声明函数指针、回调函数、函数对象------c++程序设计基础、编程抽象与算法策略
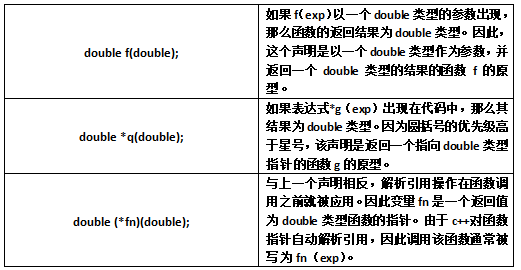
声明函数指针
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
double a(double aa) { return aa; }
int main() {int aa = 9;
a(1.0);
double(*fn)(double) = a;;
cout << a(1.0)<<endl;
cout << fn(1.0) << endl;
cout << fn << endl;
cout << &fn << endl;
cout << *fn << endl;
}
结果:
1 1 00821488 00F3FB70 00821488
回调函数
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void a(int t) { cout << t << endl; }
void aa(int t) { cout << t*t << endl; }
void callback(void(*fn)(int t),int g) { fn(g); } //映射函数
int main() {
callback(a, 9);
callback(aa,9);
}
结果
9 81
回调函数还没懂应用在哪。
回调函数的限制
向回调函数中所传递的信息超过了映射函数所能提供的参数。
解决
函数指针在它们的效用中被限制,因为它们无法将函数与用户提供的数据一起提供。所以需要一种策略:它将回调函数与用户提供的数据封装成一个单独的单元。即函数类(function class)(通过重载operateor()将对象本身作为方法)。这些类的实例称为函数对象(function object)或函子(functor)。
函数对象的简单例子
例如,函数对其参数值加1:
int add1(int x)
{return x+1;}
现在改需求了,给定一个整型常量k,对参数值加k。
int addk(int x)
{return x+k;}
k可为任意整数。你不可能实现与k相同数目的函数。你需要创建一个封装两个构件的函数类:一个变量记录k的值,另一个重载operator(),以便给操作符向其参数增加存储的k值。示例
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class AddFunction {
public:
AddFunction(int k) { this->k = k; }
int operator()(int x) { return x + k; }
private:
int k;
};
int main() {
AddFunction add1 = AddFunction(1);
AddFunction add17 = AddFunction(17);
cout << add1(100) << endl;
cout << add17(25) << endl;
}
结果
101 42
向映射函数传递函数对象
使用函数对象的策略可以解决映射函数向回调函数传递额外信息的问题。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class AddFunction {
public:
AddFunction(int k) { this->k = k; }
int operator()(int x) { return x + k; }
private:
int k;
};
void callback(AddFunction a, int g) { cout << a(g) << endl; }
int main() {
AddFunction aa(8);
callback(aa,9);
}
结果
17
编写以函数作为参数的函数
1、函数指针
void callback(void(*fn)(int t),int g) { fn(g); }
2、函数对象
c++通过使用模板函数来实现任何以函数对象作为参数的函数的方式来解决这个问题。原型如下
template <typename FunctionClass> void callback(FunctionClass a, int g)
示例
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class AddFunction {
public:
AddFunction(int k) { this->k = k; }
int operator()(int x) { return x + k; }
private:
int k;
};
template <typename FunctionClass>
void callback(FunctionClass a, int g) { cout << a(g) << endl; }
int main() {
AddFunction aa(8);
callback(aa,9);
}
传递给callback的值可以是任何类型。当编译器试图展开callback模板函数时,如果该类型不能重载函数调用操作符以至于不能获得期望的参数,那么编译器就会报错。
c++程序设计基础、编程抽象与算法策略


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号