SpringBoot--- 使用SpringSecurity进行授权认证
SpringBoot--- 使用SpringSecurity进行授权认证
前言
在未接触 SpringSecurity 、Shiro 等安全认证框架之前,如果有页面权限需求需要满足,通常可以用拦截器,过滤器来实现。
但是,这需要大量配置类去完成,代码编写工作量是巨大的。为提高工作效率,学习SpringSecurity 等框架变得十分必要。
环境
IDEA :2020.1
Maven:3.5.6
SpringBoot: 2.3.2
1、导入正确的依赖
重要依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
也可以在构建工程师勾选
另外,笔者使用的模板引擎是 Thymeleaf ,因此也需要导入该依赖,不适用该模板引擎的不需要导入该依赖。
<!-- thymeleaf-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-java8time</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、编写或导入页面素材,HTML页面等
读者可以自行编写,除了login 页面必须要有 form 表单提交,以便处理登录请求外,其他页面可根据需要编写。
关于页面,登录提交表单有一个注意事项
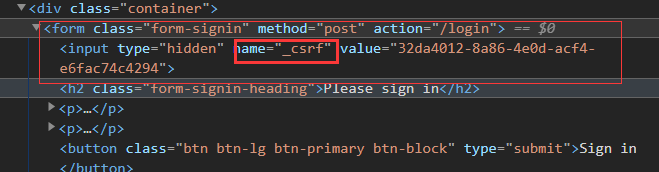
<form class="form-signin" method="post" action="/login">
一般提交表单,这样写是没有问题的,但是,我们添加了 spring-boot-starter-security 依赖,使用了SpringSecurity ,提交所有表单(包括这次的登录表单),都会交由SpringSecurity 处理。
SpringSecurity 默认开启了防止跨域攻击的功能,任何 POST 提交到后台的表单都要验证是否带有 _csrf 参数,一旦传来的 _csrf 参数不正确,服务器便返回 403 错误;
上述写法,我们可以访问后,在调试模式查看元素。
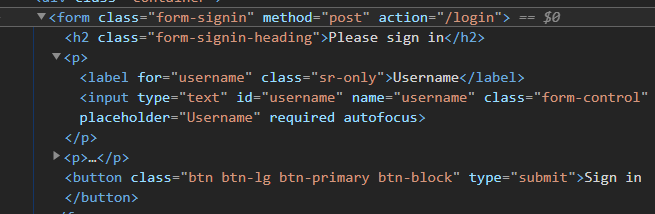
是没有 _csrf 参数的,这样提交的时候将会被拦截。
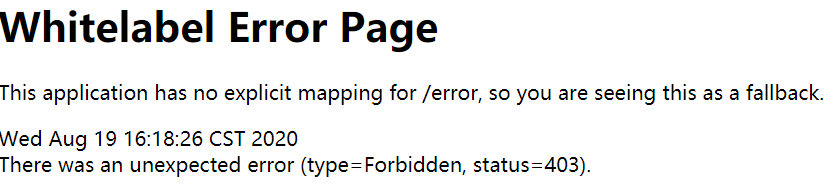
提交表单403解决方法
1、直接关闭防止域攻击功能。(可以在下面介绍到的配置类中使用)
http.csrf().disable()
这样的做法是不建议的,安全级别会降低。有违使用 SpringSecurity 的初衷。
2、使用 Thymeleaf 在 form 表单添加 th:action 元素,Thymeleaf 会自动为我们添加 _csrf 元素。
<form class="form-signin" method="post" th:action="@{/toLogin}">
3、在 form 表单中手动添加隐藏 _csrf
在 form 表单中手动添加隐藏 _csrf,比较麻烦,这里不做过多介绍。都用SpringBoot 了,还手动配置这么多,这不有违初衷了吗?当然,感兴趣的可以自己摸索。
3、测试环境,保证页面访问成功
这里要做的是编写一个 Controller 类
@Controller
public class RouterController {
@RequestMapping( {"/","/index"} )
public String index(){
return "welcome";
}
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin(){
return "pages/login";
}
@RequestMapping("/level1/{id}")
public String toLevel1(@PathVariable("id") int id){
return "pages/level1/"+ id;
}
@RequestMapping("/level2/{id}")
public String toLevel2(@PathVariable("id") int id){
return "pages/level2/"+ id;
}
@RequestMapping("/level3/{id}")
public String toLevel3(@PathVariable("id") int id){
return "pages/level3/"+ id;
}
}
启动程序,访问页面。当然,测试之前,我们需要把 SpringSecurity 的依赖导入暂时注释掉,否则,SpringSecurity 将会拦截下我们的请求。


访问成功,页面是没有问题的。这样做有利于我们后面出问题时,排查问题,并非多此一举。类似于断点Debug ,相当于我们在这一阶段前的工作是无误的。问题出现应该在这一断点(阶段)后排查。
别忘了,注释掉的SpringSecurity ,我们要解除掉注释。
4、配置用户,权限
1、yml
spring:
security:
user:
name: tom001
password: 1234
roles: [level1,level2]
这样就可以配置用户名,密码和权限了,太方便了吧!
