换
字符和数字/日期之间的隐式转换
-- 字符隐式转换成数值 select '100' - 10 from dual; -- 字符隐式转化为日期 -- DD-MON-RR 默认的日期格式 select 1 from dual where sysdate > '13-May-19'; -- 查date format格式 select * from nls_session_parameters;
1.5.2 显示类型转换
|
|
1.5.2.1 to_char
把日期转化成字符
|
|
把数值格式化成字符串
|
|
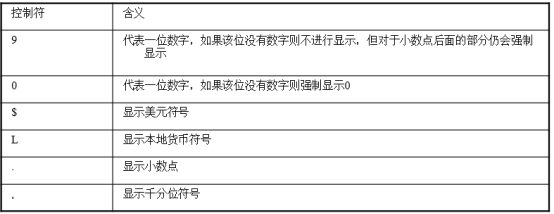
-- to_char -- 【1】把日期转化成字符 -- 按照默认格式DD-MON-RR select to_char(sysdate) from dual; -- 按指定格式 select to_char(sysdate,'YYYY"年"MM"月"DD"日" HH24:MI:SS') as t from dual; -- 【2】把数值格式化成字符串 select to_char(12345,'99999.99') from dual; select to_char(12345,'99,999.99') from dual; select to_char(12345,'999,999.99') from dual; -- 不够位置0 select to_char(12345,'000,000.00') from dual; -- 格式化成美元显示 select to_char(12345,'$000,000.00') from dual;
需求:把18612341234格式化成186-1234-1234
-- 需求:把18612341234格式化成186-1234-1234
select replace(to_char(18612341234,'999,9999,9999'),',','-') from dual;
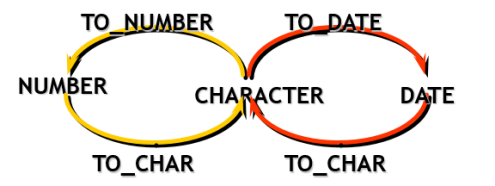
1.5.2.2 to_number、to_date
-- to_number select to_number('$12,345','$99,999') from dual; select to_number('$12,345.12','$99,999.99') from dual; -- to_date select to_date('14-May-19','DD-MON-RR') from dual; select to_date('2004-09-19','YYYY-MM-DD') from dual;
函数可以嵌套
-- 查询雇用期满6个月的下一个周一的日期。 select e.ename,e.hiredate,next_day(add_months(e.hiredate,6),'Monday') from emp e where months_between(sysdate,e.hiredate) > 6 -- 查询公司boss select e.ename || nvl(to_char(e.mgr),' is boss') from emp e where e.mgr is null
1.6 decode/case when
decode(条件,值1,“返回值1”, 值2,“返回值2”,,,“默认值”)
-- 需求:查询员工所在的部门名称 select e.ename, e.deptno, decode(e.deptno,10,'部门1',20,'部门2',30,'部门3','未知') from emp e;
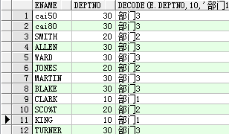
|
case when
-- case when select e.ename, e.deptno, case e.deptno when 10 then '部门1' when 20 then '部门2' when 30 then '部门3' else '未知' end from emp e;
