封装与继承
1.1 封装
封装:将类的某些信息隐藏在类内部,不允许外部程序直接访问,而是通过该类提供的方法来实现对隐藏信息的操作和访问。
封装的步骤
[1]属性私有化
[2]提供公共的设置器和访问器
[3]在设置器和访问器中添加业务校验逻辑,判断输入内容合法性.
1 public class Dog{ 2 3 // 【1】private 私有的,对外不可见 4 private String name; 5 private int health; 6 private int love; 7 private String strain; 8 9 // 【2】提供公共的设置器(setter)和访问器(getter) 10 public void setName(String name){ 11 // 【3】逻辑校验 12 if(name.equals("")){ 13 System.out.println("姓名不能为空."); 14 }else{ 15 this.name = name; 16 } 17 } 18 public String getName(){ 19 return this.name; 20 } 21 22 public void setHealth(int health){ 23 if(health < 0){ 24 System.out.println("健康值不合法."); 25 this.health = 0; 26 }else{ 27 this.health = health; 28 } 29 } 30 public int getHealth(){ 31 return this.health; 32 } 33 34 public void setLove(int love){ 35 if(love < 0){ 36 System.out.println("亲密度不合法."); 37 this.love = 0; 38 }else{ 39 this.love = love; 40 } 41 } 42 public int getLove(){ 43 return this.love; 44 } 45 46 public void setStrain(String strain){ 47 if(strain.equals("")){ 48 System.out.println("品种不能为空."); 49 }else{ 50 this.strain = strain; 51 } 52 } 53 public String getStrain(){ 54 return this.strain; 55 } 56 57 58 public Dog(){ 59 60 } 61 62 public Dog(String name,int health,int love,String strain){ 63 this.setName(name); 64 this.setHealth(health); 65 this.setLove(love); 66 this.setStrain(strain); 67 } 68 69 public void showInfo(){ 70 System.out.print("我的名字叫"+this.name); 71 System.out.print(",健康值"+this.health); 72 System.out.print(",亲密度"+this.love); 73 System.out.println(",我是一只"+this.strain); 74 } 75 }
1.1 继承
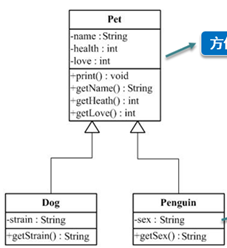
1.1.1 为什么要使用继承?
|
为了提取两个类中公共的代码,可以使用继承抽取重复性的代码到一个公共类中,这个公共的类称为父类(super class)。继承于父类的类称为子类(sub class).
java继承的特性
[1] 单根性。在java中,一个类只能有一个直接父类。
[2] 传递性。C继承于B,B继承于A,C具有A的特性和行为。
类B继承于类A,使用关键字extends,B拥有了A中非私有的属性和方法。
|
public class Person{ String name; int age;
public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("姓名:"+name); System.out.println(",年龄:"+age); } } |
|
public class Student extends Person{
} |
|
public class Test01{ public static void main(String[] args){ Student s = new Student(); s.name = "张三"; s.age = 20; s.showInfo(); } } |
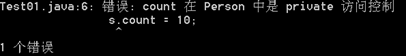
如果Person中定义了private 属性count,则不能被直接访问
|
1.2 Super
super关键字表示父类对象,只是一个关键字,里面没有引用。
[1]super访问父类构造方法
|
public Dog(String name,int health,int love,String strain){ /* this.setName(name); this.setHealth(health); this.setLove(love); */ super(name,health,love); this.setStrain(strain);
} |
super调用父类构造方法时,必须写到构造方法有效代码第一句
|
[2] super调用父类的非私有属性
super可以访问父类的非私有属性。私有的属性不能用super访问。
|
public class Fruit{ float price; } |
|
public class Apple extends Fruit{
public void showInfo(){ // 不推荐使用 //System.out.println("价格:"+price); //System.out.println("价格:"+this.price); // 当需要访问父类的属性时,优先使用super System.out.println("价格:"+super.price); }
} |
变量隐藏(C)
当子类定义了一个和父类同名的属性时,在子类中优先访问子类的属性,如果要访问父类属性一定要加super。
|
public class Fruit{ float price;
private String color;
int weight = 100; } |
|
public class Apple extends Fruit{
int weight = 200;
public void showInfo(){ // 不推荐使用 //System.out.println("价格:"+price); //System.out.println("价格:"+this.price); // [1]当需要访问父类的属性时,优先使用super System.out.println("价格:"+super.price);
// [2]不能访问父类的私有属性 // System.out.println("颜色:"+super.color);
// [3] 访问和父类同名的变量weight System.out.println("重量:"+weight); //无法访问到父类 System.out.println("重量:"+this.weight); //可以访问父类 System.out.println("重量:"+super.weight); }
} |
一句话:如果要访问父类属性,通过super;如果要访问子类属性,通过this.