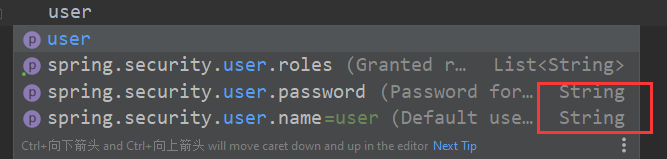
但是,却只能添加一个用户,因为user,password 等属性都只是String类型的,只有roles 才是List 类型的。笔者内问百度博客,外问谷歌,Stack Overflow 都没有找到SpringSecurity可以在yml配置文件下配置多用户的方法。如果你知道,请评论留言告诉我,小弟谢过了。
2、配置类
所以最后还是回到配置类上来吧,很多问题还可以从官方和源码中找到正确的配置方法。(虽然不能用 yml 提【tou】高【gong】效【jian】率【liao】了 T_T )
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//定义访问权限规则
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("level1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("level2")
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("level3");
//没有权限将跳转到登录页面
http.formLogin();
}
}
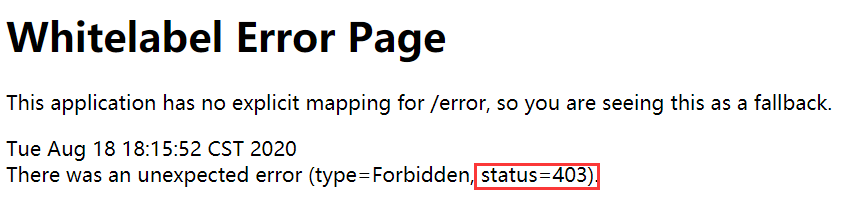
很遗憾,主页依然可以访问,在访问需要权限的页面时候,被服务器拒绝访问(403 表示服务器拒绝该访问请求)。
http.formLogin();
上面这个方法值得我们来分析一下,因为我们 Controller 配置的并没有 login 而是 toLogin 。
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin(){
return "pages/login";
}
SpringSecurity 是如何帮我们自动配置的呢?
我们去到 formLogin() 方法即可一探究竟。
* Specifies to support form based authentication. If
* {@link FormLoginConfigurer#loginPage(String)} is not specified a default login page
* will be generated.
*
* <h2>Example Configurations</h2>
*
* The most basic configuration defaults to automatically generating a login page at
* the URL "/login", redirecting to "/login?error" for authentication failure. The
* details of the login page can be found on
* {@link FormLoginConfigurer#loginPage(String)}
*
在方法体上,找到了注释。请特别注意以下这句话:
The most basic configuration defaults to automatically generating a login page at
the URL "/login", redirecting to "/login?error" for authentication failure.