-- 需求:对各个部门进行涨薪,10->1.1 20->1.2 30->1.3 其他->1.0 select e.deptno, e.ename, e.sal "涨薪前", decode(e.deptno,10,e.sal*1.1,20,e.sal*1.2,30,e.sal*1.3,e.sal) "涨薪后" from emp e -- 需求:根据工资分布输出以下信息 /* <1000 真屌丝 (1001,2000] 屌丝 (2001,3000] 白领 (3001,5000] 高富帅 (5001,10000] 土豪 */ select e.ename "姓名", e.sal "工资", case when e.sal <= 1000 then '真屌丝' when e.sal <= 2000 then '屌丝' when e.sal <= 3000 then '白领' when e.sal <= 5000 then '高富帅' when e.sal <= 10000 then '土豪' else '未知' end "描述" from emp e;
decode 多用于等值匹配;case when可以用于等值,多用于条件分支。
1.7 组函数
组函数把多行数据经过运算后返回单个值。也称聚合函数。
|
|
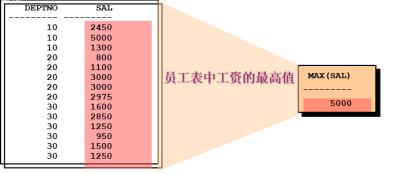
-- 求公司雇员的数量 select count(*) from emp e; select count(e.empno) from emp e; select count(1) from emp e; -- avg:对多个记录的某个字段求平均值 -- 需求:求底薪的平均值 select avg(e.sal) from emp e; -- 需求:求雇员的最高薪资/最低薪资 select max(e.sal),min(e.sal),avg(e.sal) from emp e; -- 需求:求公司一个月的员工基本开销 select sum(e.sal) from emp e;
注意:
[1] 组函数或聚合函数是对一个数据集(表数据、查询出来的表、分组的表)进行聚合。
[2] 聚合函数对字段是null的值进行忽略。count(*)
|
-- 求有津贴的员工的数量 select count(e.comm) from emp e;
|
[3] max/min 适合任意数据类型,sum/avg 只适用于数值类型。
聚合函数的结果可以作为其他查询条件。
|
-- 最早入职的员工 select e.ename,e.hiredate from emp e where e.hiredate = (select min(e.hiredate) from emp e); |
1.8 分组(group by)
在处理统计或聚合数据时,很多时候需要对数据进行分组 语法
|
select field1,。。。 from tableName group by field1[,field2,…] |
按照field1[,field2,…] 分组,字段值相同的记录分到一组。
1.8.1 group by的工作原理
|
|
对数据进行分组后,select语句的字段值只能是分组字段或者聚合函数。
1.8.1.1 [1]分组和聚合函数
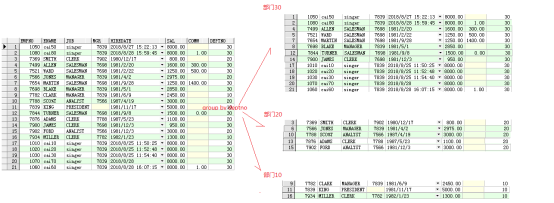
-- 需求:求各个部门的人数
select e.deptno,e.ename
from emp e
group by e.deptno;
-- 需求:统计部门10的人数
select count(1)
from emp e
where e.deptno = 10;
-- 需求:求各个部门的人数
select e.deptno,e.ename
from emp e
group by e.deptno;
-- 需求:求各个部门的平均薪资
select e.deptno,avg(e.sal)
from emp e
group by e.deptno
-- 需求:求各个部门的月收入平均值
select e.deptno,avg(e.sal+nvl(e.comm,0))
from emp e
group by e.deptno
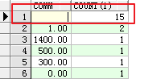
1.8.1.2 [2]null值归为一组
|
-- 特例:按照津贴分组 select e.comm,count(1) from emp e group by e.comm |
|
|
1.8.1.3 [3]having
如果需要对分组的数据进行条件过滤,必须使用having!!!