[3] super访问非私有父类方法
|
public void print(){ /* System.out.print("我的姓名"+super.getName()); System.out.print(",健康值"+super.getHealth()); System.out.print(",亲密度"+super.getLove()); */ super.showInfo(); System.out.println(",我是一只"+this.getStrain()); } |
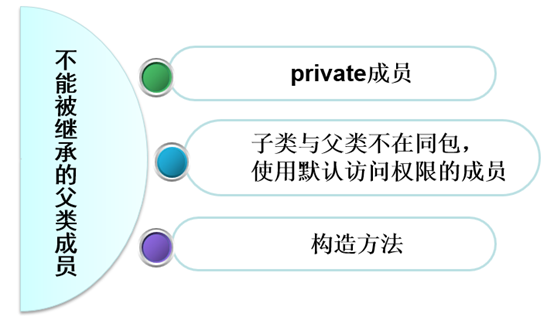
1.3 子类继承父类的资源
|
1.4 访问修饰符
java中存在4类访问修饰符,分别是private、默认、protected、public。
|
修饰符 |
本类✘ |
同包子类 |
同包其他类 |
不同包子类 |
不同包其他类 |
|
private |
✔ |
✘ |
✘ |
✘ |
✘ |
|
默认 |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✘ |
✘ |
|
protected |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✘ |
|
public |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
private:私有的,只能在本类可以访问。
friendly:默认的,同包可访问,也称包访问权限。
protected:受保护的, ①子类可访问 ②同包可访问
public:公共的,都可以访问
1.5 继承关系的初始化顺序
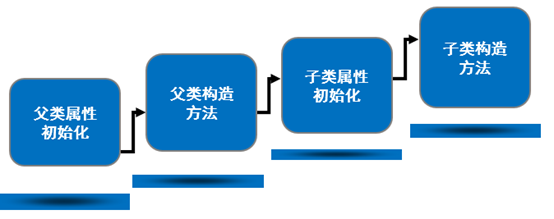
|
继承关系内存图
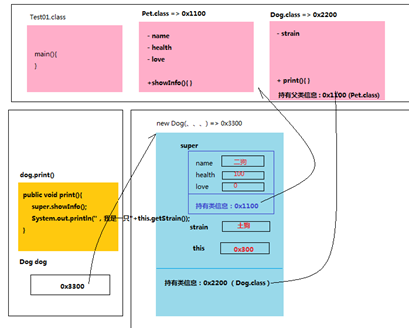
|
1.6 方法的重写
当子类从父类继承过来的方法不能满足自身需要时,子类可以根据自身情况进行方法重写(overwrite/override)
方法重写建立在继承的基础上,没有继承,就没有重写!
子类根据自身情况,可以选择部分重写和完全重写。
部分重写
|
public void showInfo(){ super.showInfo(); System.out.println("我是一只"+this.getStrain()); } |
完全重写
|
public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("--"+super.getName()+"--"); System.out.println("健康值:"+super.getHealth()); System.out.println("亲密度:"+super.getLove()); System.out.println("品种:"+this.getStrain()); } |
重写的规则
[1]方法名称相同
[2]参数列表相同
[3]子类的访问权限一定 >= 父类访问权限
[4]返回值和父类相同或者是其子类
|
public Pet create(){ Pet pet = new Pet(); return pet; } |
|
public Dog create(){ Dog dog = new Dog(); return dog; } |



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号