默认情况下,最基本的配置是在URL“ /login”处自动生成一个登录页面,并重定向到“ /login?error”来进行身份验证失败。
而且,调转到的 /login ,并不是我们编写的 login.html 页面,而是由 SpringSecurity 提供的登录页面。
这里跳转了很久,难道是 SpringSecurity 在后台写页面?哈哈
我们可以点进查看一下 formLogin() 方法
* @Override
* protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
* http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/**").hasRole("USER").and().formLogin()
* .usernameParameter("username") // default is username
* .passwordParameter("password") // default is password
* .loginPage("/authentication/login") // default is /login with an HTTP get
* .failureUrl("/authentication/login?failed") // default is /login?error
* .loginProcessingUrl("/authentication/login/process"); // default is /login
* // with an HTTP
* // post
原来,我们可以指定登录页面,SpringSecurity 会帮助我们跳转过去。
.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin");
这下帮刘都统接上了腿,一下子就可跳过去了吧?哈哈哈
接下来就是认证方面的工作了。我们需要编写的类可以通过查看,需要重写哪些类,它的参数一般可以标明他要做的配置工作。
既然是配置,那自然是 configure 方法,我们可以去查看下图所示的这一 configure方法。
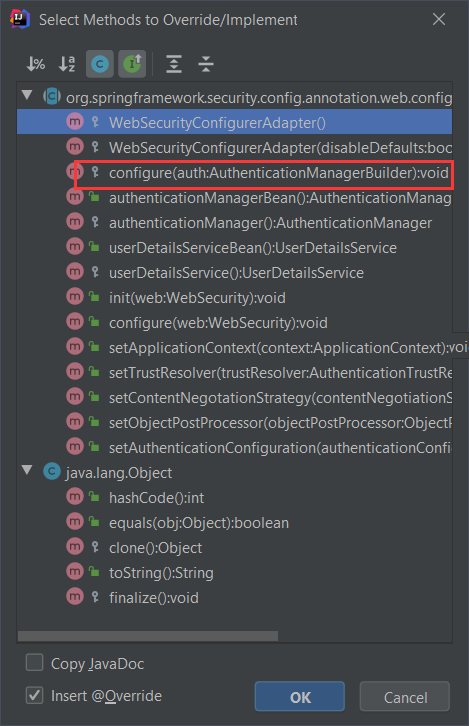
在源码,我们发现框架开发者在方法的注释上,贴心地为我们写好了配置示例。
* @Override
* protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) {
* auth
* // enable in memory based authentication with a user named
* // "user" and "admin"
* .inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("user").password("password").roles("USER").and()
* .withUser("admin").password("password").roles("USER", "ADMIN");
* }
我们按照他说要求的配置如下:
//认证
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("tom001").password("1234").roles("level1","level3");
}
哈哈,终于要完成了,我们来验证一下吧!
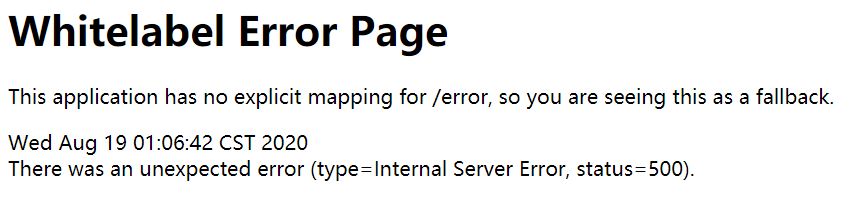
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: There is no PasswordEncoder mapped for the id "null"
密码没有编码?啥意思?
都说了是 SpringSecurity,登录密码还是明文密码,那还了得?人家一个反编译,你岂不是底裤都让人看光了?
但是官方一句提醒都没有,啊,这......
确实有点麻烦,但是我们的目的是让它起作用,还是找找方法吧。
//认证
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("tom001").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("1234")).roles("level1","level3");
}
最后加上加密类,这次总该成了吧?
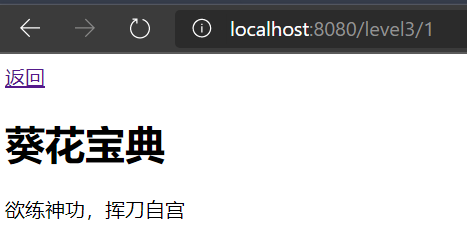
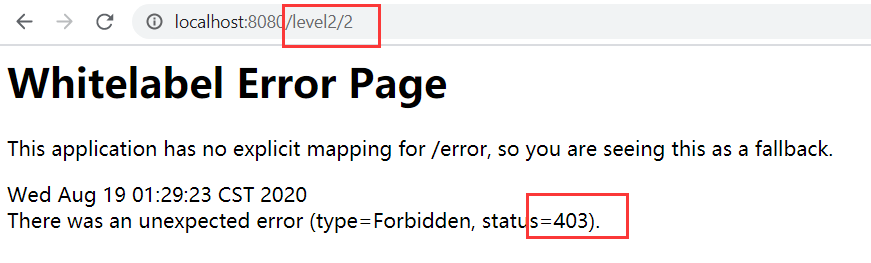
成功了!
实际使用中,还是要结合数据库获取用户密码,权限等信息的。 到总结 Shiro 的时候,我将会做介绍。