-- group by having -- 查询部门平均薪资大于3000的部门 select e.deptno from emp e group by e.deptno having avg(e.sal) > 3000 -- 查询部门薪资大于3000的雇员按部门分组的平均薪资 select e.deptno,avg(e.sal) from emp e where e.sal > 3000 group by e.deptno;
注意:
[1] Where过滤行,having过滤分组。
[2] Having支持所有where操作符。
1.9 排序 (order by)
当需要对数据集进行排序操作时,语法
|
select field1, field2,。。。 from tablename order by field1,field2 |
对数据集进行排序,先按field1排序,如果field1排序相同,按照field2排序,依次类推。
-asc 升序,默认
-desc 降序
-- order by -- 需求:按雇员薪资排序 select e.ename,e.sal from emp e order by e.sal desc -- 按薪资升序,名称降序 select e.ename,e.sal from emp e order by e.sal,e.ename desc;
order by 一般都是最后执行。
需求: 查询 薪资大于1200的 雇员在部门中平均薪资大于1500的部门,按照平均薪资升序排序。
查询 薪资大于1200的雇员所在部门的平均薪资大于1500的部门,按照平均薪资升序排序。
--薪资大于1200的雇员所在部门的平均薪资大于1500的部门,按照平均薪资升序排序 -- [1] 查询薪资大于1200的雇员 select e.* from emp e where e.sal > 1200 -- [2]按部门分组 select e.* from emp e where e.sal > 1200 group by e.deptno -- [3] 输出聚合结果 select e.deptno,avg(e.sal) from emp e where e.sal > 1200 group by e.deptno having avg(e.sal) > 1500 -- [4]对数据集进行排序 select e.deptno,avg(e.sal) from emp e where e.sal > 1200 group by e.deptno having avg(e.sal) > 1500 order by avg(e.sal) asc
order by 既可以用于数据行(记录)排序。
也可以对分组的结果进行排序,此时需要聚合函数配合。
1.10 Select 语言的执行顺序
|
from -> where -> group by -> having -> select -> order by
1.11 交集、全集、并集、差集
并集:把集合A的结果和集合B的结果合并,并去掉重复的记录。
|
-- 并集 select e.* from emp e where e.deptno = 10 union select e.* from emp e where e.deptno = 20;
-- 有重复记录取并集 select e.* from emp e where e.deptno = 10 or e.deptno = 20 union select e.* from emp e where e.deptno = 20; |
全集: 把集合A的结果和集合B的结果合并,保留重复记录
|
select e.* from emp e where e.deptno = 10 or e.deptno = 20 union all select e.* from emp e where e.deptno = 20; |
交集: 把集合A的结果和集合B的结果取相同部门
|
select e.* from emp e where e.deptno = 10 or e.deptno = 20 intersect select e.* from emp e where e.deptno = 10; |
差集: 在集合A的结果中去掉集合B的结果 (A-B)
|
select e.* from emp e where e.deptno = 10 or e.deptno = 20 minus select e.* from emp e where e.deptno = 10; |
1.12 多表关联
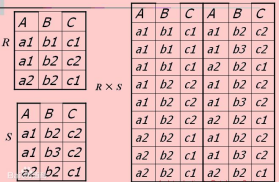
1.12.1 笛卡尔积
|
|
|
-- 笛卡尔积 select * from emp,dept |
1.12.2 等值连接
|
-- 等值连接 -- 需求:查询雇员的部门名称 select e.ename,e.deptno,d.dname from emp e,dept d where e.deptno = d.deptno |
1.12.3 不等值连接
|
-- 不等值连接 -- 查询每个雇员的薪资等级 select e.ename,e.sal,sg.grade from emp e,salgrade sg where e.sal >= sg.losal and e.sal <= sg.hisal -- where e.sal between sg.losal and sg.hisal |
1.12.4 外连接
左外连接:左边的表作为主表,右边表作为从表,主表数据都显示,从表数据没有,用null填充,用+号表示。
|
-- 左外连接(B) -- 需求:查询所有部门的雇员 select * from dept d,emp e where d.deptno = e.deptno(+) |
右外连接: 右边的表作为主表,左边表作为从表,主表数据都显示,从表数据没有,用null填充,用+号表示。
|
-- 右外连接(B) select * from emp e,dept d where e.deptno(+) = d.deptno; |
1.12.5 自连接
一个表自身连接自身时,称为自连接。自连接以不同的视角看待同一张表。
|
-- 查询每个雇员的上级领导 select e.ename "雇员",m.ename "领导" from emp e,emp m where e.mgr = m.empno
-- 优化king select e.ename "雇员",nvl(m.ename,'boss') "领导" from emp e,emp m where e.mgr = m.empno(+) |
1.12.6 多于两张表的查询
如果有多个表参与查询,先把t1xt2笛卡尔积得到一个大表T1,再把T1xt3笛卡尔积得到一个另外的大表T2,依次类推。
所有的多表查询最终都是两种表的查询。